Fans and critics of globalist theories.
... have got up. A fortunate lapse of consciousness occurs; we forget both the warmth and the cold;… the (spontaneous) idea flashes across us, "Hollo, I must lie here no longer" --- an idea which at that lucky instant awakens no contradictory or paralyzing suggestions, and consequently produces immediat ...
... have got up. A fortunate lapse of consciousness occurs; we forget both the warmth and the cold;… the (spontaneous) idea flashes across us, "Hollo, I must lie here no longer" --- an idea which at that lucky instant awakens no contradictory or paralyzing suggestions, and consequently produces immediat ...
interactions between number and space in parietal cortex
... synaesthesia for numbers, using rigorous psychophysical and neuroimaging protocols, might further illuminate our understanding of the connections between numbers and space31,32. In summary, various protocols indicate that numbers automatically elicit task-, modality- and effectorindependent spatial ...
... synaesthesia for numbers, using rigorous psychophysical and neuroimaging protocols, might further illuminate our understanding of the connections between numbers and space31,32. In summary, various protocols indicate that numbers automatically elicit task-, modality- and effectorindependent spatial ...
Sample pages PDF
... As Cabanis succinctly expressed, the brain secretes thought as the liver secretes bile [3]. The philosopher and physiologist might have added that the brain colors thoughts with emotions just as bilirubin gives bile its yellowish hue. This emotional component opens us to the joys and tragedies of li ...
... As Cabanis succinctly expressed, the brain secretes thought as the liver secretes bile [3]. The philosopher and physiologist might have added that the brain colors thoughts with emotions just as bilirubin gives bile its yellowish hue. This emotional component opens us to the joys and tragedies of li ...
Impulsivity-related brain volume deficits in schizophrenia
... the brain. Hence, our goal was to determine whether addicted and non-addicted schizophrenic patients suffer from different brain deficits. We were especially interested to determine if grey matter volumes were affected by impulsivity. We hypothesized that (comorbid) substance abuse would be associat ...
... the brain. Hence, our goal was to determine whether addicted and non-addicted schizophrenic patients suffer from different brain deficits. We were especially interested to determine if grey matter volumes were affected by impulsivity. We hypothesized that (comorbid) substance abuse would be associat ...
A unifying view of the basis of social cognition
... performing a similar action (mirror neuron system). In the second part, we will show that a similar mirroring mechanism, bridging first- and third-person experiences, also exists for emotions. Action understanding: cognitive and motor mechanisms The conventional conceptual approach for understanding ...
... performing a similar action (mirror neuron system). In the second part, we will show that a similar mirroring mechanism, bridging first- and third-person experiences, also exists for emotions. Action understanding: cognitive and motor mechanisms The conventional conceptual approach for understanding ...
The Red Nucleus: Past, Present, and Future
... it appears as though most cortical input to the RN is restricted to the RNp [3] Since RNm receives much of the cortical input in lower vertebrates, it is likely that RNm and RNp have changed functional roles in primates. Though input from the cerebral cortex is a major mode of activation in the prim ...
... it appears as though most cortical input to the RN is restricted to the RNp [3] Since RNm receives much of the cortical input in lower vertebrates, it is likely that RNm and RNp have changed functional roles in primates. Though input from the cerebral cortex is a major mode of activation in the prim ...
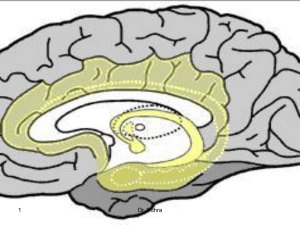
20-Limbic
... cross to the opposite side through small hippocampal commissure. The body of the fornix divides into two columns & enter the hypothalamus where the majority of the fibers terminate in the mammillary body. The mammillary body in turn projects to the anterior nuclear group of the thalamus via mammilot ...
... cross to the opposite side through small hippocampal commissure. The body of the fornix divides into two columns & enter the hypothalamus where the majority of the fibers terminate in the mammillary body. The mammillary body in turn projects to the anterior nuclear group of the thalamus via mammilot ...
7 The Nervous System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN
... Surrounds the third ventricle The relay station for sensory impulses upward to the sensory cortex Transfers impulses to the correct part of the cortex for localization and interpretation by the neurons ...
... Surrounds the third ventricle The relay station for sensory impulses upward to the sensory cortex Transfers impulses to the correct part of the cortex for localization and interpretation by the neurons ...
Human Physiology
... to specialization of each hemisphere for certain functions Each cerebral hemisphere controls movement on opposite side of body And receives sensory info from opposite side of body Hemispheres communicate thru the corpus callosum (Fig 8.1) which contains about 200 million fibers ...
... to specialization of each hemisphere for certain functions Each cerebral hemisphere controls movement on opposite side of body And receives sensory info from opposite side of body Hemispheres communicate thru the corpus callosum (Fig 8.1) which contains about 200 million fibers ...
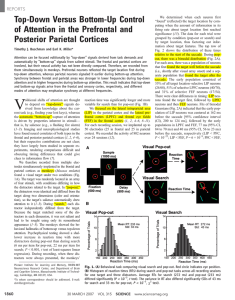
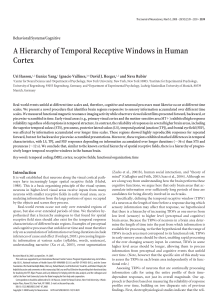
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control of Attention in the Prefrontal
... during pop-out than during search. Thus, bottomup and top-down attention may rely on different frequency bands of coherence between the frontal and parietal cortex. The source of top-down signals has largely been inferred from indirect evidence such as patterns of anatomical connections (7). In the ...
... during pop-out than during search. Thus, bottomup and top-down attention may rely on different frequency bands of coherence between the frontal and parietal cortex. The source of top-down signals has largely been inferred from indirect evidence such as patterns of anatomical connections (7). In the ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control
... during pop-out than during search. Thus, bottomup and top-down attention may rely on different frequency bands of coherence between the frontal and parietal cortex. The source of top-down signals has largely been inferred from indirect evidence such as patterns of anatomical connections (7). In the ...
... during pop-out than during search. Thus, bottomup and top-down attention may rely on different frequency bands of coherence between the frontal and parietal cortex. The source of top-down signals has largely been inferred from indirect evidence such as patterns of anatomical connections (7). In the ...
Diffuse optical imaging of brain activation
... sufficient accuracy (Sato et al., 2004; Strangman et al., 2003; Yamashita et al., 2001). We consider the question of what are the best two wavelengths for accurately characterizing the concentration changes. When choosing the optimum wavelengths, the absorption spectra of the main tissue chromophore ...
... sufficient accuracy (Sato et al., 2004; Strangman et al., 2003; Yamashita et al., 2001). We consider the question of what are the best two wavelengths for accurately characterizing the concentration changes. When choosing the optimum wavelengths, the absorption spectra of the main tissue chromophore ...
Relationship between muscle output and functional MRI
... outside of the MRI room. These included the pressure transducer (part of the transducer is made of stainless steel), EMG and force amplifiers, the associated power supply, and the data acquisition unit (laptop computer and its docking station). The electrode wires were formed into a flat cable runni ...
... outside of the MRI room. These included the pressure transducer (part of the transducer is made of stainless steel), EMG and force amplifiers, the associated power supply, and the data acquisition unit (laptop computer and its docking station). The electrode wires were formed into a flat cable runni ...
Multimodal imaging and the neural basis of EEG and fMRI
... when EPSP arrive to the deep layers. Note polarities are reversed for IPSP. ...
... when EPSP arrive to the deep layers. Note polarities are reversed for IPSP. ...
Lateral Zone
... • Ataxia: incoordinated movements due to errors in the control of rate, range, force and direction of movements. • Asynergia: normally there is synergism between agonists and antagonists. This is lost in cerebellar disease. • Dysmetria and Past pointing: dysmetria is inability to control range of mo ...
... • Ataxia: incoordinated movements due to errors in the control of rate, range, force and direction of movements. • Asynergia: normally there is synergism between agonists and antagonists. This is lost in cerebellar disease. • Dysmetria and Past pointing: dysmetria is inability to control range of mo ...
Hasson-JNeurosci2008.. - Center for Neural Science
... In the time-reversal experiment, correlation coefficients were calculated between the responses to the following conditions: the first and second presentations of the original, forward movie (CF1:F2); the first and second presentations of the backward movie (CB1:B2); response to the forward movie an ...
... In the time-reversal experiment, correlation coefficients were calculated between the responses to the following conditions: the first and second presentations of the original, forward movie (CF1:F2); the first and second presentations of the backward movie (CB1:B2); response to the forward movie an ...
Document
... nerves really had the lumen he was sure they must have. He gives directions for finding the orifices at the ends of the nerves. “For in dissections of large animals … it can be seen that a luminous pneuma is carried in those [optic] nerves since they have distinct orifices both at their beginning ab ...
... nerves really had the lumen he was sure they must have. He gives directions for finding the orifices at the ends of the nerves. “For in dissections of large animals … it can be seen that a luminous pneuma is carried in those [optic] nerves since they have distinct orifices both at their beginning ab ...
8129402
... photographed is "Missing Page(s)” . If it was possible to obtain the missing page(s) or section, they are spliced into the film along with adjacent pages. This may have necessitated cutting through an image and duplicating adjacent pages to assure you o f complete continuity. 2. When an image on the ...
... photographed is "Missing Page(s)” . If it was possible to obtain the missing page(s) or section, they are spliced into the film along with adjacent pages. This may have necessitated cutting through an image and duplicating adjacent pages to assure you o f complete continuity. 2. When an image on the ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.