Brain Questions
... Questions regarding the brain and the nervous system 1- State three functions of the nervous system 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The cen ...
... Questions regarding the brain and the nervous system 1- State three functions of the nervous system 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The cen ...
Nervous Systems - manorlakesscience
... Directs them to the various parts of the brain where they are interpreted. ...
... Directs them to the various parts of the brain where they are interpreted. ...
Angie Gelli, Ph.D. - The Hartwell Foundation
... which acts as a shield to protect our brain from harmful substances and pathogens. Although different approaches for getting chemotherapeutics into the brain have been attempted, most are too invasive and/or toxic; resulting in irreversible damage to surrounding healthy brain tissue and often causin ...
... which acts as a shield to protect our brain from harmful substances and pathogens. Although different approaches for getting chemotherapeutics into the brain have been attempted, most are too invasive and/or toxic; resulting in irreversible damage to surrounding healthy brain tissue and often causin ...
The Nervous System - Centennial Christian School
... • Is where sensory information is received and motor (movement) control is initiated • Protected by – bone • Brain – skull • Spinal cord – vertebrae ...
... • Is where sensory information is received and motor (movement) control is initiated • Protected by – bone • Brain – skull • Spinal cord – vertebrae ...
Nervous System
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
Brain 2012 - student version
... the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sensitive areas and to areas requiring precise control. Thus, the fing ...
... the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sensitive areas and to areas requiring precise control. Thus, the fing ...
MIND CONTROLLED ROBOT
... The EEG is used to evaluate several types of brain disorders like epilepsy, lesions in the brain which can result from tumors or stroke, Alzheimer's disease, certain psychoses, and a sleep disorder called narcolepsy. The EEG is also used to determine the overall electrical activity of the brain to e ...
... The EEG is used to evaluate several types of brain disorders like epilepsy, lesions in the brain which can result from tumors or stroke, Alzheimer's disease, certain psychoses, and a sleep disorder called narcolepsy. The EEG is also used to determine the overall electrical activity of the brain to e ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... • Medulla controls automatic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, coughing, and swallowing • Reticular formation regulates attention and alertness • Pons plays a role in body movement and sleep and dreaming ...
... • Medulla controls automatic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, coughing, and swallowing • Reticular formation regulates attention and alertness • Pons plays a role in body movement and sleep and dreaming ...
Early Brain Development
... 5. Provide variety, but don’t overload 6. Avoid pushing the child The rate that a child learns is different from any other child throughout their life. This is due to the fatty coating called myelin on ...
... 5. Provide variety, but don’t overload 6. Avoid pushing the child The rate that a child learns is different from any other child throughout their life. This is due to the fatty coating called myelin on ...
Unit Two: Biological Bases of Behavior
... • Which part of the brain did Gage injure? • Why did Gage feel no pain after the injury? • What were the “treatments” given to Gage after the injury? • What was the major change in Gage after the accident? • What is localization of the brain? ...
... • Which part of the brain did Gage injure? • Why did Gage feel no pain after the injury? • What were the “treatments” given to Gage after the injury? • What was the major change in Gage after the accident? • What is localization of the brain? ...
The Brain!
... speech and happiness center; while the right side is known as being more fretful, more creative, and holistic processing center. ...
... speech and happiness center; while the right side is known as being more fretful, more creative, and holistic processing center. ...
psychology - Eagan High School
... The brain has no pain, because there are no nerves that register pain within the brain itself, neurosurgeons can probe the brain while a patient is conscious. They can then use feedback from the patient to identify important regions, such as those used for speech. The brain has the largest area of u ...
... The brain has no pain, because there are no nerves that register pain within the brain itself, neurosurgeons can probe the brain while a patient is conscious. They can then use feedback from the patient to identify important regions, such as those used for speech. The brain has the largest area of u ...
Document
... Lobes of the Brain & Functions: • Frontal = Top front, responsible for emotion and reasoning. • Parietal = Middle, and is the sensory center. • Occipital = Back, used for vision and reading. • Temporal = Lower sides, hearing and memory. ...
... Lobes of the Brain & Functions: • Frontal = Top front, responsible for emotion and reasoning. • Parietal = Middle, and is the sensory center. • Occipital = Back, used for vision and reading. • Temporal = Lower sides, hearing and memory. ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
Name #_____ Date ______ Section ____ Teen Brains Under
... out how changes in the brain contribute to changes in behavior. They also want to know whether school, music, sports, diet, video games, parenting, TV-watching, medicine, or other factors influence those changes during adolescence. One goal is to learn what teachers can do to take advantage of the t ...
... out how changes in the brain contribute to changes in behavior. They also want to know whether school, music, sports, diet, video games, parenting, TV-watching, medicine, or other factors influence those changes during adolescence. One goal is to learn what teachers can do to take advantage of the t ...
7-Sheep Brain
... These are tracts: the CORPUS CALLOSUM connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres so your right hand knows what the left hand is doing. The FORNIX (part of the limbic system) is another tract down to the MAMMILARY BODY. Fornix (“arch”). Fornicates means to go to the arch under the Colleseum, wh ...
... These are tracts: the CORPUS CALLOSUM connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres so your right hand knows what the left hand is doing. The FORNIX (part of the limbic system) is another tract down to the MAMMILARY BODY. Fornix (“arch”). Fornicates means to go to the arch under the Colleseum, wh ...
Neurons and the BOLD response
... stimulation. We are looking at brain activity due to neurons firing in the right cortical region for the hand (somatosensory cortex). Notice that Rest and Task periods alternate every forty seconds or so. We can see the results of brain activity (but not as fast as the activity itself.) ...
... stimulation. We are looking at brain activity due to neurons firing in the right cortical region for the hand (somatosensory cortex). Notice that Rest and Task periods alternate every forty seconds or so. We can see the results of brain activity (but not as fast as the activity itself.) ...
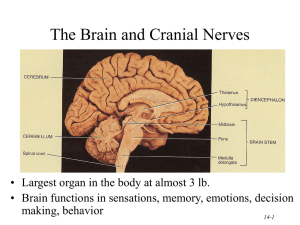
14-1
... • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury • at that time, lysosome release enzymes ...
... • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury • at that time, lysosome release enzymes ...
Psychology Chapter 19: Group Interaction
... activity b) Dendrites i. Short, thin fibers that stick out from the cell body and receive impulses from other neurons and send them to the cell body c) Axons i. Long fiber that carries the impulses away from the cell body toward the dendrites of the next neuron d) Other structures i. Myelin Sheath – ...
... activity b) Dendrites i. Short, thin fibers that stick out from the cell body and receive impulses from other neurons and send them to the cell body c) Axons i. Long fiber that carries the impulses away from the cell body toward the dendrites of the next neuron d) Other structures i. Myelin Sheath – ...
Voltage-sensitive dye Glowing thoughts RUB
... says Jancke. During that period he was able to observe how a wave of activity spreads over the visual cortex, when the brain processes visual motion. Instead of a real, physical motion, Jancke used an optical illusion that created the impression of movement. Building up his own Optical Imaging Lab a ...
... says Jancke. During that period he was able to observe how a wave of activity spreads over the visual cortex, when the brain processes visual motion. Instead of a real, physical motion, Jancke used an optical illusion that created the impression of movement. Building up his own Optical Imaging Lab a ...