gene regulation
... Lac Operon Animation http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcont ent/animations/content/lacoperon.html ...
... Lac Operon Animation http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcont ent/animations/content/lacoperon.html ...
Regulation-of-Gene
... controlled by a single operator site This provides an exception to the general rule that genes on an operon are transcribed into a single mRNA ...
... controlled by a single operator site This provides an exception to the general rule that genes on an operon are transcribed into a single mRNA ...
Molecular Pathology - Charles River Laboratories
... By combining a strong history in molecular biology and histopathology, Charles River can relate gene expression to tissue histomorphology in both normal tissues and therapeutic models of disease, providing you with that valuable functional genomics information. The end result is the best possible in ...
... By combining a strong history in molecular biology and histopathology, Charles River can relate gene expression to tissue histomorphology in both normal tissues and therapeutic models of disease, providing you with that valuable functional genomics information. The end result is the best possible in ...
Threading-based Protein Structure Prediction
... • A gene is a sequence of DNA that encodes a protein or an RNA molecule • About 30,000 – 35,000 (protein-coding) genes in human genome • For gene that encodes protein – In Prokaryotic genome, one gene corresponds to one protein – In Eukaryotic genome, one gene can corresponds to more than one protei ...
... • A gene is a sequence of DNA that encodes a protein or an RNA molecule • About 30,000 – 35,000 (protein-coding) genes in human genome • For gene that encodes protein – In Prokaryotic genome, one gene corresponds to one protein – In Eukaryotic genome, one gene can corresponds to more than one protei ...
GENE REGULATION
... In eukaryotic organisms like ourselves there are several methods of regulating protein production Most regulatory sequences are found upstream from the promoter Genes are controlled by regulatory elements in the promoter region that act like one/off switches or dimmer switches ...
... In eukaryotic organisms like ourselves there are several methods of regulating protein production Most regulatory sequences are found upstream from the promoter Genes are controlled by regulatory elements in the promoter region that act like one/off switches or dimmer switches ...
Chapter 17 Presentation
... Termination occurs when a stop codon on the mRNA reaches the “A-site” within the ribosome. Release factor then binds to the stop codon in the “A-site” causing the addition of water to the peptide instead of an aa. This signals the end of translation. ...
... Termination occurs when a stop codon on the mRNA reaches the “A-site” within the ribosome. Release factor then binds to the stop codon in the “A-site” causing the addition of water to the peptide instead of an aa. This signals the end of translation. ...
F factor
... Regulation of Genes in Prokaryotes In general, prokaryotic genes are organized (and Expressed) as operons An operon consists of: Several genes that encode enzymes under the control of a single promoter ...
... Regulation of Genes in Prokaryotes In general, prokaryotic genes are organized (and Expressed) as operons An operon consists of: Several genes that encode enzymes under the control of a single promoter ...
Exploratorium Presentation
... What is bacterial transformation? Transformation is the alteration of cells by the incorporation of foreign DNA into the cell ...
... What is bacterial transformation? Transformation is the alteration of cells by the incorporation of foreign DNA into the cell ...
Transcription, Translation, and Protein Synthesis
... acid). You may not be aware of how this code is used to make life work the way that it does. The way that the genetic code of DNA is expressed is through the production of specialized proteins that travel throughout the living being and perform a particular function. Proteins are not directly made f ...
... acid). You may not be aware of how this code is used to make life work the way that it does. The way that the genetic code of DNA is expressed is through the production of specialized proteins that travel throughout the living being and perform a particular function. Proteins are not directly made f ...
Identification of novel drug targets using model organisms
... polymerase in complex with s 9 indicate that there are extensive contacts across a large interface, which might not traditionally be considered a good target. Nevertheless, Andre et al. 10 identified a series of small molecules that inhibit the RNA polymerase-s interaction, indicating that even an e ...
... polymerase in complex with s 9 indicate that there are extensive contacts across a large interface, which might not traditionally be considered a good target. Nevertheless, Andre et al. 10 identified a series of small molecules that inhibit the RNA polymerase-s interaction, indicating that even an e ...
Delivering True Novelty
... The required properties are obtained by selecting the building blocks and the way in which they are linked. Strathclyde scientists introduced 3 new features into distamycin creating MGBs: 1. new building blocks in particular a thiazole; 2. short, branched alkyl chains as part of the thiazole; and 3. ...
... The required properties are obtained by selecting the building blocks and the way in which they are linked. Strathclyde scientists introduced 3 new features into distamycin creating MGBs: 1. new building blocks in particular a thiazole; 2. short, branched alkyl chains as part of the thiazole; and 3. ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... DNA, numerous viruses exist, in which genetic information can be in the form of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or single- or double-stranded RNA (ssRNA or dsRNA), as well as in the form of duplex DNA (dsDNA). However, viruses are not living things because they cannot replicate autonomously, without the ...
... DNA, numerous viruses exist, in which genetic information can be in the form of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or single- or double-stranded RNA (ssRNA or dsRNA), as well as in the form of duplex DNA (dsDNA). However, viruses are not living things because they cannot replicate autonomously, without the ...
Handout on the Central Dogma
... A Codon is a triplet of base pairs. Each codon corresponds to one of twenty Amino acids -- it’s the amino acids that are the building-blocks of proteins, which do the work of the cell. A gene is a sequence of codons. Each gene corresponds to a particular protein that is used by the cell to do its wo ...
... A Codon is a triplet of base pairs. Each codon corresponds to one of twenty Amino acids -- it’s the amino acids that are the building-blocks of proteins, which do the work of the cell. A gene is a sequence of codons. Each gene corresponds to a particular protein that is used by the cell to do its wo ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... structure of RNA be able to compare and contrast RNA and DNA function of three types of RNA be able to explain translation where in cell translation occurs describe how each type of RNA is involved in translation be able to transcribe DNA into RNA be able to translate RNA codons into amino acids wha ...
... structure of RNA be able to compare and contrast RNA and DNA function of three types of RNA be able to explain translation where in cell translation occurs describe how each type of RNA is involved in translation be able to transcribe DNA into RNA be able to translate RNA codons into amino acids wha ...
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS I. Bacteria
... are regulated by inducers and co-repressors. Operon regulation is often similar to allosteric regulation of enzymes: binding of a compound changes the shape of the repressor; binding of a compound changes the shape of the enzyme. A recent estimate says that there are approximately 630-700 operons in ...
... are regulated by inducers and co-repressors. Operon regulation is often similar to allosteric regulation of enzymes: binding of a compound changes the shape of the repressor; binding of a compound changes the shape of the enzyme. A recent estimate says that there are approximately 630-700 operons in ...
Transcription and genetic code
... • In eukaryotes, at a point 10-35 nucleotides downstream from the terminator sequence (AAUAAA signal), the pre-mRNA is released from the. • At a point about 10 to 35 nucleotides past this sequence, the pre-mRNA is cut from the enzyme. ...
... • In eukaryotes, at a point 10-35 nucleotides downstream from the terminator sequence (AAUAAA signal), the pre-mRNA is released from the. • At a point about 10 to 35 nucleotides past this sequence, the pre-mRNA is cut from the enzyme. ...
11/11/15 - cloudfront.net
... Keep your answers covered If you need to make up a quiz due to an absence… come see me Tues or Thurs during PLC Flip it over when you are finished and hang on to it ...
... Keep your answers covered If you need to make up a quiz due to an absence… come see me Tues or Thurs during PLC Flip it over when you are finished and hang on to it ...
16-17 Biology Fall Final Study Guide
... Passive transport (Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion) Active transport (Bulk transport, Exocytosis, Endocytosis (Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis) Receptor-mediated) Central Dogma Differences between RNA and DNA Central dogma Where does each step occur? Transcription RNA Polymerase ...
... Passive transport (Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion) Active transport (Bulk transport, Exocytosis, Endocytosis (Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis) Receptor-mediated) Central Dogma Differences between RNA and DNA Central dogma Where does each step occur? Transcription RNA Polymerase ...
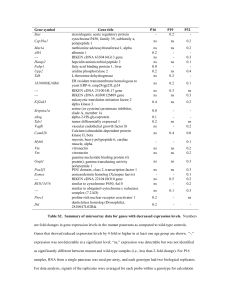
Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased
... Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased expression levels. Numbers are fold changes in gene expression levels in the mutant pancreata as compared to wild-type controls. Genes that showed reduced expression levels by 4 fold or higher in at least one age group are shown. “-,” exp ...
... Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased expression levels. Numbers are fold changes in gene expression levels in the mutant pancreata as compared to wild-type controls. Genes that showed reduced expression levels by 4 fold or higher in at least one age group are shown. “-,” exp ...
Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the
... conserved in all /3',A (respectively A') subunits of bacterial, eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fragments, whether digested with Sad, Aval, BamH ...
... conserved in all /3',A (respectively A') subunits of bacterial, eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fragments, whether digested with Sad, Aval, BamH ...
The Chromosome
... CAAT box: Contains this short sequence about 80 bp upstream (-80) of the start site. These sequences together with binding sites for other transcription factors which vary according to the gene involved, are responsible for the rate of transcription. The Initiator: is a sequence that is found ...
... CAAT box: Contains this short sequence about 80 bp upstream (-80) of the start site. These sequences together with binding sites for other transcription factors which vary according to the gene involved, are responsible for the rate of transcription. The Initiator: is a sequence that is found ...