so, where do you get all your protein? investigating
... Proteins are the most complex and functionally diverse molecules of living organisms. Proteins compose enzymes, hormones, hair, skin, blood cells and muscle tissue just to name a few and are therefore associated with meat products. The basic elements of proteins are carbon (C) hydrogen (H), oxygen ( ...
... Proteins are the most complex and functionally diverse molecules of living organisms. Proteins compose enzymes, hormones, hair, skin, blood cells and muscle tissue just to name a few and are therefore associated with meat products. The basic elements of proteins are carbon (C) hydrogen (H), oxygen ( ...
Name: Date: Block:___ Background: Proteins are the molecules that
... Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell’s day-to-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell, it is the proteins that "do the work." In this activity you will examine the structure of proteins and how their structur ...
... Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell’s day-to-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell, it is the proteins that "do the work." In this activity you will examine the structure of proteins and how their structur ...
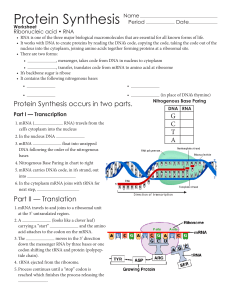
Protein Synthesis
... • It works with DNA to create proteins by reading the DNA’s code, copying the code, taking the code out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, joining amino acids together forming proteins at a ribosomal site. ...
... • It works with DNA to create proteins by reading the DNA’s code, copying the code, taking the code out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, joining amino acids together forming proteins at a ribosomal site. ...
Section 3.3 Notes
... Ribosomes and the Endoplasmic Reticulum, continued The part of the ER with attached ribosomes is called the rough ER The rough ER helps transport proteins that are made by the attached ribosomes New proteins enter the ER The portion of the ER that contains the completed protein pinches off ...
... Ribosomes and the Endoplasmic Reticulum, continued The part of the ER with attached ribosomes is called the rough ER The rough ER helps transport proteins that are made by the attached ribosomes New proteins enter the ER The portion of the ER that contains the completed protein pinches off ...
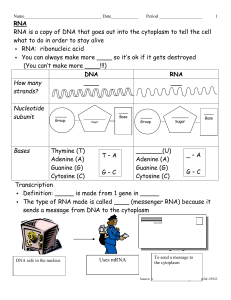
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... o Unzip one gene in _____ o Match up bases to ____side of gene in DNA o mRNA detaches from the _____ o mRNA moves out of the nucleus and into the __________ ...
... o Unzip one gene in _____ o Match up bases to ____side of gene in DNA o mRNA detaches from the _____ o mRNA moves out of the nucleus and into the __________ ...
College 5
... barrier that enables the cell to concentrate nutrients gathered from its environment and retain the products it has synthesized for its own use, while excreting waste products. Without its plasma membrane the cell could not maintain its integrity as a coordinated chemical system. Integral membrane p ...
... barrier that enables the cell to concentrate nutrients gathered from its environment and retain the products it has synthesized for its own use, while excreting waste products. Without its plasma membrane the cell could not maintain its integrity as a coordinated chemical system. Integral membrane p ...
Protein Synthesis (Translation)
... HOW DOES MRNA TELL THE CELL WHAT TO DO? mRNA is a message that codes for a protein Proteins are made in the cytoplasm and then work to keep the cell alive Translation (protein synthesis): Process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 di ...
... HOW DOES MRNA TELL THE CELL WHAT TO DO? mRNA is a message that codes for a protein Proteins are made in the cytoplasm and then work to keep the cell alive Translation (protein synthesis): Process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 di ...
In vitro RNA-peptide co-evolution system for screening ATP
... Introduction: The advent of biological polymers was a key step for the emergence of life. Modern organisms use proteins to achieve energy harvest and transfer in various ways to sustain structural organization through reproduction of molecules. Whereas “evolvability” of the biological system is main ...
... Introduction: The advent of biological polymers was a key step for the emergence of life. Modern organisms use proteins to achieve energy harvest and transfer in various ways to sustain structural organization through reproduction of molecules. Whereas “evolvability” of the biological system is main ...
No Slide Title
... Coiled-coil, three separate polypeptides called chains are supertwisted Provide strength (stronger than ??) Connective tissue (tendons, cartilage, organic matrix of bone, cornea) ...
... Coiled-coil, three separate polypeptides called chains are supertwisted Provide strength (stronger than ??) Connective tissue (tendons, cartilage, organic matrix of bone, cornea) ...
Macromolecules Notes Macromolecules Notes
... The monomer is called an amino acid •20 different kinds of amino acids 5 functions of proteins: • Transport (e.g., hemoglobin) • Provides immunity (e.g., immune system) • Regulate the body (e.g., hormones, enzymes, metabolism) • Muscle tissue (e.g., movement) • Structural components of the body (e.g ...
... The monomer is called an amino acid •20 different kinds of amino acids 5 functions of proteins: • Transport (e.g., hemoglobin) • Provides immunity (e.g., immune system) • Regulate the body (e.g., hormones, enzymes, metabolism) • Muscle tissue (e.g., movement) • Structural components of the body (e.g ...
Energy Unit SG Key
... During translation, a ribosome attaches to the mRNA at the start codon (AUG). The codons on the mRNA match with the complementary anti-codons on tRNA molecules, which carry the amino acids. The amino acids at strung together forming a polypeptide. Insulin is a hormone that carries a signal from cell ...
... During translation, a ribosome attaches to the mRNA at the start codon (AUG). The codons on the mRNA match with the complementary anti-codons on tRNA molecules, which carry the amino acids. The amino acids at strung together forming a polypeptide. Insulin is a hormone that carries a signal from cell ...
Chapter 13.1 and 13.2 RNA, Ribosomes, and Protein Synthesis
... RNA. The bases complement each other. • Eukaryotes – happens in nucleus and moves to cytoplasm to produce protein. ...
... RNA. The bases complement each other. • Eukaryotes – happens in nucleus and moves to cytoplasm to produce protein. ...
Digestion of Biomolecules
... environment • Pepsin begins work • Acidic, partially digested food enters intestine – Activates secretin to neutralize adic – Activates hormone causing release of pancreatic zymogens and bile salts ...
... environment • Pepsin begins work • Acidic, partially digested food enters intestine – Activates secretin to neutralize adic – Activates hormone causing release of pancreatic zymogens and bile salts ...
Document
... Cryogenic protein storage and assessment of protein purity Flash freezing of protein for long term storage. Mass spectrometry and SDS-PAGE for determination of purity and molecular weight. Preparation of buffers for experiments in following weeks. ...
... Cryogenic protein storage and assessment of protein purity Flash freezing of protein for long term storage. Mass spectrometry and SDS-PAGE for determination of purity and molecular weight. Preparation of buffers for experiments in following weeks. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Kent City School District
... Carries the instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to initiate translation Contains 3-base sequences called “codons” Made in transcription ...
... Carries the instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to initiate translation Contains 3-base sequences called “codons” Made in transcription ...
Appendices Enzyme Endurance Review of Protein Structure Great
... significant change in protein shape. Most enzymes are allosteric proteins that can exist in two conformations that differ in catalytic activity, and the enzyme can be turned on or off by ligands that bind to a distinct regulatory site to stabilize either the active or the inactive conformation. The ...
... significant change in protein shape. Most enzymes are allosteric proteins that can exist in two conformations that differ in catalytic activity, and the enzyme can be turned on or off by ligands that bind to a distinct regulatory site to stabilize either the active or the inactive conformation. The ...
RNA polymerases
... This could be a protein or some functional RNA The difference between various cells in a specific organism is due to difference in gene expression ...
... This could be a protein or some functional RNA The difference between various cells in a specific organism is due to difference in gene expression ...
AP gene regulation
... produce the enzymes (proteins) that digest lactose all of the time. No, only when the environment requires it. – Most prokaryotic controls are transcriptional controls ...
... produce the enzymes (proteins) that digest lactose all of the time. No, only when the environment requires it. – Most prokaryotic controls are transcriptional controls ...
Protein Synthesis Review
... Enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions Build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
... Enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions Build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
Organic Molecule Notes
... --has e- for 4 covalent bonds to form. -Natural forms of Carbon --Macro-molecule ...
... --has e- for 4 covalent bonds to form. -Natural forms of Carbon --Macro-molecule ...
TIGR_ISS
... Visually inspect alignments, look for conserved active sites, look for (generally) at least 35% identity across the full lengths of both proteins. If matches are not full length, look to see if there are recognized functional domains in the area where the match occurs. Decide how much information ca ...
... Visually inspect alignments, look for conserved active sites, look for (generally) at least 35% identity across the full lengths of both proteins. If matches are not full length, look to see if there are recognized functional domains in the area where the match occurs. Decide how much information ca ...
מצגת של PowerPoint - The ICNC PhD Program
... amino acid sequence determines protein 3D structure and the structure determines the function. ...
... amino acid sequence determines protein 3D structure and the structure determines the function. ...
breakfast proteins
... Write out a template for the cereal chain using letters to correspond to the different colors of the cereal (ie. YOPPRRGYYOP). Tape this down somewhere in the corner of the room and section off this area with some string. Put some scrap paper and things to write with next to the template. To do and ...
... Write out a template for the cereal chain using letters to correspond to the different colors of the cereal (ie. YOPPRRGYYOP). Tape this down somewhere in the corner of the room and section off this area with some string. Put some scrap paper and things to write with next to the template. To do and ...
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins Essential Cell Biology
... Proteins are by far the most structurally and functionally complex molecules that are known a. They can range in size from approximately 30 amino acids to more than 10,000 but most are between 50 and 2,000 amino acids b. They can be globular, fibrous, filamentous, sheets, rings, spheres, and many ot ...
... Proteins are by far the most structurally and functionally complex molecules that are known a. They can range in size from approximately 30 amino acids to more than 10,000 but most are between 50 and 2,000 amino acids b. They can be globular, fibrous, filamentous, sheets, rings, spheres, and many ot ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.