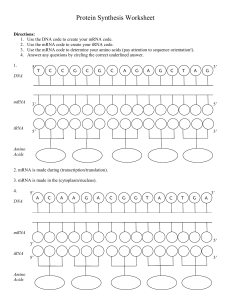
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
Lecture 27
... • DNA strands are simultaneously replicated. • Takes place at replication fork - junction where the two parental DNA are pried apart and where the two daughter strands are synthesized. • Leading strand is continuously copied from the 3’ to 5’ parental template in the 5’ to 3’ direction • Lagging str ...
... • DNA strands are simultaneously replicated. • Takes place at replication fork - junction where the two parental DNA are pried apart and where the two daughter strands are synthesized. • Leading strand is continuously copied from the 3’ to 5’ parental template in the 5’ to 3’ direction • Lagging str ...
NucleicAcids
... • Organisms inherit DNA from their parents. • Each DNA molecule is very long and usually consists of hundreds to thousands of genes. ...
... • Organisms inherit DNA from their parents. • Each DNA molecule is very long and usually consists of hundreds to thousands of genes. ...
6.5 - Institut für Philosophie (HU Berlin)
... 6.3 Molecular Genetics transcription & translation ...
... 6.3 Molecular Genetics transcription & translation ...
14 Diversity of BCR BA
... the variable domains of Igs HV3 in the light-chain is at the junction between rearranged V and J segments In the heavy chain HV3 is formed by the D segment and the residues between the rearranged V and D segments and the D and J segments . ...
... the variable domains of Igs HV3 in the light-chain is at the junction between rearranged V and J segments In the heavy chain HV3 is formed by the D segment and the residues between the rearranged V and D segments and the D and J segments . ...
Gene Reg Flyer 0113_D3.indd
... DNA methylation and histone modifications, as well as the role of noncoding RNAs in regulatory pathways. Agilent provides the tools needed to gain a better understanding of epigenetic control mechanisms that play a role in cancer, human diseases, and cell development. ...
... DNA methylation and histone modifications, as well as the role of noncoding RNAs in regulatory pathways. Agilent provides the tools needed to gain a better understanding of epigenetic control mechanisms that play a role in cancer, human diseases, and cell development. ...
AP Biology DNA Technology: The manipulation of organisms or their
... o Foreign DNA is inserted into a plasmid, and the recombinant plasmid is inserted into a bacterial cell. o Reproduction in the bacterial cell results in cloning of the plasmid including the foreign DNA o This results in the production of multiple copies of a single gene. This gene must be distingu ...
... o Foreign DNA is inserted into a plasmid, and the recombinant plasmid is inserted into a bacterial cell. o Reproduction in the bacterial cell results in cloning of the plasmid including the foreign DNA o This results in the production of multiple copies of a single gene. This gene must be distingu ...
Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
... genes together so that they can be regulated together. This grouping is called an operon. The clustered genes are transcribed together from one promoter giving a polycistronic messenger. ...
... genes together so that they can be regulated together. This grouping is called an operon. The clustered genes are transcribed together from one promoter giving a polycistronic messenger. ...
Antibiotics - Dr Magrann
... CELL MEMBRANE TARGETS Lipopeptides are amphiphilic, contain D-amino acids, disrupt CM, are potent but not selective; for “compassionate use” Polymyxins Gramicidins INHIBITORS OF mRNA SYNTHESIS Rifamycins: Bind to DNA-dependent RNA polymerase β subunit, prohibits mRNA transcription. Rifampin INHIBITO ...
... CELL MEMBRANE TARGETS Lipopeptides are amphiphilic, contain D-amino acids, disrupt CM, are potent but not selective; for “compassionate use” Polymyxins Gramicidins INHIBITORS OF mRNA SYNTHESIS Rifamycins: Bind to DNA-dependent RNA polymerase β subunit, prohibits mRNA transcription. Rifampin INHIBITO ...
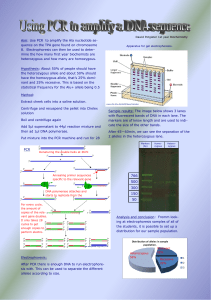
App1PCR - FSU Biology
... The polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, is a technique that allows for the amplification of a specific target DNA sequence within a larger population of DNA (such as the human genome). Using PCR, picogram quantities of target DNA can be amplified to yield microgram quantities for subsequent biochemic ...
... The polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, is a technique that allows for the amplification of a specific target DNA sequence within a larger population of DNA (such as the human genome). Using PCR, picogram quantities of target DNA can be amplified to yield microgram quantities for subsequent biochemic ...
Central Dogma of Biology Nucleic Acids
... are unmistakably similar. Although their body plans are strikingly different, humans and whales are built from the same proteins. Despite the length of time since humans and whales diverged, the nucleotide sequences of many of their genes are still closely similar. The sequences of a part of the gen ...
... are unmistakably similar. Although their body plans are strikingly different, humans and whales are built from the same proteins. Despite the length of time since humans and whales diverged, the nucleotide sequences of many of their genes are still closely similar. The sequences of a part of the gen ...
functional protein
... After reading this chapter and attending lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Compare the organization of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. 2. Describe the current model for progressive levels of DNA packing. 3. Explain how histones influence folding in eukaryotic DNA. 4. Distinguish between ...
... After reading this chapter and attending lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Compare the organization of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. 2. Describe the current model for progressive levels of DNA packing. 3. Explain how histones influence folding in eukaryotic DNA. 4. Distinguish between ...
Lecture 1
... RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose sugar. The base uracil (U) replaces thymine (T) in RNA. Most RNA is single stranded, although tRNA will form a "cloverleaf" structure due to complementary base pairing. ...
... RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose sugar. The base uracil (U) replaces thymine (T) in RNA. Most RNA is single stranded, although tRNA will form a "cloverleaf" structure due to complementary base pairing. ...
Lecture 6 - U of L Class Index
... Negative Control of the lac Operon 9 The off-regulation is done by the lac repressor – Product of the lacI gene – Tetramer of 4 identical polypeptides – Binds the operator just right of promoter 9 When repressor binds the operator, operon is repressed – Operator and promoter are contiguous – Repres ...
... Negative Control of the lac Operon 9 The off-regulation is done by the lac repressor – Product of the lacI gene – Tetramer of 4 identical polypeptides – Binds the operator just right of promoter 9 When repressor binds the operator, operon is repressed – Operator and promoter are contiguous – Repres ...
RNA Structure
... B. The fact that bases paired led directly to a theory of how DNA codes for proteins. It took a few years to determine that the bases spell threeletter “words” called codons ...
... B. The fact that bases paired led directly to a theory of how DNA codes for proteins. It took a few years to determine that the bases spell threeletter “words” called codons ...
1 - PLOS
... Presence of chloroquine on infected mosquito’s blood meal increased transcription of five genes associated with signal transduction, more specifically, transcripts associated with cell-cycle control (prohibitin B cell receptor), regulation of intracellular ion levels (sodium/potassium transporting A ...
... Presence of chloroquine on infected mosquito’s blood meal increased transcription of five genes associated with signal transduction, more specifically, transcripts associated with cell-cycle control (prohibitin B cell receptor), regulation of intracellular ion levels (sodium/potassium transporting A ...
MK+12-096-Multiplex-Reverse-Transcription-PCR-for
... identify as few as 100 individual molecules of RNA from as little as 10 nanograms of cellular RNA. Reverse transcription PCR converts a target sequence of viral RNA into DNA, which then acts as a template for amplification by PCR. Simultaneously, a known quantity of synthetic reference RNA is includ ...
... identify as few as 100 individual molecules of RNA from as little as 10 nanograms of cellular RNA. Reverse transcription PCR converts a target sequence of viral RNA into DNA, which then acts as a template for amplification by PCR. Simultaneously, a known quantity of synthetic reference RNA is includ ...
The genetic code
... spatially and temporally separated. Transcription occurs in the nucleus to produce a pre-mRNA molecule. The pre-mRNA is typically processed to produce the mature mRNA, which exits the nucleus and is translated in the cytoplasm. ...
... spatially and temporally separated. Transcription occurs in the nucleus to produce a pre-mRNA molecule. The pre-mRNA is typically processed to produce the mature mRNA, which exits the nucleus and is translated in the cytoplasm. ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... Now that we’ve made the library, we need to find the clones that contain the gene o We can use probes complementary to the desired gene sequence o These are often homologous sequences from different organisms ...
... Now that we’ve made the library, we need to find the clones that contain the gene o We can use probes complementary to the desired gene sequence o These are often homologous sequences from different organisms ...
DNA RNA
... • A telomere is a repeating DNA sequence (for example, TTAGGG) at the end of the body's chromosomes. • The telomere can reach a length of 15,000 base pairs. • Telomeres function by preventing chromosomes from losing base pair sequences at their ends. They also stop chromosomes from fusing to each ot ...
... • A telomere is a repeating DNA sequence (for example, TTAGGG) at the end of the body's chromosomes. • The telomere can reach a length of 15,000 base pairs. • Telomeres function by preventing chromosomes from losing base pair sequences at their ends. They also stop chromosomes from fusing to each ot ...
Central Dogma Review Sheet
... 2. Likewise, be able to describe the structure of RNA. Be able to list differences between DNA and RNA, and recognize the two by sight. 3. Understand how base pairing works. Know that A hydrogen-bonds with T, and C bonds with G. Be able to give the reasons why the base pairing is so specific. DNA Re ...
... 2. Likewise, be able to describe the structure of RNA. Be able to list differences between DNA and RNA, and recognize the two by sight. 3. Understand how base pairing works. Know that A hydrogen-bonds with T, and C bonds with G. Be able to give the reasons why the base pairing is so specific. DNA Re ...
T. Hill
... A light-emitting DNA probe can also be used for detection of the PCR product. Various probe designs exist but use the bringing together or separation of two fluorophores (when the DNA probe binds to the target) and exploit the transfer of fluorescence resonance energy between them (excitation of one ...
... A light-emitting DNA probe can also be used for detection of the PCR product. Various probe designs exist but use the bringing together or separation of two fluorophores (when the DNA probe binds to the target) and exploit the transfer of fluorescence resonance energy between them (excitation of one ...