Cortical Motor Organization, Mirror Neurons, and
... neuroimaging techniques. For example, the transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) technique, that allows either to excite or to inactivate limited cortical regions, enabled several researchers to demonstrate the existence of a mirror matching system at the level of the motor cortex. In fact, if a TM ...
... neuroimaging techniques. For example, the transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) technique, that allows either to excite or to inactivate limited cortical regions, enabled several researchers to demonstrate the existence of a mirror matching system at the level of the motor cortex. In fact, if a TM ...
Functional Connectivity of the Secondary Somatosensory Cortex of
... (S1) and secondary somatosensory cortex (S2) is controversial. The existence of a direct thalamocortical projection from ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus (VPL) to S2 is a key factor in determining the relative position of S2 in the processing flow. In this study, the inter-connections of forep ...
... (S1) and secondary somatosensory cortex (S2) is controversial. The existence of a direct thalamocortical projection from ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus (VPL) to S2 is a key factor in determining the relative position of S2 in the processing flow. In this study, the inter-connections of forep ...
Brain, Mood and Cognition in Hypothyroidism
... residual symptoms include firstly independent effects of autoimmune processes on the brain (Grabe et al., 2005), secondly brain hypothyroidism in spite of normal serum hormone levels (Panicker et al., 2009a), thirdly comorbidities leading to a selection bias in seeking health care (Kong et al., 2002 ...
... residual symptoms include firstly independent effects of autoimmune processes on the brain (Grabe et al., 2005), secondly brain hypothyroidism in spite of normal serum hormone levels (Panicker et al., 2009a), thirdly comorbidities leading to a selection bias in seeking health care (Kong et al., 2002 ...
the anatomy and neurosecretory system of the
... stages in the evolution of mushroom bodies can be found in various species. Clark identifies three types of ganglion cell within the brain of Nephtys: ...
... stages in the evolution of mushroom bodies can be found in various species. Clark identifies three types of ganglion cell within the brain of Nephtys: ...
Neurodevelopmental mechanisms of schizophrenia: understanding
... There is epidemiological support for the association of SZ with adverse events during prenatal and perinatal periods [3]. Among such events, birth complications, especially hypoxia, and viral infection in association with SZ provide some clues to the mechanisms underlying the initial risk of this di ...
... There is epidemiological support for the association of SZ with adverse events during prenatal and perinatal periods [3]. Among such events, birth complications, especially hypoxia, and viral infection in association with SZ provide some clues to the mechanisms underlying the initial risk of this di ...
The Anterior Midline Field: Coercion or decision making? Brain and
... the same as in the previously studied begin the book construction, we predicted that (1a) should elicit increased AMF amplitudes if the AMF indeed reflects coercion. However, the effect might occur somewhat later than the 400–450 ms time-window implicated in our previous MEG study, given that the coe ...
... the same as in the previously studied begin the book construction, we predicted that (1a) should elicit increased AMF amplitudes if the AMF indeed reflects coercion. However, the effect might occur somewhat later than the 400–450 ms time-window implicated in our previous MEG study, given that the coe ...
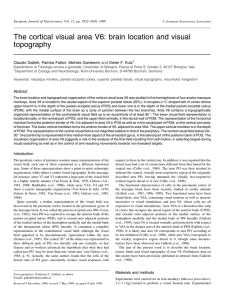
The cortical visual area V6: brain location and visual topography
... V3 occupies most of the cortex around the posterior branch of the POS, while area V6 occupies the large fundus of POS, between its two branches, as well as the posterior wall of the anterior branch of POS, just in front of area V3. The lateral edge of area V6 in the POS is often recognizable even ma ...
... V3 occupies most of the cortex around the posterior branch of the POS, while area V6 occupies the large fundus of POS, between its two branches, as well as the posterior wall of the anterior branch of POS, just in front of area V3. The lateral edge of area V6 in the POS is often recognizable even ma ...
“Attention for Action” and “Response Selection” in Primate Anterior
... ACC might particularly have a function of monitoring the conflicts among feature or category to select proper actions as part of the anterior attention system (conflict monitoring). On the other hand, it has previously been shown that the ACC and its adjacent cingulate areas are involved in motor-re ...
... ACC might particularly have a function of monitoring the conflicts among feature or category to select proper actions as part of the anterior attention system (conflict monitoring). On the other hand, it has previously been shown that the ACC and its adjacent cingulate areas are involved in motor-re ...
Can the Psycho-Emotional State be Optimized by Regular Use of
... impact of training. Therefore, here we explored the effect of selfguided emotion-centered imagery, trying to answer not only the question “whether”, according to the subjects, there was an effect on their state of emotional well-being, but also “how” functioning of the brain was affected by training ...
... impact of training. Therefore, here we explored the effect of selfguided emotion-centered imagery, trying to answer not only the question “whether”, according to the subjects, there was an effect on their state of emotional well-being, but also “how” functioning of the brain was affected by training ...
How Does the Brain Produce Movement?
... at her canvas and her selection of paints; then, she considers what she wants to paint; The brain tells the hand to reach, and the hand tells the brain that it has sucand, finally, she executes her painting. These sequentially organized behaviors are dicceeded. Movements such as reaching for tated b ...
... at her canvas and her selection of paints; then, she considers what she wants to paint; The brain tells the hand to reach, and the hand tells the brain that it has sucand, finally, she executes her painting. These sequentially organized behaviors are dicceeded. Movements such as reaching for tated b ...
Implications on visual apperception: energy, duration
... (Waagepetersen et al., 1999). In addition, monoamine oxidase (MAO) flavo-enzyme, which is localized to the outer mitochondrial membrane, plays a crucial metabolic role in the turnover of dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine in the central nervous system (Cohen and Natasa, 1999 Cohen ...
... (Waagepetersen et al., 1999). In addition, monoamine oxidase (MAO) flavo-enzyme, which is localized to the outer mitochondrial membrane, plays a crucial metabolic role in the turnover of dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine in the central nervous system (Cohen and Natasa, 1999 Cohen ...
decision-making in the primate brain
... effect lies in the fact that because stimulus A fully predicted reward in stage 1, stimulus X was redundant and was therefore not highlighted for learning (Rescorla and Wagner 1972). Reward prediction error models, such as the Rescorla-Wagner model or temporal difference learning models (Sutton and Ba ...
... effect lies in the fact that because stimulus A fully predicted reward in stage 1, stimulus X was redundant and was therefore not highlighted for learning (Rescorla and Wagner 1972). Reward prediction error models, such as the Rescorla-Wagner model or temporal difference learning models (Sutton and Ba ...
Somatotopic mapping of natural upper- and lower
... four patients, and observed values in the same range as for upper extremities (analyzed in six patients). Speech-related responses in the three investigated patients, however, exhibited only a very low sensitivity. The present findings indicate that localization of not only upper- but also lower-extr ...
... four patients, and observed values in the same range as for upper extremities (analyzed in six patients). Speech-related responses in the three investigated patients, however, exhibited only a very low sensitivity. The present findings indicate that localization of not only upper- but also lower-extr ...
Different representations of pleasant and unpleasant odours in the
... cortex showing a correlation with the subjective pleasantness ratings of the odours. Thus the results suggest that there is a hedonic map of the sense of smell in brain regions such as the orbitofrontal cortex, and these results have implications for understanding the psychiatric and related problem ...
... cortex showing a correlation with the subjective pleasantness ratings of the odours. Thus the results suggest that there is a hedonic map of the sense of smell in brain regions such as the orbitofrontal cortex, and these results have implications for understanding the psychiatric and related problem ...
Cognitive neuroscience of self-regulation failure
... occurs whenever the balance is tipped in favor of subcortical areas, either due to particularly strong impulses or when prefrontal function itself is impaired. Such a model is consistent with recent findings in the cognitive neuroscience of addictive behavior, emotion regulation and decision-making. ...
... occurs whenever the balance is tipped in favor of subcortical areas, either due to particularly strong impulses or when prefrontal function itself is impaired. Such a model is consistent with recent findings in the cognitive neuroscience of addictive behavior, emotion regulation and decision-making. ...
Motor Areas of the Medial Wall: A Review of Their Location and
... Although to date very few physiological studies have specifically investigated the cingulate motor areas, recent evidence indicates that functional differences complement the anatomical divisions. Luppino et al. (1991) described two areas of the cingulate sulcus where intracortical microstimulation ...
... Although to date very few physiological studies have specifically investigated the cingulate motor areas, recent evidence indicates that functional differences complement the anatomical divisions. Luppino et al. (1991) described two areas of the cingulate sulcus where intracortical microstimulation ...
PREFRONTAL AND MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE INTERACTIONS IN
... deficits13,24. The importance of the perirhinal cortex for familiarity-based memory is less controversial. Electrophysiological studies have found perirhinal neurons that show diminished responses to repeated stimuli25,26, whereas few such neurons have been found in the hippocampus27,28. The perirhi ...
... deficits13,24. The importance of the perirhinal cortex for familiarity-based memory is less controversial. Electrophysiological studies have found perirhinal neurons that show diminished responses to repeated stimuli25,26, whereas few such neurons have been found in the hippocampus27,28. The perirhi ...
Brain-implantable biomimetic electronics as the next era in neural
... structural and functional characteristics of the brain will necessitate adaptation of each prosthetic device to the individual patient. Some provision for “personalizing” an implantable prosthetic must be anticipated and included in the neuron/network model and the device design. Finally, there is t ...
... structural and functional characteristics of the brain will necessitate adaptation of each prosthetic device to the individual patient. Some provision for “personalizing” an implantable prosthetic must be anticipated and included in the neuron/network model and the device design. Finally, there is t ...
(2003). Prefrontal and medial temporal lobe interactions in
... deficits13,24. The importance of the perirhinal cortex for familiarity-based memory is less controversial. Electrophysiological studies have found perirhinal neurons that show diminished responses to repeated stimuli25,26, whereas few such neurons have been found in the hippocampus27,28. The perirhi ...
... deficits13,24. The importance of the perirhinal cortex for familiarity-based memory is less controversial. Electrophysiological studies have found perirhinal neurons that show diminished responses to repeated stimuli25,26, whereas few such neurons have been found in the hippocampus27,28. The perirhi ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.