Lecture 14a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Solvent: DMSO (cannot be used in Chem 30CL), PTC conditions, solid state reaction An one-pot reaction is not advisable here because the reactants, the intermediate and the product are very difficult to separate from each other (anhydrous ZnI2 is not available!) The Corey-Chaykovsky reagent can ...
... Solvent: DMSO (cannot be used in Chem 30CL), PTC conditions, solid state reaction An one-pot reaction is not advisable here because the reactants, the intermediate and the product are very difficult to separate from each other (anhydrous ZnI2 is not available!) The Corey-Chaykovsky reagent can ...
Problem Set: Empirical and Molecular Formulas
... 1. Carbon monoxide can be combined with hydrogen to produce methanol, CH 3OH. If you had 152.5 g CO and 24.50 g H2, how many kilograms of CH3OH would be produced? (Hint: make sure equation is balanced first!) CO ...
... 1. Carbon monoxide can be combined with hydrogen to produce methanol, CH 3OH. If you had 152.5 g CO and 24.50 g H2, how many kilograms of CH3OH would be produced? (Hint: make sure equation is balanced first!) CO ...
+ Y
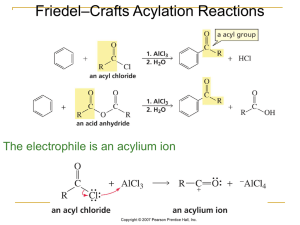
... has an electron-poor atom (e.g H+, CH3+ ) and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile ...
... has an electron-poor atom (e.g H+, CH3+ ) and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile ...
Diels-Alder Reaction
... all three rings cannot have benzenoid character simultaneously so the resonance energy per ring is lower than that of benzene and naphthalene (resonance energies: benzene, 36 kcal/mole; naphthalene, 60 kcal/mole; anthracene, 84 kcal/mole). DielsAlder addition across the center ring of anthracene is ...
... all three rings cannot have benzenoid character simultaneously so the resonance energy per ring is lower than that of benzene and naphthalene (resonance energies: benzene, 36 kcal/mole; naphthalene, 60 kcal/mole; anthracene, 84 kcal/mole). DielsAlder addition across the center ring of anthracene is ...
File - chemistryworkshopjr
... Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher reaction rate at the same temperature and for the same reactant concentrations. However, the mechanistic explanation of catalysis is complex ...
... Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher reaction rate at the same temperature and for the same reactant concentrations. However, the mechanistic explanation of catalysis is complex ...
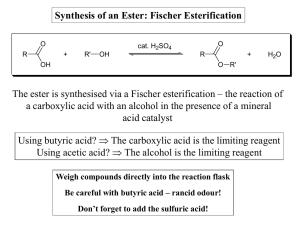
Synthesis of an Ester: Fischer Esterification The ester is synthesised
... in some cases, the ester product has appreciable water solubility, an additional H2O wash is omitted. Instead, the organic layer is washed a final time with NaCl solution. This serves to remove the bulk of the water from the organic layer. ...
... in some cases, the ester product has appreciable water solubility, an additional H2O wash is omitted. Instead, the organic layer is washed a final time with NaCl solution. This serves to remove the bulk of the water from the organic layer. ...
Chemical Reactions
... Reactants and Products • In a chemical reaction, the substances that undergo change are called reactants • The new substances formed as a result of that change are called products • The arrow in the equation means that the reaction of the reactants yields to the product ...
... Reactants and Products • In a chemical reaction, the substances that undergo change are called reactants • The new substances formed as a result of that change are called products • The arrow in the equation means that the reaction of the reactants yields to the product ...
study note 3 33
... double bond when the addition is to a triple bond). Halogenation, and hydrogenation are types of addition reactions. Oxidation and hydrolysis are, in some cases, addition reactions. Polymerization, in some cases, may also proceed via addition reactions. Hydrolysis is a reaction in which water is one ...
... double bond when the addition is to a triple bond). Halogenation, and hydrogenation are types of addition reactions. Oxidation and hydrolysis are, in some cases, addition reactions. Polymerization, in some cases, may also proceed via addition reactions. Hydrolysis is a reaction in which water is one ...
CHAPTER-6 DEHYDROHALOGENATION OF ALKYL HALIDES
... – Approach to carbon is extremely hindered and elimination predominates especially at high temperatures ...
... – Approach to carbon is extremely hindered and elimination predominates especially at high temperatures ...
Organic Chemistry 1 1st Hour Exam Student ID # Name
... (b) Explain why one product is the major isomer based on their reaction coordinate diagrams that show the two different reaction progresses (or pathways) to give the two different products, the major and the minor products. Explain the reaction results using the Hammond postulate. ...
... (b) Explain why one product is the major isomer based on their reaction coordinate diagrams that show the two different reaction progresses (or pathways) to give the two different products, the major and the minor products. Explain the reaction results using the Hammond postulate. ...
Heck Reactions
... The Complex. Among Pd(0) and Pd(II) complexes commonly used are Pd(PPh3)4, Pd2(dba)2, and Pd2(dba)2CHCl3. Pd(PPh3)4 should be stored cold and under inert gas; the dibenzylideneacetone complexes are more stable catalyst precursors. Both phosphine structure and phosphine/Pd ratio effect catalyst struc ...
... The Complex. Among Pd(0) and Pd(II) complexes commonly used are Pd(PPh3)4, Pd2(dba)2, and Pd2(dba)2CHCl3. Pd(PPh3)4 should be stored cold and under inert gas; the dibenzylideneacetone complexes are more stable catalyst precursors. Both phosphine structure and phosphine/Pd ratio effect catalyst struc ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.