Types of Chemical Reactions - Celebrity Examples
... y Emission of heat and y Giving off light y Formation of a precipitate y Formation of a gas y Color change ...
... y Emission of heat and y Giving off light y Formation of a precipitate y Formation of a gas y Color change ...
expanding the art of synthesis - Chemistry at Illinois
... mainstay of organic chemistry for many years, but is starting to be challenged with the discovery of reagents and catalysts that are capable of selectively functionalizing C–H bonds3–6. Thus, C–H bonds that would have previously been assumed to be unreactive can now be considered as reactive sites f ...
... mainstay of organic chemistry for many years, but is starting to be challenged with the discovery of reagents and catalysts that are capable of selectively functionalizing C–H bonds3–6. Thus, C–H bonds that would have previously been assumed to be unreactive can now be considered as reactive sites f ...
DMC (double metal cyanide) catalyst DMC catalyst is used
... DMC catalyst is used for epoxide polymerization, that is, for polymerizing alkylene oxides such as propylene oxide and ethylene oxide to yield high molecular weight polether polyols. In conventional base catalyzed oxyalkylation reaction, propylene oxide and certain other alkylene oxides are subject ...
... DMC catalyst is used for epoxide polymerization, that is, for polymerizing alkylene oxides such as propylene oxide and ethylene oxide to yield high molecular weight polether polyols. In conventional base catalyzed oxyalkylation reaction, propylene oxide and certain other alkylene oxides are subject ...
Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Norbornene Catalyzed
... Ru-carbene and Ru-vinylidene complexes have been proven to be highly efficient catalysts for a variety of olefin transformations. These include examples of ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) [1-7], ring-closing metathesis (RCM) [8,9], polycyclization reactions [9,10] and synthesis of natu ...
... Ru-carbene and Ru-vinylidene complexes have been proven to be highly efficient catalysts for a variety of olefin transformations. These include examples of ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) [1-7], ring-closing metathesis (RCM) [8,9], polycyclization reactions [9,10] and synthesis of natu ...
10.4b Organic Practice Test Version 2
... a) Carbon atoms in the organic product are bonded to fewer atoms than the carbon atoms in the organic reactant. b) A hydrogen atom or functional group is replaced with a different atom or functional group. c) Atoms are added to a double or triple carbon–carbon bond. d) Two molecules are combined and ...
... a) Carbon atoms in the organic product are bonded to fewer atoms than the carbon atoms in the organic reactant. b) A hydrogen atom or functional group is replaced with a different atom or functional group. c) Atoms are added to a double or triple carbon–carbon bond. d) Two molecules are combined and ...
types of organic reactions
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
5_slides_olefin_complexes_VIPEr
... Created by Margaret L. Scheuermann, Princeton University; Abby R. O’Connor, The College of New Jersey, [email protected]. Copyright Scheuermann and O’Connor, 2014. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercialShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this licens ...
... Created by Margaret L. Scheuermann, Princeton University; Abby R. O’Connor, The College of New Jersey, [email protected]. Copyright Scheuermann and O’Connor, 2014. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercialShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this licens ...
Exam 2 Review A
... steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure of electrophile, nature of leaving group- halogens or sulfonate esters], nature of the nucleophile ...
... steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure of electrophile, nature of leaving group- halogens or sulfonate esters], nature of the nucleophile ...
Redox Reactions
... Hydride reagents provide H- as a nucleophile, therefore they only react with polar substrates containing an electrophile. They do not react with alkenes or alkynes, so they provide additional selectivity between the functional groups. The reaction mechanism involves the nucleophilic attack of the ca ...
... Hydride reagents provide H- as a nucleophile, therefore they only react with polar substrates containing an electrophile. They do not react with alkenes or alkynes, so they provide additional selectivity between the functional groups. The reaction mechanism involves the nucleophilic attack of the ca ...
Lecture 2 - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... If the reaction was carried out at room temperature, the yield of the reaction will be poor (theoretically: 73 % at 25 oC). The literature reports an isolated yield of 85 % for the reaction when using concentrated phosphoric acid as catalyst. How? The yield can be improved using the Le Châtelier Pri ...
... If the reaction was carried out at room temperature, the yield of the reaction will be poor (theoretically: 73 % at 25 oC). The literature reports an isolated yield of 85 % for the reaction when using concentrated phosphoric acid as catalyst. How? The yield can be improved using the Le Châtelier Pri ...
Exam 2 Review A
... steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure of electrophile, nature of leaving group- halogens or sulfonate esters], nature of the nucleophile ...
... steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure of electrophile, nature of leaving group- halogens or sulfonate esters], nature of the nucleophile ...
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
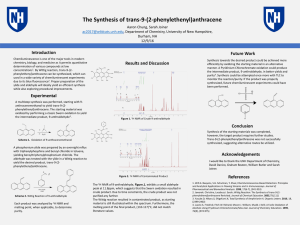
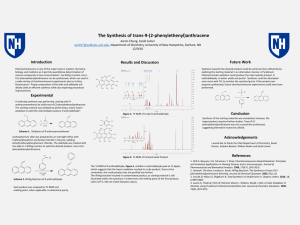
... Chemiluminescence is one of the major tools in modern chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent ...
... Chemiluminescence is one of the major tools in modern chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent ...
The Synthesis of trans-9-(2
... 1. W.R.G. Baeyens, S.G. Schulman, Y. Zhao; Chemiluminescence-Based Detection: Principles and Analytical Applications in Flowing Streams and in Immunoassays. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 1998, 17(6-7), (941-953) 2. Jaworek. Christine, Lacobucci. Sarah; Wittig Reaction: The Synth ...
... 1. W.R.G. Baeyens, S.G. Schulman, Y. Zhao; Chemiluminescence-Based Detection: Principles and Analytical Applications in Flowing Streams and in Immunoassays. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 1998, 17(6-7), (941-953) 2. Jaworek. Christine, Lacobucci. Sarah; Wittig Reaction: The Synth ...
Exam 2 Review A
... steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure of electrophile, nature of leaving group- halogens or sulfonate esters], nature of the nucleophile ...
... steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure of electrophile, nature of leaving group- halogens or sulfonate esters], nature of the nucleophile ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.