Chemistry Comes Alive: Part B Classes of Compounds • Inorganic
... • adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) ...
... • adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) ...
The six elements that make up 99.9% of all living things include
... down reactions and prevent overheating of the cells 5. they usually speed up chemical reactions ...
... down reactions and prevent overheating of the cells 5. they usually speed up chemical reactions ...
Bio1A Unit 1-3 The Cell Notes File
... • the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings • exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others • Basis for permeability is the hydrophobic nature of the tails of phospholipids - Lipid bilayer - Naturally forms do to hydrophillic in ...
... • the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings • exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others • Basis for permeability is the hydrophobic nature of the tails of phospholipids - Lipid bilayer - Naturally forms do to hydrophillic in ...
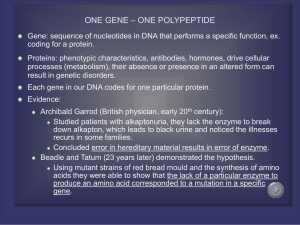
ONE GENE – ONE POLYPEPTIDE
... There are 20 amino acids found in proteins, only 4 bases in mRNA (U C A G) Codons: sequences of three bases used to code for an a.a. 43=64 possible codons (some amino acids have more than one codon) Ex. UUU UUC, UCU, UCC all code for phenylalanine (a.a.) This redundancy helps to reduce errors AUG: s ...
... There are 20 amino acids found in proteins, only 4 bases in mRNA (U C A G) Codons: sequences of three bases used to code for an a.a. 43=64 possible codons (some amino acids have more than one codon) Ex. UUU UUC, UCU, UCC all code for phenylalanine (a.a.) This redundancy helps to reduce errors AUG: s ...
Ch 3
... • In some individuals, protein appears to have correct amino acid sequence but fails to fold Denaturation • Protein loses structure and function • Due to environmental conditions – pH – Temperature – Ionic concentration of solution • Dissociation – subunits may be dissociated – without losing their ...
... • In some individuals, protein appears to have correct amino acid sequence but fails to fold Denaturation • Protein loses structure and function • Due to environmental conditions – pH – Temperature – Ionic concentration of solution • Dissociation – subunits may be dissociated – without losing their ...
From Gene to Protein
... RNA vs. DNA • there are 3 major differences between the 2 forms of nucleic acids – Composition of sugar backbone (reflects name) • RNA - ribonucleic acid (ribose) • DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid (deoxyribose) – number of strands: RNA = 1 and DNA = 2 – RNA does not have thymine as a nitrogen base, ins ...
... RNA vs. DNA • there are 3 major differences between the 2 forms of nucleic acids – Composition of sugar backbone (reflects name) • RNA - ribonucleic acid (ribose) • DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid (deoxyribose) – number of strands: RNA = 1 and DNA = 2 – RNA does not have thymine as a nitrogen base, ins ...
Transcription - smithlhhsb121
... The interaction of tRNA and mRNA takes place in a ribosome Consists of two protein subunits and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Within the ribosome are three binding sites ◦ P site (peptidyl-tRNA site) where the tRNA holding the polypepetide chain ◦ A site (aminoacyl-tRNA site) where next tRNA in line is held ...
... The interaction of tRNA and mRNA takes place in a ribosome Consists of two protein subunits and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Within the ribosome are three binding sites ◦ P site (peptidyl-tRNA site) where the tRNA holding the polypepetide chain ◦ A site (aminoacyl-tRNA site) where next tRNA in line is held ...
presentation source
... Sample (tissue, serum, cell extract) is solubilized and the proteins are denatured into polypeptide components This mixture is separated by isoelectric focusing (IEF); on the application of a current, the charged polypeptide subunits migrate in a polyacrylamide gel strip that contains an immobilized ...
... Sample (tissue, serum, cell extract) is solubilized and the proteins are denatured into polypeptide components This mixture is separated by isoelectric focusing (IEF); on the application of a current, the charged polypeptide subunits migrate in a polyacrylamide gel strip that contains an immobilized ...
Biological Sequences: DNA, RNA, Protein
... addition to the nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA sequences that encode for the proteins and RNAs unique to those organelles. • RNA occurs in multiple copies and various forms. Cells contain as much as 8 times more RNA than DNA material. RNA molecules are categorized into sev ...
... addition to the nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA sequences that encode for the proteins and RNAs unique to those organelles. • RNA occurs in multiple copies and various forms. Cells contain as much as 8 times more RNA than DNA material. RNA molecules are categorized into sev ...
What is the chemical makeup?
... What do they do? Store energy and used as building blocks for structure (example wood is just a long chain of sugars connected together) What is the chemical makeup? C6H12O6 Where have you seen this molecule before? Test: Lugar’s Iodine turns black when it comes in contact with a starch. Drop a samp ...
... What do they do? Store energy and used as building blocks for structure (example wood is just a long chain of sugars connected together) What is the chemical makeup? C6H12O6 Where have you seen this molecule before? Test: Lugar’s Iodine turns black when it comes in contact with a starch. Drop a samp ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
Chapter 14 Oxidative Phosphorylation Prokaryotes are bacteria
... Part 1: Electron Flow High G electrons from glycolysis, TCA cycle, AA, and fatty acid oxidation are funneled into universal electron carriers: NADH / NADPH / FADH2 The e- are then transferred to a chain of e- carriers in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. This is called the respiratory chain. ...
... Part 1: Electron Flow High G electrons from glycolysis, TCA cycle, AA, and fatty acid oxidation are funneled into universal electron carriers: NADH / NADPH / FADH2 The e- are then transferred to a chain of e- carriers in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. This is called the respiratory chain. ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 22. _____________ and ______________ are the two types of nucleic acids. 23. Name the function of nucleic acids. _________________________________________ 24. Describe/Draw the structure of DNA. ( What does it look like?) ____________________________ Energy and Enzymes 25. ______________________ are ...
... 22. _____________ and ______________ are the two types of nucleic acids. 23. Name the function of nucleic acids. _________________________________________ 24. Describe/Draw the structure of DNA. ( What does it look like?) ____________________________ Energy and Enzymes 25. ______________________ are ...
Conclusion: a) The nuclear localization signal (NLS)
... 2) Receptors for NLS: In vitro assay of nuclear transport: permeabilized animal culture cells---plus the labeled protein---does not go into the nucleus even when NLS is present---plus ATP and cell lysate (cytoplasmic components)---goes to nucleus: Conclusion: ATP and cytoplasmic proteins/factors ar ...
... 2) Receptors for NLS: In vitro assay of nuclear transport: permeabilized animal culture cells---plus the labeled protein---does not go into the nucleus even when NLS is present---plus ATP and cell lysate (cytoplasmic components)---goes to nucleus: Conclusion: ATP and cytoplasmic proteins/factors ar ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS AND PROCESSING Protein biosynthesis is
... more inhibitory peptides that can be activated when the inhibitory sequence is removed byproteolysis during posttranslational modification. A preprotein is a form that contains a signal sequence (an N-terminal signal peptide) that specifies its insertion into or through membranes, i.e., targets them ...
... more inhibitory peptides that can be activated when the inhibitory sequence is removed byproteolysis during posttranslational modification. A preprotein is a form that contains a signal sequence (an N-terminal signal peptide) that specifies its insertion into or through membranes, i.e., targets them ...
BioIIch17notesRNAfilled.p pt
... acid that lie between coding regions -Exons: coding regions that are eventually expressed -both introns and exons are originally transcribed -but, introns are cut out and exons are spliced together to form an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence -this leaves the nucleus and enters the cyt ...
... acid that lie between coding regions -Exons: coding regions that are eventually expressed -both introns and exons are originally transcribed -but, introns are cut out and exons are spliced together to form an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence -this leaves the nucleus and enters the cyt ...
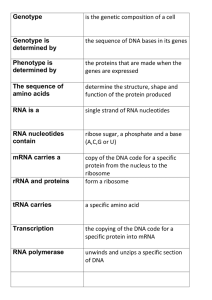
The sequence of amino acids
... multiple translation on the same mRNA strand may be required to enable a protein to perform its specific function ...
... multiple translation on the same mRNA strand may be required to enable a protein to perform its specific function ...
Protein Synthesis - Doral Academy High School
... the mRNA into a polypeptide chain • Ribosomes read mRNA 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins • tRNA carrying the amino acid specified by the codon binds and a peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids. • This process continues until a stop codon is reached. • The ribosome then falls ...
... the mRNA into a polypeptide chain • Ribosomes read mRNA 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins • tRNA carrying the amino acid specified by the codon binds and a peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids. • This process continues until a stop codon is reached. • The ribosome then falls ...
• - Cambridge Isotope Laboratories
... The core business of M-fold is the manufacture, crystallization and structural analysis of human membrane proteins or receptors. M-fold has developed methods for expressing G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in bacteria utilizing stable isotope labeled media and refolding proteins into biologically ...
... The core business of M-fold is the manufacture, crystallization and structural analysis of human membrane proteins or receptors. M-fold has developed methods for expressing G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in bacteria utilizing stable isotope labeled media and refolding proteins into biologically ...
PG1005 Lecture 17 Gene Transcription
... • Define transcription as the key event in gene expression during which the genetic code is read and transcribed into a portable template set of instructions for protein synthesis • Detail the sequence of events occurring during the initiation, elongation and termination of transcription • Descri ...
... • Define transcription as the key event in gene expression during which the genetic code is read and transcribed into a portable template set of instructions for protein synthesis • Detail the sequence of events occurring during the initiation, elongation and termination of transcription • Descri ...
Proteins Behaving badly - The University of Oklahoma
... disease. We are particularly interested in the mechanism by which the protein transthyretin regulates beta-amyloid aggregation kinetics, because there is evidence in transgenic mice studies that transthyretin protects the mice from beta-amyloid toxicity. Second, we are developing methods to examine ...
... disease. We are particularly interested in the mechanism by which the protein transthyretin regulates beta-amyloid aggregation kinetics, because there is evidence in transgenic mice studies that transthyretin protects the mice from beta-amyloid toxicity. Second, we are developing methods to examine ...
Proteins
... Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur Serve as structural components of animals Serve as control molecules (enzymes) Serve as transport and messenger molecules Basic building block is the amino acid General characteristics Molecular size: Proteins are macromolecules. ...
... Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur Serve as structural components of animals Serve as control molecules (enzymes) Serve as transport and messenger molecules Basic building block is the amino acid General characteristics Molecular size: Proteins are macromolecules. ...
ppt file
... inspecting the top 100 pairs, the author found that in >95% of them both proteins have similar functions. ...
... inspecting the top 100 pairs, the author found that in >95% of them both proteins have similar functions. ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there
... through control of the activities of the enzymes that catalyze them. • An important type of regulation of enzyme activity is feedback inhibition (Figure 8.2), in which the final product of a biosynthetic pathway inhibits the first enzyme unique to that pathway. ...
... through control of the activities of the enzymes that catalyze them. • An important type of regulation of enzyme activity is feedback inhibition (Figure 8.2), in which the final product of a biosynthetic pathway inhibits the first enzyme unique to that pathway. ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.