Cell and Cell Metabolism Quiz
... The membrane is permeable only during optimal cell conditions. It allows some substances to pass through and keeps others out. It is selective about what enters but will allow everything to leave the cell. ...
... The membrane is permeable only during optimal cell conditions. It allows some substances to pass through and keeps others out. It is selective about what enters but will allow everything to leave the cell. ...
Biology Genetics Unit: Online Activities 1.) Go to the link: http://learn
... What is the interesting, and funny message that you received after a while of DNA building? (Keep on going! It may take more bases than you think to get to this pop up!) _________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
... What is the interesting, and funny message that you received after a while of DNA building? (Keep on going! It may take more bases than you think to get to this pop up!) _________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
AP Biology Objectives
... 6. Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 7. Explain the general process of transcription, including the 3 major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 8. Explain how RNA is modified after ...
... 6. Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 7. Explain the general process of transcription, including the 3 major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 8. Explain how RNA is modified after ...
From Gene to Protein Genes code for... Proteins RNAs Remember
... mRNA transcript is brought to the ribosome Initiation = the rRNA, mRNA transcript, and tRNA carrying methionine bind together Elongation = amino acids are added one by one to create the polypeptide Termination = when a stop codon is reached on the mRNA ...
... mRNA transcript is brought to the ribosome Initiation = the rRNA, mRNA transcript, and tRNA carrying methionine bind together Elongation = amino acids are added one by one to create the polypeptide Termination = when a stop codon is reached on the mRNA ...
Transcription - My Teacher Pages
... Once the entire gene has been transcribed, the RNA strand detaches completely from the DNA. Exactly how RNA polymerase recognizes the end of a gene is very complicated but we will discuss as it reaching a Stop signal. ...
... Once the entire gene has been transcribed, the RNA strand detaches completely from the DNA. Exactly how RNA polymerase recognizes the end of a gene is very complicated but we will discuss as it reaching a Stop signal. ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Explain the differences and
... are codons and anticodons found? A codon is sequence of 3 nucleotides that together form a genetic code in DNA & RNA. 3 nucleotides make up one codon. An anticodon is the complementary sequence on the tRNA that matches the codon on the mRNA. Codons are found in DNA and mRNA, anticodons are found on ...
... are codons and anticodons found? A codon is sequence of 3 nucleotides that together form a genetic code in DNA & RNA. 3 nucleotides make up one codon. An anticodon is the complementary sequence on the tRNA that matches the codon on the mRNA. Codons are found in DNA and mRNA, anticodons are found on ...
ppt slides
... several steps and many proteins (enzymes) • RNA polymerase synthesizes a single strand of RNA against the DNA template strand (anti-sense strand), adding nucleotides to the 3’ end of the RNA chain • Initiation is regulated by transcription factors, including promoters, usually an initiator element a ...
... several steps and many proteins (enzymes) • RNA polymerase synthesizes a single strand of RNA against the DNA template strand (anti-sense strand), adding nucleotides to the 3’ end of the RNA chain • Initiation is regulated by transcription factors, including promoters, usually an initiator element a ...
Transcription and RNA processing
... In bacterial cells, the holoenzyme (RNA polymerase plus sigma) recognizes and binds directly to sequences in the promoter. In eukaryotic cells, promoter recognition is carried out by accessory proteins (transcription factors) that bind to the promoter and then recruit a specific RNA polymerase (I, II ...
... In bacterial cells, the holoenzyme (RNA polymerase plus sigma) recognizes and binds directly to sequences in the promoter. In eukaryotic cells, promoter recognition is carried out by accessory proteins (transcription factors) that bind to the promoter and then recruit a specific RNA polymerase (I, II ...
Microbial Overview: Physiology and Evolution
... Scope of Mutation: • A mutation is any change in the proper nucleic acid sequence of a specific gene in a cell’s genome. It may result from a single base pair mismatch during DNA replication. • Mutation can create genetic diversity within a population; either beneficial, neutral, bad, or lethal. • ...
... Scope of Mutation: • A mutation is any change in the proper nucleic acid sequence of a specific gene in a cell’s genome. It may result from a single base pair mismatch during DNA replication. • Mutation can create genetic diversity within a population; either beneficial, neutral, bad, or lethal. • ...
Characterization of Genes Expressed During the Early Stages of
... clones were identified. After DNA sequence characterization, the majority of these clones were identified by sequence homology and categorized by function. The largest group of genes encodes a range of proteins involved in ribosome biosynthesis, translation and post-translational modification. This ...
... clones were identified. After DNA sequence characterization, the majority of these clones were identified by sequence homology and categorized by function. The largest group of genes encodes a range of proteins involved in ribosome biosynthesis, translation and post-translational modification. This ...
transfer RNA
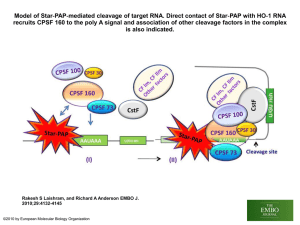
... To the 3’ end, a poly-tail of about 100 to 300 nucleotides is found, which will help the newly formed mRNA bind to a location on the ribosome. ...
... To the 3’ end, a poly-tail of about 100 to 300 nucleotides is found, which will help the newly formed mRNA bind to a location on the ribosome. ...
S4 Table.
... "ASF-1 binding site" in CaMV 35S promoter; ASF-1 binds to two TGACG motifs; TGACG motifs are found in many promoters and are involved in transcriptional activation of several genes by auxin and/or salicylic acid; May be relevant to light regulation; Binding site of tobacco TGA1a (a member of the bZi ...
... "ASF-1 binding site" in CaMV 35S promoter; ASF-1 binds to two TGACG motifs; TGACG motifs are found in many promoters and are involved in transcriptional activation of several genes by auxin and/or salicylic acid; May be relevant to light regulation; Binding site of tobacco TGA1a (a member of the bZi ...
Molecular Genetics
... • RNA polymerase will initiate the making of mRNA in the same way that DNA polymerase replicates DNA. We call this the start codon. • A codon is a set of three bases and all RNA is divided up in sets of three. • The transcription continues until the stop codon is reached. Then, the polymerase releas ...
... • RNA polymerase will initiate the making of mRNA in the same way that DNA polymerase replicates DNA. We call this the start codon. • A codon is a set of three bases and all RNA is divided up in sets of three. • The transcription continues until the stop codon is reached. Then, the polymerase releas ...
DNA 2 - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Found before start of transcription Promoters are NOT transcribed (TQ) In E. Coli Pribnow box -35 sequence Strong promoter v. Weak promoter (binding RNA Pol) Sigma Factor Needed for initiation Helps RNA Pol recognize promoter Helps separate DNA strands Inhibited by Rifamyacin & Rifampicin (in clinic ...
... Found before start of transcription Promoters are NOT transcribed (TQ) In E. Coli Pribnow box -35 sequence Strong promoter v. Weak promoter (binding RNA Pol) Sigma Factor Needed for initiation Helps RNA Pol recognize promoter Helps separate DNA strands Inhibited by Rifamyacin & Rifampicin (in clinic ...
protein synthesis
... Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein • Genes provide the instructions for making specific proteins. • The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is RNA. • RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the n ...
... Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein • Genes provide the instructions for making specific proteins. • The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is RNA. • RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the n ...
Nabil Bashir 10-21
... 1- the DNA-RNA hybrid is double stranded , but when its transcribed its single stranded RNA .. how is that ? - this hybrid formation is temporary and as it proceeds 5’ to 3’ ,, note that the 5’ end of the RNA leaves the complex so the tail is outside the RNA polymerase and only about 20 nucleotide a ...
... 1- the DNA-RNA hybrid is double stranded , but when its transcribed its single stranded RNA .. how is that ? - this hybrid formation is temporary and as it proceeds 5’ to 3’ ,, note that the 5’ end of the RNA leaves the complex so the tail is outside the RNA polymerase and only about 20 nucleotide a ...
Gene expression - El Camino College
... Mutations are changes in a sequence of DNA These can be inherited or acquired These changes get transcribed And translated ...
... Mutations are changes in a sequence of DNA These can be inherited or acquired These changes get transcribed And translated ...
Chapter 8 Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 6
... regulators and controls expression of the same gene at different times and places in responsible to different signals. Insulators or boundary elements are regulatory sequences between enhancers and promoters. They block activation of the promoter by activator bound at the enhancer, and therefore ens ...
... regulators and controls expression of the same gene at different times and places in responsible to different signals. Insulators or boundary elements are regulatory sequences between enhancers and promoters. They block activation of the promoter by activator bound at the enhancer, and therefore ens ...
Aim 24: How does DNA code for the production of proteins through
... Aim 24: How does DNA code for the production of proteins through the process of translation? Recall: Protein synthesis begins with the transcription of DNA to mRNA (The RNA that is synthesized from a DNA molecule). This process occurs in the nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus wit ...
... Aim 24: How does DNA code for the production of proteins through the process of translation? Recall: Protein synthesis begins with the transcription of DNA to mRNA (The RNA that is synthesized from a DNA molecule). This process occurs in the nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus wit ...