A Truncated Laminin Chain Homologous to the B2 Chain: Structure
... This structure is stabilized by ionic interactions between the chains. Calculations of these interactions show that only heterotrimeric molecules with one A-type chain, one Bl-type chain, and one B2-type chain are favorable (20). Studies on the expression of laminin subunit genes and distribution of ...
... This structure is stabilized by ionic interactions between the chains. Calculations of these interactions show that only heterotrimeric molecules with one A-type chain, one Bl-type chain, and one B2-type chain are favorable (20). Studies on the expression of laminin subunit genes and distribution of ...
Regulation of Ketone Body Metabolism and the Role of PPAR
... a nodal point in the ketogenic pathway and is strictly controlled by other transcription factors and various posttranslational mechanisms. The Hmgcs2 gene contains the consensus peroxisome proliferator responsive element (PPRE) sequence localized at −104–92 bp in the promoter [20,21]. One of the mos ...
... a nodal point in the ketogenic pathway and is strictly controlled by other transcription factors and various posttranslational mechanisms. The Hmgcs2 gene contains the consensus peroxisome proliferator responsive element (PPRE) sequence localized at −104–92 bp in the promoter [20,21]. One of the mos ...
Saccharomyces species in the Production of Beer
... come from the genus Saccharomyces—a minority of non-Saccharomyces yeast cultures employed in brewing will be discussed in Section 8. Yeast is cultured in an acidic aqueous sugary solution called wort prepared from barley malt and other cereals such as corn (maize), wheat, rice, sorghum, and also can ...
... come from the genus Saccharomyces—a minority of non-Saccharomyces yeast cultures employed in brewing will be discussed in Section 8. Yeast is cultured in an acidic aqueous sugary solution called wort prepared from barley malt and other cereals such as corn (maize), wheat, rice, sorghum, and also can ...
An Investigation of Acetobacter aceti N5
... the role of two conserved histidines. A pH-rate comparison of AaPurE and the active mutant AaPurE-H59D was used to identify His59 as the key active site acid/base residue. The thermostability of Escherichia coli PurE (EcPurE) over a range of pH was also assessed and compared to AaPurE. AaPurE was fo ...
... the role of two conserved histidines. A pH-rate comparison of AaPurE and the active mutant AaPurE-H59D was used to identify His59 as the key active site acid/base residue. The thermostability of Escherichia coli PurE (EcPurE) over a range of pH was also assessed and compared to AaPurE. AaPurE was fo ...
Supplementary materials - Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
... regulatory network is not acyclic. (a) Learning the regulatory program: Given a set of modules, we learned the regulatory association for each module by using the candidate expression (e-) and genotype (g-) regulators as candidate genetic regulators. As described above, the association between the g ...
... regulatory network is not acyclic. (a) Learning the regulatory program: Given a set of modules, we learned the regulatory association for each module by using the candidate expression (e-) and genotype (g-) regulators as candidate genetic regulators. As described above, the association between the g ...
Characterization of the cDNA and Gene Coding for the Biotin
... Ward (personal communication) and to the partia1 sequence reported in GenBank accession number L34413. The major differences between these three sequences are at the 5' and 3' noncoding ends. At the 5' end, the pBS-1 sequence is 122 nucleotides longer than the sequence shown in GenBank accession num ...
... Ward (personal communication) and to the partia1 sequence reported in GenBank accession number L34413. The major differences between these three sequences are at the 5' and 3' noncoding ends. At the 5' end, the pBS-1 sequence is 122 nucleotides longer than the sequence shown in GenBank accession num ...
D3.1 - transPLANT
... ENVO is a very general ontology maintained by known experts of bioontologies (S. Lewis, C. Mungall, M. Ashburner, B. Smith, …). ENVO contains terms for biomes, environmental features, and environmental material. The drawback of this general approach is that only a very small subset of the ontology m ...
... ENVO is a very general ontology maintained by known experts of bioontologies (S. Lewis, C. Mungall, M. Ashburner, B. Smith, …). ENVO contains terms for biomes, environmental features, and environmental material. The drawback of this general approach is that only a very small subset of the ontology m ...
and Rhizobiales-Like PPP-Family Protein Phosphatases from
... Reversible protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases and phosphatases represents the most prolific and currently best-characterized post-translational modification. Over the last decade advancements in genome sequencing technologies has massively increased genomic databases, resulting in ...
... Reversible protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases and phosphatases represents the most prolific and currently best-characterized post-translational modification. Over the last decade advancements in genome sequencing technologies has massively increased genomic databases, resulting in ...
Full-Text PDF
... The activity of the PPP is also directly controlled by p53 through interaction with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), the first and rate-limiting enzyme of this pathway. Binding of p53 to G6PD prevents formation of the active enzyme dimer, leading to a decrease in enzyme activity. Mutants of ...
... The activity of the PPP is also directly controlled by p53 through interaction with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), the first and rate-limiting enzyme of this pathway. Binding of p53 to G6PD prevents formation of the active enzyme dimer, leading to a decrease in enzyme activity. Mutants of ...
Defining the Schistosoma haematobium kinome enables the
... Recent research efforts to identify new molecular targets for chemotherapeutic intervention have focused on protein kinases13,14, because they are involved in signalling cascades of essential regulatory and developmental processes15–17, particular kinase groups have relatively conserved structures18 ...
... Recent research efforts to identify new molecular targets for chemotherapeutic intervention have focused on protein kinases13,14, because they are involved in signalling cascades of essential regulatory and developmental processes15–17, particular kinase groups have relatively conserved structures18 ...
Sucrose breakdown in the potato tuber - publish.UP
... In this work different approaches are undertaken to improve the understanding of the sucroseto-starch pathway in developing potato tubers. At first an inducible gene expression system from fungal origin is optimised for the use of studying metabolism in the potato tuber. It is found that the alc sys ...
... In this work different approaches are undertaken to improve the understanding of the sucroseto-starch pathway in developing potato tubers. At first an inducible gene expression system from fungal origin is optimised for the use of studying metabolism in the potato tuber. It is found that the alc sys ...
David Gilbert - National e
... “A major challenge of computational protein design is the creation of novel proteins with arbitrarily chosen three-dimensional structures. Here, we used a general computational strategy that iterates between sequence design and structure prediction to design a 93-residue /ß protein called Top7 with ...
... “A major challenge of computational protein design is the creation of novel proteins with arbitrarily chosen three-dimensional structures. Here, we used a general computational strategy that iterates between sequence design and structure prediction to design a 93-residue /ß protein called Top7 with ...
Identity elements in tRNA-mediated transcription
... Fig. 3. Effect of native and chimeric tRNAs on transcription antitermination in the trpE-lacZ fusion. RNA was isolated from L. lactis cells after a growth medium shift as indicated in Methods and used to prepare a Northern blot that was hybridized with a lacZ-specific probe to visualize full length ...
... Fig. 3. Effect of native and chimeric tRNAs on transcription antitermination in the trpE-lacZ fusion. RNA was isolated from L. lactis cells after a growth medium shift as indicated in Methods and used to prepare a Northern blot that was hybridized with a lacZ-specific probe to visualize full length ...
Lessons from the Genome Sequence of Neurospora crassa: Tracing
... Department of Plant Pathology, University of California, Riverside, California 925211; Department of Chemistry, California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, California 917682; Department of Plant Pathology and Microbiology, Faculty of Agricultural, Food and Environmental Quality Sciences, The He ...
... Department of Plant Pathology, University of California, Riverside, California 925211; Department of Chemistry, California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, California 917682; Department of Plant Pathology and Microbiology, Faculty of Agricultural, Food and Environmental Quality Sciences, The He ...
Guidelines on Similar Biologics: Regulatory Requirements for
... and robust. If the host cell line used for the production of reference biologic is disclosed, it is desired to use the same cell line as the reference biologic. Alternatively any cell line that is adequately characterized and appropriate for intended use can be used to develop a similar biologic, wi ...
... and robust. If the host cell line used for the production of reference biologic is disclosed, it is desired to use the same cell line as the reference biologic. Alternatively any cell line that is adequately characterized and appropriate for intended use can be used to develop a similar biologic, wi ...
Glucose metabolism in Trypanosoma cruzi
... instance, a cMDH [cytosolic MDH (malate dehydrogenase)] is not present in T. cruzi, having mutated to an l‑α‑aromatic hydroxyacid dehydrogenase that is unable to reduce oxaloacetate [13]. The enzymes converting glucose into 3‑phosphoglycerate are present inside the glycosome in T. cruzi, whereas the ...
... instance, a cMDH [cytosolic MDH (malate dehydrogenase)] is not present in T. cruzi, having mutated to an l‑α‑aromatic hydroxyacid dehydrogenase that is unable to reduce oxaloacetate [13]. The enzymes converting glucose into 3‑phosphoglycerate are present inside the glycosome in T. cruzi, whereas the ...
Major roles of isocitrate lyase and malate synthase in
... a pseudogene and the ICL gene is absent (Kondrashov et al., 2006). In addition to allowing the growth of bacteria on C2 compounds, the glyoxylate cycle is important for the growth of higher plant seedlings under most environmental conditions, since it participates in the conversion of stored lipids ...
... a pseudogene and the ICL gene is absent (Kondrashov et al., 2006). In addition to allowing the growth of bacteria on C2 compounds, the glyoxylate cycle is important for the growth of higher plant seedlings under most environmental conditions, since it participates in the conversion of stored lipids ...
Applied Biosystems Real-Time PCR Rapid Assay Development
... SYBR® Green Primers The use of SYBR® Green reagents in real-time PCR is based on the exceptionally high affinity of SYBR® Green dye for double-stranded DNA. The progress of a real-time run using SYBR® reagent chemistry can be measured by monitoring this increase in fluorescence as SYBR® Green dye b ...
... SYBR® Green Primers The use of SYBR® Green reagents in real-time PCR is based on the exceptionally high affinity of SYBR® Green dye for double-stranded DNA. The progress of a real-time run using SYBR® reagent chemistry can be measured by monitoring this increase in fluorescence as SYBR® Green dye b ...
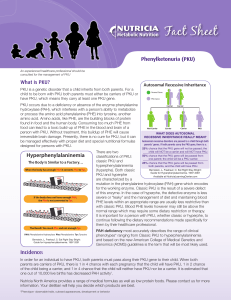
PKU - Nutricia Learning Center
... Symptoms of Elevated Blood PHE Levels: All patients with PKU, who are not started on diet immediately, will begin to build-up PHE in the blood and brain. In an infant with classic PKU, poorly controlled PHE levels will result in irreversible brain damage. Therefore, it is essential that each infant ...
... Symptoms of Elevated Blood PHE Levels: All patients with PKU, who are not started on diet immediately, will begin to build-up PHE in the blood and brain. In an infant with classic PKU, poorly controlled PHE levels will result in irreversible brain damage. Therefore, it is essential that each infant ...
Autotrophic CO2 fixation via the reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle in
... genome sequence (A. aeolicus) or carbon isotopic measurements (Tc. ruber) both organisms were previously suspected to use this pathway, but direct evidence had been lacking (Deckert et al., 1998; Jahnke et al., 2001). Isocitrate dehydrogenase, as well as malate dehydrogenase, was found to be NAD(H)- ...
... genome sequence (A. aeolicus) or carbon isotopic measurements (Tc. ruber) both organisms were previously suspected to use this pathway, but direct evidence had been lacking (Deckert et al., 1998; Jahnke et al., 2001). Isocitrate dehydrogenase, as well as malate dehydrogenase, was found to be NAD(H)- ...
Gene Section GAST (gastrin) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... The two principal biologically active forms of circulating gastrin are gastrin-17 (G17) and gastrin-34 (G34). In rodent and human G cells of antrum and proximal duodenum, approximately 95% of the progastrin is processed to partially sulfated G17 (85%) and G34 (10%). Although G17 is the predominant p ...
... The two principal biologically active forms of circulating gastrin are gastrin-17 (G17) and gastrin-34 (G34). In rodent and human G cells of antrum and proximal duodenum, approximately 95% of the progastrin is processed to partially sulfated G17 (85%) and G34 (10%). Although G17 is the predominant p ...
+ΔFosB
... - Nave is the mean N value for the control - Ctave is the mean Ct value for the control. - Fold differences (stress ChIP relative to control ChIP) were then determined by raising 2 to the Ct power. Input : One hundred microliters of the pre-immunoprecipitated lysate Control ChIP : samples were immun ...
... - Nave is the mean N value for the control - Ctave is the mean Ct value for the control. - Fold differences (stress ChIP relative to control ChIP) were then determined by raising 2 to the Ct power. Input : One hundred microliters of the pre-immunoprecipitated lysate Control ChIP : samples were immun ...
Chapter X-1: The Plant Cell and the Cell Cycle
... It involves multiple rounds of DNA synthesis. It provides a mechanism for increasing the level of gene expression. It may result in thousands of copies of each gene. It usually occurs following the differentiation of cells. ...
... It involves multiple rounds of DNA synthesis. It provides a mechanism for increasing the level of gene expression. It may result in thousands of copies of each gene. It usually occurs following the differentiation of cells. ...
Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli and Corynebacterium glutamicum for the -threonine
... Selection criteria would include reduced by-product formation and expanded substrate spectra. By all accounts, it is by genetic engineering that breakthroughs in efficient and clean L-threonine production will be achieved. This review covers development of L-threonine producers of E. coli and C. glut ...
... Selection criteria would include reduced by-product formation and expanded substrate spectra. By all accounts, it is by genetic engineering that breakthroughs in efficient and clean L-threonine production will be achieved. This review covers development of L-threonine producers of E. coli and C. glut ...
Cyclic-‐di-‐AMP: another second messenger enters the fray
... Nucleotides are indispensible components of all living cells as they make up DNA and RNA, and serve as important energy sources. In addition to these functions, nucleotides also play key roles in signal ...
... Nucleotides are indispensible components of all living cells as they make up DNA and RNA, and serve as important energy sources. In addition to these functions, nucleotides also play key roles in signal ...
Gene regulatory network

A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of regulators thatinteract with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins.The regulator can be DNA, RNA, protein and their complex. The interaction can be direct or indirect (through their transcribed RNA or translated protein).In general, each mRNA molecule goes on to make a specific protein (or set of proteins). In some cases this protein will be structural, and will accumulate at the cell membrane or within the cell to give it particular structural properties. In other cases the protein will be an enzyme, i.e., a micro-machine that catalyses a certain reaction, such as the breakdown of a food source or toxin. Some proteins though serve only to activate other genes, and these are the transcription factors that are the main players in regulatory networks or cascades. By binding to the promoter region at the start of other genes they turn them on, initiating the production of another protein, and so on. Some transcription factors are inhibitory.In single-celled organisms, regulatory networks respond to the external environment, optimising the cell at a given time for survival in this environment. Thus a yeast cell, finding itself in a sugar solution, will turn on genes to make enzymes that process the sugar to alcohol. This process, which we associate with wine-making, is how the yeast cell makes its living, gaining energy to multiply, which under normal circumstances would enhance its survival prospects.In multicellular animals the same principle has been put in the service of gene cascades that control body-shape. Each time a cell divides, two cells result which, although they contain the same genome in full, can differ in which genes are turned on and making proteins. Sometimes a 'self-sustaining feedback loop' ensures that a cell maintains its identity and passes it on. Less understood is the mechanism of epigenetics by which chromatin modification may provide cellular memory by blocking or allowing transcription. A major feature of multicellular animals is the use of morphogen gradients, which in effect provide a positioning system that tells a cell where in the body it is, and hence what sort of cell to become. A gene that is turned on in one cell may make a product that leaves the cell and diffuses through adjacent cells, entering them and turning on genes only when it is present above a certain threshold level. These cells are thus induced into a new fate, and may even generate other morphogens that signal back to the original cell. Over longer distances morphogens may use the active process of signal transduction. Such signalling controls embryogenesis, the building of a body plan from scratch through a series of sequential steps. They also control and maintain adult bodies through feedback processes, and the loss of such feedback because of a mutation can be responsible for the cell proliferation that is seen in cancer. In parallel with this process of building structure, the gene cascade turns on genes that make structural proteins that give each cell the physical properties it needs.It has been suggested that, because biological molecular interactions are intrinsically stochastic, gene networks are the result of cellular processes and not their cause (i.e. cellular Darwinism). However, recent experimental evidence has favored the attractor view of cell fates.