student notes protein synthesis mutation
... The ___________on the mRNA dictate the amino acids that the tRNA brings to the ribosome. The ________________ on the tRNA hooks up with the CODON and the a.a. is brought to the appropriate location. Translation starts at the start codon (AUG) and ends at the stop codon (UGA, UAG, UAA) ...
... The ___________on the mRNA dictate the amino acids that the tRNA brings to the ribosome. The ________________ on the tRNA hooks up with the CODON and the a.a. is brought to the appropriate location. Translation starts at the start codon (AUG) and ends at the stop codon (UGA, UAG, UAA) ...
C - TeacherWeb
... The exception to this is that uracil is used for nucleotide sequencing of RNA molecules rather than thymine. ...
... The exception to this is that uracil is used for nucleotide sequencing of RNA molecules rather than thymine. ...
Ontology Alignment
... – Synthesis of gene products (RNA and proteins) – Two steps: transcription and translation – Transcription: Gene RNA (mediated by transcription factor proteins (TF) that regulate (up / down) the synthesis of RNA by a polymerase enzyme) – Translation: RNA protein ...
... – Synthesis of gene products (RNA and proteins) – Two steps: transcription and translation – Transcription: Gene RNA (mediated by transcription factor proteins (TF) that regulate (up / down) the synthesis of RNA by a polymerase enzyme) – Translation: RNA protein ...
Protein Synthesis - BLI-Research-SynBio-2016-session-2
... •Now we have mature mRNA transcribed from the cell’s DNA. It is leaving the nucleus through a nuclear pore. Once in the cytoplasm, it finds a ribosome so that translation can begin. We know how mRNA is made, but how do we “read” the code? ...
... •Now we have mature mRNA transcribed from the cell’s DNA. It is leaving the nucleus through a nuclear pore. Once in the cytoplasm, it finds a ribosome so that translation can begin. We know how mRNA is made, but how do we “read” the code? ...
Molecular Biology
... as the carrier of genetic information from the DNA to the translational machinery and usually makes up less than 5% of total cellular RNA. The anatomy of gene Although there is no such thing as a ‘typical’ gene, there are certain basic requirements for any gene to function. The most obvious is that ...
... as the carrier of genetic information from the DNA to the translational machinery and usually makes up less than 5% of total cellular RNA. The anatomy of gene Although there is no such thing as a ‘typical’ gene, there are certain basic requirements for any gene to function. The most obvious is that ...
Digitally Programmed Cells
... Use existing in vivo biochemical mechanisms • stage I: cooperative binding found in many genetic regulatory networks ...
... Use existing in vivo biochemical mechanisms • stage I: cooperative binding found in many genetic regulatory networks ...
DNA Functions
... Translation begins when an mRNA molecule in the cytoplasm attaches to a ribosome. As each codon of the mRNA moves through the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brought into the ribosome by tRNA. In the ribosome, the amino acid is transferred to the growing polypeptide chain [protein]. Each tRNA mol ...
... Translation begins when an mRNA molecule in the cytoplasm attaches to a ribosome. As each codon of the mRNA moves through the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brought into the ribosome by tRNA. In the ribosome, the amino acid is transferred to the growing polypeptide chain [protein]. Each tRNA mol ...
Student work sheets for Power Point Slides
... 13) The protein structure is three dimensional because of the folding of the amino acids. 14) Endoplasmic reticulum is located outside the nucleus. 15) An anticodon consists of three base pairs which are opposite to the base pairs in the mRNA. Slide 4 16) Describe what you see from this slide. Slide ...
... 13) The protein structure is three dimensional because of the folding of the amino acids. 14) Endoplasmic reticulum is located outside the nucleus. 15) An anticodon consists of three base pairs which are opposite to the base pairs in the mRNA. Slide 4 16) Describe what you see from this slide. Slide ...
DNA RNA Protein Hwk KEY
... and synthesize functional human protein. Instead, the protein produced is found to contain many fewer amino acids and doesn't work. What could have gone wrong? Perhaps the human gene contained one or more introns. Prokaryotes like bacteria do not have introns in their genes and do not have cutting & ...
... and synthesize functional human protein. Instead, the protein produced is found to contain many fewer amino acids and doesn't work. What could have gone wrong? Perhaps the human gene contained one or more introns. Prokaryotes like bacteria do not have introns in their genes and do not have cutting & ...
Key MW
... IS: mutant lacI -> encodes a repressor protein to which lactose can no longer bind -> the repressor remains bound to the operator -> constitutive transcriptional repression Note: I+ is the wildtype lacI gene and encodes a normal repressor protein Order of dominance: P- > OC > IS > I+ > ILac represso ...
... IS: mutant lacI -> encodes a repressor protein to which lactose can no longer bind -> the repressor remains bound to the operator -> constitutive transcriptional repression Note: I+ is the wildtype lacI gene and encodes a normal repressor protein Order of dominance: P- > OC > IS > I+ > ILac represso ...
What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... Original template strand of DNA: 3 TAC GCA AGC AAT ACC GAC GAA 5 a. If this DNA strand produces an mRNA, what is the sequence of the mRNA? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _ ...
... Original template strand of DNA: 3 TAC GCA AGC AAT ACC GAC GAA 5 a. If this DNA strand produces an mRNA, what is the sequence of the mRNA? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _ ...
What is some basic information about DNA?
... 4 nucleotides make Up DNA: Nucleotides can be thought of as building blocks. These building blocks can be arranged in sequences. The human genome contains about 3 billion of these building blocks. Some sequences of the building blocks encode genes. Some sequences are related to the regulation of gen ...
... 4 nucleotides make Up DNA: Nucleotides can be thought of as building blocks. These building blocks can be arranged in sequences. The human genome contains about 3 billion of these building blocks. Some sequences of the building blocks encode genes. Some sequences are related to the regulation of gen ...
CHAPTER 17 - HCC Learning Web
... • A primary transcript is the initial RNA transcript from any gene prior to processing • The central dogma is the concept that cells are governed by a cellular chain of command: DNA RNA protein ...
... • A primary transcript is the initial RNA transcript from any gene prior to processing • The central dogma is the concept that cells are governed by a cellular chain of command: DNA RNA protein ...
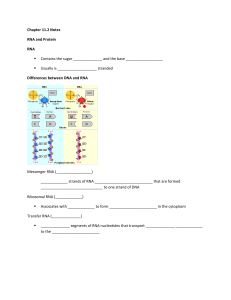
Chapter 11.2 Notes RNA and Protein RNA Contains the sugar and
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
TRANSCRIPTION & TRANSLATION: From DNA to Protein
... Amino acids to protein • Amino acid chains start to fold creating 3dimensional structures • Several of these 3D structures combine to form a functional protein • These proteins then carry out cellular functions ...
... Amino acids to protein • Amino acid chains start to fold creating 3dimensional structures • Several of these 3D structures combine to form a functional protein • These proteins then carry out cellular functions ...
Discussion Guide Chapter 15
... 6. Differentiate between the three main replication enzymes. (see Science Focus p. 218) Helicase DNA Polymerase DNA Ligase ...
... 6. Differentiate between the three main replication enzymes. (see Science Focus p. 218) Helicase DNA Polymerase DNA Ligase ...
PHYS 498 Quiz 1 Solution Starting with double
... protein. Tell about what are (thermodynamically) stable molecules and how to make them chemically reactive, including small molecules or other molecules/proteins which need to interact with them. There are three parts to this question: 1. Transcription of DNA to RNA 2. Translation of RNA to protein ...
... protein. Tell about what are (thermodynamically) stable molecules and how to make them chemically reactive, including small molecules or other molecules/proteins which need to interact with them. There are three parts to this question: 1. Transcription of DNA to RNA 2. Translation of RNA to protein ...
Framework for Teachable Unit
... The aim of this unit is to help students understand the mechanisms of epigenetics and the role of epigenetics in organism health and development ...
... The aim of this unit is to help students understand the mechanisms of epigenetics and the role of epigenetics in organism health and development ...
dnachap12_12-3
... separates strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble an RNA copy. ...
... separates strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble an RNA copy. ...