Major Brain Structures and Functions
... Brain (Neural) Plasticity • The brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of damage • Severed neurons do not usually regenerate • Instead, the brain’s neural tissue can reorganize itself • One brain area can take on functions not normally “assigned” to that area • Brain’s are most plastic w ...
... Brain (Neural) Plasticity • The brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of damage • Severed neurons do not usually regenerate • Instead, the brain’s neural tissue can reorganize itself • One brain area can take on functions not normally “assigned” to that area • Brain’s are most plastic w ...
• Ch 49 • Nervous Systems • Neuronal Circuits • Each single
... The cerebrospinal fluid is filtered from blood and functions to cushion the brain and spinal cord as well as to provide nutrients and remove wastes ...
... The cerebrospinal fluid is filtered from blood and functions to cushion the brain and spinal cord as well as to provide nutrients and remove wastes ...
Exercise and the Bra..
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
ANATOMY
... system connects the central nervous system to various body structures. Cranial nerves carry impulses to and from the brain, spinal nerves carry impulses to and from the spinal cord. ...
... system connects the central nervous system to various body structures. Cranial nerves carry impulses to and from the brain, spinal nerves carry impulses to and from the spinal cord. ...
REPLACING THE HUMAN BRAIN: WILD IDEA PROMISES
... thousand-fold. We could even control the speed of our thoughts, shifting from 100 milliseconds, the response time of today’s brains, to fifty nanoseconds, millions of times faster. Creating thoughts at high speeds would slow everything down; at least that’s how it would seem in our mind. Our percept ...
... thousand-fold. We could even control the speed of our thoughts, shifting from 100 milliseconds, the response time of today’s brains, to fifty nanoseconds, millions of times faster. Creating thoughts at high speeds would slow everything down; at least that’s how it would seem in our mind. Our percept ...
Lesson Plan
... do that? How does it make your muscle get so big and strong? Explain the brain sends a connection called a nerve down the spine and to the muscles. How about people who can’t move their muscles? Some people have to be in wheelchairs because they can’t use their brain to move their muscles. Sometimes ...
... do that? How does it make your muscle get so big and strong? Explain the brain sends a connection called a nerve down the spine and to the muscles. How about people who can’t move their muscles? Some people have to be in wheelchairs because they can’t use their brain to move their muscles. Sometimes ...
Chapter 11
... the lobes (main part) • Cerebellum - back part • Brain Stem - spinal cord • Meninges - fluid that protects brain ...
... the lobes (main part) • Cerebellum - back part • Brain Stem - spinal cord • Meninges - fluid that protects brain ...
Document
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
CNS
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
synthesis of cariporide derviatives for sodium
... Western Kentucky University, Department of Chemistry, 1906 College Heights Boulevard, Bowling Green, KY 42101 Each year, more than 200,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with malignant brain tumors, the most prevalent and deadly type of adult brain cancer. The life expectancy of these ind ...
... Western Kentucky University, Department of Chemistry, 1906 College Heights Boulevard, Bowling Green, KY 42101 Each year, more than 200,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with malignant brain tumors, the most prevalent and deadly type of adult brain cancer. The life expectancy of these ind ...
NS Student Notes 2
... _____________. This fluid also found within _________________ of the spinal cord and _____________ of brain. (Spinal Tap- withdraw fluid to test for meningitis). ...
... _____________. This fluid also found within _________________ of the spinal cord and _____________ of brain. (Spinal Tap- withdraw fluid to test for meningitis). ...
Exam Notes #1 - A Guide to Treatment of Aphasia
... Meninges (s. meninx)-layers that protect the brain as well as couching0 PADP: pia mater-adheres to the brain-like saran wrap. -two layers-closest to the brain -outer layer has only veins and arteries -bleeding occurs in this layer: it is called a subarachnoid hemorrhage. -subarachnoid means below t ...
... Meninges (s. meninx)-layers that protect the brain as well as couching0 PADP: pia mater-adheres to the brain-like saran wrap. -two layers-closest to the brain -outer layer has only veins and arteries -bleeding occurs in this layer: it is called a subarachnoid hemorrhage. -subarachnoid means below t ...
BRAIN FACTS
... • His brain is similar in size to a normal human’s brain but in the region responsible for math and science, is 35% wider • His brain was slightly larger than a normal brain because he exercised it more ...
... • His brain is similar in size to a normal human’s brain but in the region responsible for math and science, is 35% wider • His brain was slightly larger than a normal brain because he exercised it more ...
15_Neuro
... Autonomic Nervous System emotional responses/behavior body temperature food intake= hunger water balance and thirst sleep-wake cycles endocrine system activity ...
... Autonomic Nervous System emotional responses/behavior body temperature food intake= hunger water balance and thirst sleep-wake cycles endocrine system activity ...
General PLTW Document - Buncombe County Schools
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
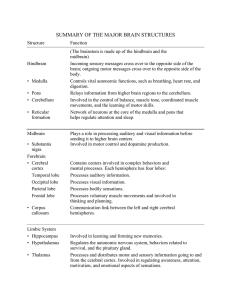
SUMMARY OF THE MAJOR BRAIN STRUCTURES
... Function (The brainstem is made up of the hindbrain and the midbrain) Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays ...
... Function (The brainstem is made up of the hindbrain and the midbrain) Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays ...
Unit 03B
... can be identified by the text being underlined and a different color (usually purple). – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take ...
... can be identified by the text being underlined and a different color (usually purple). – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take ...
Neuroanatomy - UCSD Cognitive Science
... • Brain is composed of two hemispheres connected by a set of fibers (corpus callosum) • 200-250 million fibers • Monotremes and marsupials do not have a corpus callosum • Agenesis and split brain patients ...
... • Brain is composed of two hemispheres connected by a set of fibers (corpus callosum) • 200-250 million fibers • Monotremes and marsupials do not have a corpus callosum • Agenesis and split brain patients ...
Cognitive Development - Oakland Schools Moodle
... Extremely important medical research area Research continues to show that a baby’s brain capacity is even greater than we ever imagined Our brains are stimulated through our senses Brain function is due to the brain’s capabilities as well as outside experiences ...
... Extremely important medical research area Research continues to show that a baby’s brain capacity is even greater than we ever imagined Our brains are stimulated through our senses Brain function is due to the brain’s capabilities as well as outside experiences ...
Part I - QIBA Wiki
... offered to act on our behalf, but did not hear back. Although this was promising, when we evaluated the data (after registering) it was difficult to find high-quality MRI image sets that were suitable for segmentation. University of Washington patient images AT UW the neuroradiology team maintains ...
... offered to act on our behalf, but did not hear back. Although this was promising, when we evaluated the data (after registering) it was difficult to find high-quality MRI image sets that were suitable for segmentation. University of Washington patient images AT UW the neuroradiology team maintains ...
Outline of Achievements
... tomography (CT) from the late 1960s to 1970s that brought about groundbreaking advances in diagnostic imaging technology. It was this technology that made cross-sectional images of the body possible and enabled more detailed investigation of internal organs. Today in the field of medicine various me ...
... tomography (CT) from the late 1960s to 1970s that brought about groundbreaking advances in diagnostic imaging technology. It was this technology that made cross-sectional images of the body possible and enabled more detailed investigation of internal organs. Today in the field of medicine various me ...
Neurobiology of Addiction
... DEPENDENCE Exogenous administration of drug replaces brain’s production of endogenous chemical ...
... DEPENDENCE Exogenous administration of drug replaces brain’s production of endogenous chemical ...