Chapter 3 - Proteins
... • Name one polar and one nonpolar amino acid, then make a list of all the additional amino acids that you remember. • What are the four weak (noncovalent) interactions that determine the conformation of a protein? • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or gr ...
... • Name one polar and one nonpolar amino acid, then make a list of all the additional amino acids that you remember. • What are the four weak (noncovalent) interactions that determine the conformation of a protein? • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or gr ...
Fundamentals of Cell Biology
... Figure 08.09: Eukaryotic mRNA has a methylated 5' cap. The cap protects the 5' end of mRNA from nucleases and may be methylated at several positions. ...
... Figure 08.09: Eukaryotic mRNA has a methylated 5' cap. The cap protects the 5' end of mRNA from nucleases and may be methylated at several positions. ...
RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
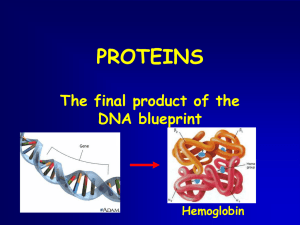
... GENE: coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins in the cell ...
... GENE: coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins in the cell ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... complementary bases using uracil instead of thymine • Continues until the polymerase reaches the termination signal • What do you think a termination signal does? • Termination signal causes the polymerase to release the DNA and RNA ...
... complementary bases using uracil instead of thymine • Continues until the polymerase reaches the termination signal • What do you think a termination signal does? • Termination signal causes the polymerase to release the DNA and RNA ...
Biochemistry - mrmitchellbiowiki
... GET ME SOME PROTEIN Structure of Proteins: 20 different amino acids Combined in numerous ways to form MILLIONS of proteins Number, order and type of amino acid determines the protein DNA directs proteins ...
... GET ME SOME PROTEIN Structure of Proteins: 20 different amino acids Combined in numerous ways to form MILLIONS of proteins Number, order and type of amino acid determines the protein DNA directs proteins ...
051607
... Chapter 6 3/16, 19, 21, 26, 27, 28 • Catalysis in general – Activation energy (EA or DG‡ ) is a kinetic barrier to reaction – Enzymes lower this barrier (don’t change DG or the equilibrium constant) • Create a new reaction pathway with better DH or (and) better DS ...
... Chapter 6 3/16, 19, 21, 26, 27, 28 • Catalysis in general – Activation energy (EA or DG‡ ) is a kinetic barrier to reaction – Enzymes lower this barrier (don’t change DG or the equilibrium constant) • Create a new reaction pathway with better DH or (and) better DS ...
BICH/GENE 431 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Chapter 13 – RNA
... - steric hindrance when intron is too small: both U1 snRNP and U2 snRNP cannot bind at same time to same intron; leads to mutually exclusive exons, like for troponin T - combination of GU-AG and AT-AC splice sites in same pre-mRNA can lead to different combinations; but cannot splice together two di ...
... - steric hindrance when intron is too small: both U1 snRNP and U2 snRNP cannot bind at same time to same intron; leads to mutually exclusive exons, like for troponin T - combination of GU-AG and AT-AC splice sites in same pre-mRNA can lead to different combinations; but cannot splice together two di ...
Molecules of life
... larger structure ◦ Most proteins made of multiple domains that perform different parts of the protein’s function ...
... larger structure ◦ Most proteins made of multiple domains that perform different parts of the protein’s function ...
Slide 1
... primary, secondary, tertiary structure Structure function relationships Biological roles of proteins ...
... primary, secondary, tertiary structure Structure function relationships Biological roles of proteins ...
Long Noncoding RNAs Add Another Layer to Pre
... Loci encoding long ncRNAs often overlap with or are interspersed between multiple protein-coding or noncoding genes in the genome, where they may regulate the expression of their neighbors. Moreover, long ncRNAs have been shown to act as chromatin modifiers, as transcriptional regulators that affect ...
... Loci encoding long ncRNAs often overlap with or are interspersed between multiple protein-coding or noncoding genes in the genome, where they may regulate the expression of their neighbors. Moreover, long ncRNAs have been shown to act as chromatin modifiers, as transcriptional regulators that affect ...
Proteins
... Secondary Structure – some chains form an alpha helix (coil) or a beta sheet (accordion). ...
... Secondary Structure – some chains form an alpha helix (coil) or a beta sheet (accordion). ...
PowerPoint Slides
... • Proteins which have >~50% of their secondary structure elements arranged the in the same order in the protein chain and in three dimensions are classified as having the same fold • No evolutionary relation between proteins *confusingly also called fold classes ...
... • Proteins which have >~50% of their secondary structure elements arranged the in the same order in the protein chain and in three dimensions are classified as having the same fold • No evolutionary relation between proteins *confusingly also called fold classes ...
The Molecular Genetics of Gene Expression
... genes), each protein coding region is preceded by its own ribosome-binding site and AUG initiation codon • The genes contained in a polycistronic mRNA often encode the different proteins of a metabolic pathway. ...
... genes), each protein coding region is preceded by its own ribosome-binding site and AUG initiation codon • The genes contained in a polycistronic mRNA often encode the different proteins of a metabolic pathway. ...
Lecture_9_2005
... • Uses of microarrays is cancer research and diagnosis. – 2733 papers published on microarrays and cancer – 1038 papers published on microarrays, gene expression, cancer diagnosis – 0 since 1997 ...
... • Uses of microarrays is cancer research and diagnosis. – 2733 papers published on microarrays and cancer – 1038 papers published on microarrays, gene expression, cancer diagnosis – 0 since 1997 ...
Chapter 4 - WordPress.com
... • Glucose is the primary source of energy. • Glucose can be stored as glycogen, and converted to and stored as fat. • Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose is incompletely broken down (glycolysis) into lactic acid and small amounts of ATP. Aerobically, gluc ...
... • Glucose is the primary source of energy. • Glucose can be stored as glycogen, and converted to and stored as fat. • Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose is incompletely broken down (glycolysis) into lactic acid and small amounts of ATP. Aerobically, gluc ...
Slide 1
... • called fatty acids Fats can be saturated, which means that they are a solid at room temperature like lard, or unsaturated, which are liquids at room temperature like vegetable ...
... • called fatty acids Fats can be saturated, which means that they are a solid at room temperature like lard, or unsaturated, which are liquids at room temperature like vegetable ...
Biochemistry Review Game
... • Each of the following slides will list a characteristic of one (or more) of the biomolecules. • You will need to be the first group to hold up the correct white board in order to get points! ...
... • Each of the following slides will list a characteristic of one (or more) of the biomolecules. • You will need to be the first group to hold up the correct white board in order to get points! ...
Prep 101
... mRNA is exported out to be translated All post transcriptional modifications have multiple steps and different enzymes are involved which must be known Cleavage and polyadenylation occurs in the same process Splicing occurs at introns and alternative splicing can lead to different proteins from the ...
... mRNA is exported out to be translated All post transcriptional modifications have multiple steps and different enzymes are involved which must be known Cleavage and polyadenylation occurs in the same process Splicing occurs at introns and alternative splicing can lead to different proteins from the ...
Molecular Interactions of Collagen-binding Proteins
... Investigate the interactions of collagen-binding proteins with collagen and other extracellular matrix protein using techniques such as co-immunoprecipitation and bead-based assays. Collagen-fibrillation assays using Microplate-reader. Structural/biophysical characterization of collagenbinding prote ...
... Investigate the interactions of collagen-binding proteins with collagen and other extracellular matrix protein using techniques such as co-immunoprecipitation and bead-based assays. Collagen-fibrillation assays using Microplate-reader. Structural/biophysical characterization of collagenbinding prote ...
Proteins & Nucleic Acids - St. Mary Catholic Secondary School
... Tertiary structure is also aided by prosthetic groups that are inorganic compounds that act as a central point for bonding within the protein. ...
... Tertiary structure is also aided by prosthetic groups that are inorganic compounds that act as a central point for bonding within the protein. ...
SOME SUMMARY INFORMATION ON ORGANELLES Plasma (cell
... Membrane-bound sacs containing digestive (hydrolytic) enzymes Functions a. In conjunction with phagocytosis: Destroys engulfed particles (e.g. bacteria) b. Autophagy (“self eating”) Breaks down worn out cell components for recycling ...
... Membrane-bound sacs containing digestive (hydrolytic) enzymes Functions a. In conjunction with phagocytosis: Destroys engulfed particles (e.g. bacteria) b. Autophagy (“self eating”) Breaks down worn out cell components for recycling ...
They do NOT like water!
... Humans have at least 30,000 different proteins, each with a unique structure and function. – Functions include structural support, storage, transport of materials, intercellular signaling, movement, and defense. – Enzymes are one class of proteins that regulate metabolism by moderating chemical reac ...
... Humans have at least 30,000 different proteins, each with a unique structure and function. – Functions include structural support, storage, transport of materials, intercellular signaling, movement, and defense. – Enzymes are one class of proteins that regulate metabolism by moderating chemical reac ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... Ribosomes are large protein / RNA complexes that are the site of translation. The structure of ribosomes reflects ribosomal function. Each ribosome consists of large and small subunits, with binding sites for mRNA and three tRNA molecules. During translation, the growing polypeptide is atached to t ...
... Ribosomes are large protein / RNA complexes that are the site of translation. The structure of ribosomes reflects ribosomal function. Each ribosome consists of large and small subunits, with binding sites for mRNA and three tRNA molecules. During translation, the growing polypeptide is atached to t ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.