A Novel Knowledge Based Method to Predicting Transcription
... A Novel Knowledge Based Method to Predicting Transcription Factor Targets [email protected] ...
... A Novel Knowledge Based Method to Predicting Transcription Factor Targets [email protected] ...
Chapter 11 Lecture PowerPoint - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • TAFs are not universally required for transcription of class II genes • Even TBP is not universally required • Some promoters in higher eukaryotes respond to an alternative protein such as TRF1 (TBPrelated factor 1) ...
... • TAFs are not universally required for transcription of class II genes • Even TBP is not universally required • Some promoters in higher eukaryotes respond to an alternative protein such as TRF1 (TBPrelated factor 1) ...
WLHS / AP Bio / Monson
... REVIEW QUESTIONS: (some may done on a separate sheet of paper and attached) 1) Explain (or use a sketch/diagram) how Hershey & Chase used radioactively labeled viruses to show that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material. 2) Briefly explain the function of each protein / enzyme listed below: A) He ...
... REVIEW QUESTIONS: (some may done on a separate sheet of paper and attached) 1) Explain (or use a sketch/diagram) how Hershey & Chase used radioactively labeled viruses to show that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material. 2) Briefly explain the function of each protein / enzyme listed below: A) He ...
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE
... C. DHFR amplification in cultured cells The chemotherapeutic drug methotrexate (MTX) is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) which is required for the synthesis of nucleic acids. In laboratory cultured cells, resistance arises at a frequency 1 in 106. The resistance is due ...
... C. DHFR amplification in cultured cells The chemotherapeutic drug methotrexate (MTX) is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) which is required for the synthesis of nucleic acids. In laboratory cultured cells, resistance arises at a frequency 1 in 106. The resistance is due ...
a specific short sequence on DNA at which RNA transcription ends
... Summary of RNA Transcription Mechanism 1) Transcription begins when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to DNA at a promoter region. 2) The enzyme separates the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds, and then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand o ...
... Summary of RNA Transcription Mechanism 1) Transcription begins when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to DNA at a promoter region. 2) The enzyme separates the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds, and then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand o ...
transcription - Geneticskippnyc
... A messenger RNA molecule for making a protein is made in the nucleus and sent out to a ribosome. The ribosome reads the mRNA message and makes a protein containing 120 amino acids. The mRNA consisted of at least how many codons? ...
... A messenger RNA molecule for making a protein is made in the nucleus and sent out to a ribosome. The ribosome reads the mRNA message and makes a protein containing 120 amino acids. The mRNA consisted of at least how many codons? ...
Unit III: Introduction to Cells Unit IV: Cell Processes
... 2. List the inputs and outputs of photosynthesis; 3. List five reasons why photosynthesis is the most important biologic process on earth? 4. List the inputs and outputs of aerobic cell respiration: 5. Discuss alcohol fermentation & lactic acid fermentation; Identify three products humans benefit as ...
... 2. List the inputs and outputs of photosynthesis; 3. List five reasons why photosynthesis is the most important biologic process on earth? 4. List the inputs and outputs of aerobic cell respiration: 5. Discuss alcohol fermentation & lactic acid fermentation; Identify three products humans benefit as ...
PowerPoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... make that give us our traits – freckles, brown eyes, blond hair, etc. ...
... make that give us our traits – freckles, brown eyes, blond hair, etc. ...
{alpha}-Lipoic Acid Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation by Regulating
... Obesity is associated with a number of pathological disorders such as non-insulindependent diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular diseases. alphaLipoic acid (LA) has been demonstrated to activate the insulin signaling pathway and to exert insulin-like actions in adipose and muscl ...
... Obesity is associated with a number of pathological disorders such as non-insulindependent diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular diseases. alphaLipoic acid (LA) has been demonstrated to activate the insulin signaling pathway and to exert insulin-like actions in adipose and muscl ...
Protein Synthesis-Part Two - Halton District School Board
... attaches to these promoter sites. This ensures that transcription begins at the right place. ...
... attaches to these promoter sites. This ensures that transcription begins at the right place. ...
Answers to the Study Guide for C12 Molecular Genetics Labeled
... Deletion – when a base is taken out which also changes the reading frame. These two things are considered frameshift mutations and can be considered point mutations. 13. When a specific kind of protein is not continually used by a cell, the gene for that protein is usually repressible. 14. The lac o ...
... Deletion – when a base is taken out which also changes the reading frame. These two things are considered frameshift mutations and can be considered point mutations. 13. When a specific kind of protein is not continually used by a cell, the gene for that protein is usually repressible. 14. The lac o ...
Document
... Lactose is not the preferred carbohydrate source for E. coli. If lactose and glucose are present, the cell will use all of the glucose before the lac operon is turned on. This type of control is termed catabolite repression. To prevent lactose metabolism, a second level of control of gene expression ...
... Lactose is not the preferred carbohydrate source for E. coli. If lactose and glucose are present, the cell will use all of the glucose before the lac operon is turned on. This type of control is termed catabolite repression. To prevent lactose metabolism, a second level of control of gene expression ...
Summary notes on Genetics and Gene expression
... Making pre–mRNA from DNA as a template PROCESS: 1. DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bond in a specific region of DNA to expose unpaired bases 2. RNA polymerase moves along a one of the DNA strands, causing nucleotides to join with free nucleotides 3. C links to G // T links to A // A links to U! 4. ...
... Making pre–mRNA from DNA as a template PROCESS: 1. DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bond in a specific region of DNA to expose unpaired bases 2. RNA polymerase moves along a one of the DNA strands, causing nucleotides to join with free nucleotides 3. C links to G // T links to A // A links to U! 4. ...
Summary
... into the complex mechanisms governing the three-dimensional folding of genomes. This thesis describes the investigation of three mechanisms of DNA compaction and organization: DNA bridging (by the bacterial chromatin protein H-NS) and DNA bending and wrapping (by the archaeal chromatin proteins HMfA ...
... into the complex mechanisms governing the three-dimensional folding of genomes. This thesis describes the investigation of three mechanisms of DNA compaction and organization: DNA bridging (by the bacterial chromatin protein H-NS) and DNA bending and wrapping (by the archaeal chromatin proteins HMfA ...
Transcription
... Eukaryotic– monocistronic Leader sequence—non-translated at 5’ end May contain a regulatory region (attenuator) Also untranslated regions at 3’ end. Spacers (untranslated intercistronic sequences) Prokaryotic mRNA—short lived Eukaryotic mRNA-can be long lived ...
... Eukaryotic– monocistronic Leader sequence—non-translated at 5’ end May contain a regulatory region (attenuator) Also untranslated regions at 3’ end. Spacers (untranslated intercistronic sequences) Prokaryotic mRNA—short lived Eukaryotic mRNA-can be long lived ...
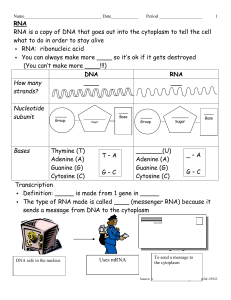
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... mRNA is a _________ that codes for a ____________ Proteins are made in the ________ and then work to keep the cell alive Translation (__________synthesis): process of making a protein Proteins are made up of ________ _______ (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino aci ...
... mRNA is a _________ that codes for a ____________ Proteins are made in the ________ and then work to keep the cell alive Translation (__________synthesis): process of making a protein Proteins are made up of ________ _______ (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino aci ...
Genetic Code Review.cwk
... This section describes RNAand its role in transcription and translation. The Structure of RNA(page 300) 1. List the three main differences between RNAand DNA. a. ______________________________________________________________________ b. ________________________________________________________________ ...
... This section describes RNAand its role in transcription and translation. The Structure of RNA(page 300) 1. List the three main differences between RNAand DNA. a. ______________________________________________________________________ b. ________________________________________________________________ ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... The highly repetitive sequences have greater amounts of guanine. B. The highly repetitive sequences have greater amounts of cytosine. C. The highly repetitive sequences are not transcribed. D. The highly repetitive sequences are not replicated. ...
... The highly repetitive sequences have greater amounts of guanine. B. The highly repetitive sequences have greater amounts of cytosine. C. The highly repetitive sequences are not transcribed. D. The highly repetitive sequences are not replicated. ...
Gene Regulation Is Necessary
... Complex multicellular organisms are produced by cells that switch genes on and off during development. A typical human cell normally expresses about 3% to 5% of its genes at any given time. Cancer results from genes that do not turn off properly. Cancer cells have lost their ability to regulate mito ...
... Complex multicellular organisms are produced by cells that switch genes on and off during development. A typical human cell normally expresses about 3% to 5% of its genes at any given time. Cancer results from genes that do not turn off properly. Cancer cells have lost their ability to regulate mito ...
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA - Tenafly Public Schools
... Transcription begins at a special “start” sequence on the DNA (promoter) and ends at a “stop” sequence ...
... Transcription begins at a special “start” sequence on the DNA (promoter) and ends at a “stop” sequence ...
ppt
... Repression of genetic expression can be reversed by changing the cytoplasmic environment ...
... Repression of genetic expression can be reversed by changing the cytoplasmic environment ...
Protein Synthesis - OpotikiCollegeBiology
... and proteins are built out of amino acids. • How does the chromosome alphabet get changed into structures that join up to make proteins? ...
... and proteins are built out of amino acids. • How does the chromosome alphabet get changed into structures that join up to make proteins? ...