No Slide Title
... short DNA sequence with many A-Ts TATA box - typically 25 nucleotides upstream from the transcription start site. This binding causes a dramatic distortion in the DNA. Figure 24. ...
... short DNA sequence with many A-Ts TATA box - typically 25 nucleotides upstream from the transcription start site. This binding causes a dramatic distortion in the DNA. Figure 24. ...
Transcription and Translation
... Remember: MR CATAP (mRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, tRNA, amino acid, polypeptide) • mRNA binds to a ribosome which initiates translation • The mRNA is read in codons (from start codon = AUG) • Anticodons on tRNA align opposite appropriate codons ...
... Remember: MR CATAP (mRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, tRNA, amino acid, polypeptide) • mRNA binds to a ribosome which initiates translation • The mRNA is read in codons (from start codon = AUG) • Anticodons on tRNA align opposite appropriate codons ...
Trnascription in eucaryotes
... defined tissues. Nevertheless in nearly all cell types the DNA is the same. • Some genes are present in nearly all cells – these are housekeeping genes. ...
... defined tissues. Nevertheless in nearly all cell types the DNA is the same. • Some genes are present in nearly all cells – these are housekeeping genes. ...
Histone modifications
... Epigenetic memory: heritable traits (over rounds of cell division and sometimes transgenerationally) that do not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence. (e.g. chromatin state) ...
... Epigenetic memory: heritable traits (over rounds of cell division and sometimes transgenerationally) that do not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence. (e.g. chromatin state) ...
Quiz on protein expression (Chiu lecture 3)
... front of the gene in pET vectors, which prevents T7 RNA polymerase from binding to the T7 promoter. b) Is the gene for T7 Polymerase encoded on the host or vector DNA? host c) What is the purpose of IPTG? IPTG competes with the lac repressor for binding to the lac O operator. Addition of IPTG then k ...
... front of the gene in pET vectors, which prevents T7 RNA polymerase from binding to the T7 promoter. b) Is the gene for T7 Polymerase encoded on the host or vector DNA? host c) What is the purpose of IPTG? IPTG competes with the lac repressor for binding to the lac O operator. Addition of IPTG then k ...
Biology 105: Biology Science for Life with Physiology, 3rd Ed., Belk
... replication; 14 frameshift mutation;15 galls;16 germ-line gene therapy; 17 gene gun; 18 gene therapy; 19 generally recognized as safe (GRAS); 20 genetically modified organism (GMO); 21 genetic code; 22 genome;23 helicase; 24 in vitro; 25 messenger RNA (mRNA); 26 model organisms; 27 mutations; 28 nit ...
... replication; 14 frameshift mutation;15 galls;16 germ-line gene therapy; 17 gene gun; 18 gene therapy; 19 generally recognized as safe (GRAS); 20 genetically modified organism (GMO); 21 genetic code; 22 genome;23 helicase; 24 in vitro; 25 messenger RNA (mRNA); 26 model organisms; 27 mutations; 28 nit ...
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology states that
... RNAP will bind to the wrong site of the DNA and transcribe the wrong gene ...
... RNAP will bind to the wrong site of the DNA and transcribe the wrong gene ...
Introduction to Microarray Data Analysis and Gene Networks
... Four different nucleotides : adenosine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. They are usually referred to as bases and denoted by their initial letters, A,C ,G and T 5' C-G-A-T-T-G-C-A-A-C-G-A-T-G-C 3' ...
... Four different nucleotides : adenosine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. They are usually referred to as bases and denoted by their initial letters, A,C ,G and T 5' C-G-A-T-T-G-C-A-A-C-G-A-T-G-C 3' ...
258927_Fx_DNA-RNA
... 12. What are the names of the gene and the enzyme responsible for the glowing in a firefly’s tail? 13. After finding the correct gene, what does RNA Polymerase actually do? 14. After transcription, what happens to the mRNA strand? (Where in the cell ...
... 12. What are the names of the gene and the enzyme responsible for the glowing in a firefly’s tail? 13. After finding the correct gene, what does RNA Polymerase actually do? 14. After transcription, what happens to the mRNA strand? (Where in the cell ...
Name:
... 12. What are the names of the gene and the enzyme responsible for the glowing in a firefly’s tail? 13. After finding the correct gene, what does RNA Polymerase actually do? 14. After transcription, what happens to the mRNA strand? (Where in the cell ...
... 12. What are the names of the gene and the enzyme responsible for the glowing in a firefly’s tail? 13. After finding the correct gene, what does RNA Polymerase actually do? 14. After transcription, what happens to the mRNA strand? (Where in the cell ...
power point presentation
... The data collected through different approach can be used as reference to each other for possible final confidential result. ...
... The data collected through different approach can be used as reference to each other for possible final confidential result. ...
Gene to Protein
... DNA – forms Hydrogen bonds and reforms double helix mRNA is edited (remove introns, exons are to be expressed) mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters cytoplasm for translation ...
... DNA – forms Hydrogen bonds and reforms double helix mRNA is edited (remove introns, exons are to be expressed) mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters cytoplasm for translation ...
5 Chapter 12 DNA RNA
... Resulting in extra chromosome in one cell and a missing chromosome in another (involving one chromosome) l Polyploidy can result when entire sets of chromosomes are involved l ...
... Resulting in extra chromosome in one cell and a missing chromosome in another (involving one chromosome) l Polyploidy can result when entire sets of chromosomes are involved l ...
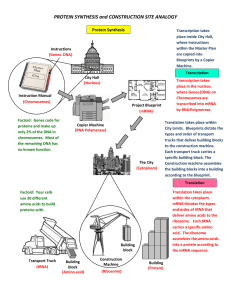
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
Transcription and Translation computer lab test review
... During transcription, RNA is developed from a strand of DNA. List the base pairs used to make RNA. What is the name of the DNA strand used in transcription? Where does transcription occur? Where does translation occur? Name the RNA codon that is used to start translation. Which three codons will sto ...
... During transcription, RNA is developed from a strand of DNA. List the base pairs used to make RNA. What is the name of the DNA strand used in transcription? Where does transcription occur? Where does translation occur? Name the RNA codon that is used to start translation. Which three codons will sto ...
UNIT 6 lecture part 3regulation
... TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS EUKARYOTES Genes can be regulated at the level of transcription. ...
... TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS EUKARYOTES Genes can be regulated at the level of transcription. ...
Transcription
... • Chemical signals turn gene for a specific protein on. • Enzymes attach to DNA at the gene’s location and unzip only where that gene is on the DNA. – DNA A T C G ...
... • Chemical signals turn gene for a specific protein on. • Enzymes attach to DNA at the gene’s location and unzip only where that gene is on the DNA. – DNA A T C G ...
Powerpoint file
... •Different macromolecules accumulate to different levels under different growth conditions and in different cell types. •Diseases can be caused by aberrant control of gene expression: too much or too little of a protein; wrong time and wrong place for a protein. ...
... •Different macromolecules accumulate to different levels under different growth conditions and in different cell types. •Diseases can be caused by aberrant control of gene expression: too much or too little of a protein; wrong time and wrong place for a protein. ...
CHAPTER 12
... • The Role of Transcription Factors in Regulating Gene Expression – Transcription factors are the proteins that either acts as transcription activators or transcription inhibitors. • A single gene can be controlled by different regulatory proteins. • A single DNA-binding protein may control the expr ...
... • The Role of Transcription Factors in Regulating Gene Expression – Transcription factors are the proteins that either acts as transcription activators or transcription inhibitors. • A single gene can be controlled by different regulatory proteins. • A single DNA-binding protein may control the expr ...
CHAPTER 19 AP Bio Rauch
... MORE THAN ONE SOMATIC MUTATION IS NEEDED TO TRANSFORM NORMAL CELLS TO CANCER CELLS ...
... MORE THAN ONE SOMATIC MUTATION IS NEEDED TO TRANSFORM NORMAL CELLS TO CANCER CELLS ...