General Virology - California State University, Fullerton
... Host-induced modification • Viral property that varies depending on the host • Phage DNA hydroxymethyl cytosine (HMC) replaces C – Viral enzymes: C to HMC – Viral DNA polymerase: adds HMC not C – What is advantage of HMC? • Glucose is attached to HMC – Host enzyme needed to prepare glucose – Protec ...
... Host-induced modification • Viral property that varies depending on the host • Phage DNA hydroxymethyl cytosine (HMC) replaces C – Viral enzymes: C to HMC – Viral DNA polymerase: adds HMC not C – What is advantage of HMC? • Glucose is attached to HMC – Host enzyme needed to prepare glucose – Protec ...
Viruses
... Translates RNA into DNA, integration into cellular DNA called provirus Provirus DNA is transcribed to make new HIV viruses that leave cell Provirus never leaves cell ...
... Translates RNA into DNA, integration into cellular DNA called provirus Provirus DNA is transcribed to make new HIV viruses that leave cell Provirus never leaves cell ...
Contributions/Accomplishments
... - viruses contain either DNA or RNA but not both of them. Living cells have both of them. These nucleic acids can either double stranded or single stranded. (Next lecture we will learn about DNA and RNA and how living cells use them.) The Membrane Envelope (if present) - some viruses have a fatty (l ...
... - viruses contain either DNA or RNA but not both of them. Living cells have both of them. These nucleic acids can either double stranded or single stranded. (Next lecture we will learn about DNA and RNA and how living cells use them.) The Membrane Envelope (if present) - some viruses have a fatty (l ...
Taxonomy/Microorganisms Test Review Sheet Name: Please
... kingdom whose members exhibit these traits: multicellular, true nucleus, possess cell walls, must obtain food, representative organisms include mushrooms and yeast? OR Multicellular eukaryotes that are usually mobile and obtain food from other organisms probably belong to what kingdom? ...
... kingdom whose members exhibit these traits: multicellular, true nucleus, possess cell walls, must obtain food, representative organisms include mushrooms and yeast? OR Multicellular eukaryotes that are usually mobile and obtain food from other organisms probably belong to what kingdom? ...
Bacteria and Viruses
... Virus DNA enters host, becomes part of Hosts DNA. Host Cell copies its DNA and Virus DNA and reproduces normally but passes on Virus DNA to all its offspring. Cell with Virus DNA but not active is called a prophage. Prophage can become active and ...
... Virus DNA enters host, becomes part of Hosts DNA. Host Cell copies its DNA and Virus DNA and reproduces normally but passes on Virus DNA to all its offspring. Cell with Virus DNA but not active is called a prophage. Prophage can become active and ...
Viruses -Virus : obligate intracellular parasites .
... Viruses -Virus : obligate intracellular parasites . -Virus contain two genomes DNA or RNA But not both . which contain :- ss : single stranded . ds : double stranded -Capsid :- protein shell that enclose the viral genome . -Capsid symmetry : (( cabic – helical – complex )) -Viral Enveloped : help in ...
... Viruses -Virus : obligate intracellular parasites . -Virus contain two genomes DNA or RNA But not both . which contain :- ss : single stranded . ds : double stranded -Capsid :- protein shell that enclose the viral genome . -Capsid symmetry : (( cabic – helical – complex )) -Viral Enveloped : help in ...
What occurs during the viral replication step of penetration?
... Viral DNA gets incorporated into the host cell's genome. ...
... Viral DNA gets incorporated into the host cell's genome. ...
Viruses
... composed of a core of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. 4. A virus’s protein coat is called a capsid. 5. The capsid enables a virus to enter a host cell. ...
... composed of a core of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. 4. A virus’s protein coat is called a capsid. 5. The capsid enables a virus to enter a host cell. ...
Viruses - CSUN.edu
... o Cause infectious diseases – from common cold to rabies and AIDS Size and Structure 1892 – first virus (tobacco mosaic disease) was discovered 1935 – tobacco mosaic virus was chemically isolated Plants – leaf cells Viruses infect ...
... o Cause infectious diseases – from common cold to rabies and AIDS Size and Structure 1892 – first virus (tobacco mosaic disease) was discovered 1935 – tobacco mosaic virus was chemically isolated Plants – leaf cells Viruses infect ...
Viruses and infectious agents
... 1. Viruses are extremely small. One billionth of a meter. A thousand times smaller than a bacteria. 2. Viruses infect animals, plants, fungi, protista, and monera. 3. Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages. 4. Viruses that infect other viruses are called virophage. First discovered i ...
... 1. Viruses are extremely small. One billionth of a meter. A thousand times smaller than a bacteria. 2. Viruses infect animals, plants, fungi, protista, and monera. 3. Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages. 4. Viruses that infect other viruses are called virophage. First discovered i ...
Name
... 10. What would happen to a virus that never came in contact with a living cell? Explain your answer. ...
... 10. What would happen to a virus that never came in contact with a living cell? Explain your answer. ...
013368718X_CH20_313-324.indd
... 10. What would happen to a virus that never came in contact with a living cell? Explain your ...
... 10. What would happen to a virus that never came in contact with a living cell? Explain your ...
Name - MrKanesSciencePage
... Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. Lesson Summary The Discovery of Viruses In 1935, the American biochemist Wendell Stanley isolated a virus for the first time. A virus is a particle made of nucleic acid, protein, and, in some cases, lipids. A typical virus is compos ...
... Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. Lesson Summary The Discovery of Viruses In 1935, the American biochemist Wendell Stanley isolated a virus for the first time. A virus is a particle made of nucleic acid, protein, and, in some cases, lipids. A typical virus is compos ...
Virus Power Point
... Viruses are strands of DNA or RNA inside a protective coat. They cannot live on their own, but invade cells in your body and use them as factories to make more viruses. ...
... Viruses are strands of DNA or RNA inside a protective coat. They cannot live on their own, but invade cells in your body and use them as factories to make more viruses. ...
Name Class Date Viruses vs. Cells Make Up #15 Viruses Lesson
... The diagram below shows the lytic cycle of a viral infection. Label the bacterial DNA, host bacterium, viral DNA, and virus. Then, circle the step that shows lysis of the host cell. ...
... The diagram below shows the lytic cycle of a viral infection. Label the bacterial DNA, host bacterium, viral DNA, and virus. Then, circle the step that shows lysis of the host cell. ...
Bacteria and Viruses Powerpoint
... • HIV is a RETROVIRUS_ which is a virus that contains RNA and _REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE____. Reverse transcriptase- enzyme that copies viral RNA into DNA. HIV is an infection of the _WHITE BLOOD CELLS_____. The infected person’s white blood cells are damaged and their immune system fails which lead to ...
... • HIV is a RETROVIRUS_ which is a virus that contains RNA and _REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE____. Reverse transcriptase- enzyme that copies viral RNA into DNA. HIV is an infection of the _WHITE BLOOD CELLS_____. The infected person’s white blood cells are damaged and their immune system fails which lead to ...
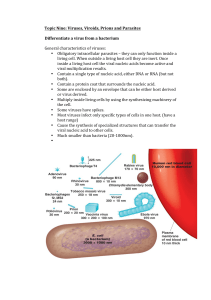
Viruses, Viroids, Prions and Parasites Differentiate a virus from a
... inside a living host cell the viral nucleic acids become active and viral multiplication results. • Contain a single type of nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA (but not both). • Contain a protein coat that surrounds the nucleic acid. • Some are enclosed by an envelope that can be either host deri ...
... inside a living host cell the viral nucleic acids become active and viral multiplication results. • Contain a single type of nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA (but not both). • Contain a protein coat that surrounds the nucleic acid. • Some are enclosed by an envelope that can be either host deri ...
viruses - skippysciences
... • Most viruses have no enzymes • Cannot make protein on its own • Require the protein synthesis machinery of its host cell • Cannot make their own ATP • Act as intracellular parasites • Replicate themselves by making copies if their parts which are assembled using host building block materials ...
... • Most viruses have no enzymes • Cannot make protein on its own • Require the protein synthesis machinery of its host cell • Cannot make their own ATP • Act as intracellular parasites • Replicate themselves by making copies if their parts which are assembled using host building block materials ...
Viruses - Intermediate School Biology
... Viruses are obligate parasites. What does this mean in relation to viruses? ...
... Viruses are obligate parasites. What does this mean in relation to viruses? ...
Viruses
... A. They cannot survive outside a host cell. B. They infect host cells in order to steal the cell's genome. C. They are dependent on host cell organelles and enzymes for their replication. D. They infect host cells in order to cause tumors. ...
... A. They cannot survive outside a host cell. B. They infect host cells in order to steal the cell's genome. C. They are dependent on host cell organelles and enzymes for their replication. D. They infect host cells in order to cause tumors. ...
BACTERIA - Virus and Bacteria worksheet
... 5. ________________________ Made up of only protein only; cause of “Mad Cow disease” ...
... 5. ________________________ Made up of only protein only; cause of “Mad Cow disease” ...
Viral Structure and Life Cycles : Notes - Mr. Lesiuk
... - Another way in which some viruses affect a cell is through a __________________ ______________. The virus does not reproduce and lyse of the host cell (as was the case in the lytic cycle) – at least not right away. -______________________________________________________________________ ___________ ...
... - Another way in which some viruses affect a cell is through a __________________ ______________. The virus does not reproduce and lyse of the host cell (as was the case in the lytic cycle) – at least not right away. -______________________________________________________________________ ___________ ...
3-3 Viruses
... the ‘living’ designation since they do not metabolize energy, they Viruses attacking bacteria cannot reproduce on their own, and they do not grow. They consist simply of a strand of genetic information – either DNA or RNA – surrounded by a shell of protein called the capsid1. Although they can do fe ...
... the ‘living’ designation since they do not metabolize energy, they Viruses attacking bacteria cannot reproduce on their own, and they do not grow. They consist simply of a strand of genetic information – either DNA or RNA – surrounded by a shell of protein called the capsid1. Although they can do fe ...
Plant virus

Plant viruses are viruses that affect plants. Like all other viruses, plant viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that do not have the molecular machinery to replicate without a host. Plant viruses are pathogenic to higher plants. While this article does not intend to list all plant viruses, it discusses some important viruses as well as their uses in plant molecular biology.