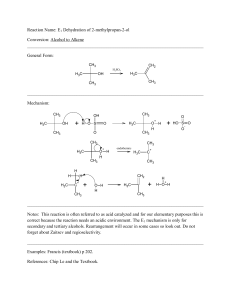
19-20 - TAMU Chemistry
... The (NH2)- ligand is formed in the first step. This compound is reactive with Y- and later protonation restores the NH2- ligand to NH3. Base catalyzed. ...
... The (NH2)- ligand is formed in the first step. This compound is reactive with Y- and later protonation restores the NH2- ligand to NH3. Base catalyzed. ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
... Addition yields a hydroxy ether, called a hemiacetal (reversible); further reaction can occur Protonation of the OH and loss of water leads to an oxonium ion, R2C=OR+ to which a second alcohol adds to form the acetal ...
... Addition yields a hydroxy ether, called a hemiacetal (reversible); further reaction can occur Protonation of the OH and loss of water leads to an oxonium ion, R2C=OR+ to which a second alcohol adds to form the acetal ...
Zn(BH ) /2NaCl: A Novel Reducing System for Efficient Reduction of
... Cu(BH4)2, 6Zn(BH4)2, 7Ti(BH4)3, 8Zr(BH4)4 and others.8b LiBH4, Ca(BH4)2 and Zn(BH4)2 are the modified borohydride agents which have better solubility in aprotic solvents, so their uses and applications are interesting in organic synthesis. Among these reagents, zinc borohydride is unique because of ...
... Cu(BH4)2, 6Zn(BH4)2, 7Ti(BH4)3, 8Zr(BH4)4 and others.8b LiBH4, Ca(BH4)2 and Zn(BH4)2 are the modified borohydride agents which have better solubility in aprotic solvents, so their uses and applications are interesting in organic synthesis. Among these reagents, zinc borohydride is unique because of ...
LECTURE 7 REDUCTIVE ELIMINATIONSa
... • The reverse reaction, reductive elimination, leads to the extrusion of A−B from an M(A)(B) complex and is often the product‐forming step in a catalytic reaction. • In the oxidative addition direction, we break the A−B bond and form an M−A and an M−B bond. • The oxidation state (OS), electron count ...
... • The reverse reaction, reductive elimination, leads to the extrusion of A−B from an M(A)(B) complex and is often the product‐forming step in a catalytic reaction. • In the oxidative addition direction, we break the A−B bond and form an M−A and an M−B bond. • The oxidation state (OS), electron count ...
CHEM 203 Material
... state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will tend to react with electron acceptors. Likewise, one may predict that hypothetical reactions ...
... state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will tend to react with electron acceptors. Likewise, one may predict that hypothetical reactions ...
Transition Metal Reagents and Catalysts
... ®rst by giving a simple mechanistic explanation in chapter 2. Then a number of important types of reactions classi®ed mainly by representative substrates such as organic halides and allylic derivatives are surveyed with pertinent examples. For this purpose, I cited many references; these were select ...
... ®rst by giving a simple mechanistic explanation in chapter 2. Then a number of important types of reactions classi®ed mainly by representative substrates such as organic halides and allylic derivatives are surveyed with pertinent examples. For this purpose, I cited many references; these were select ...
Document
... acid promoter. Reductions with chelating agents, such as titanium tetrachloride, and with nonchelating agents, such as cerium trichloride, proceed through a cyclic or a Felkin-Ahn transition state respectively, leading to opposite stereochemical outcomes. Prof. Bartoli found that the complex formed ...
... acid promoter. Reductions with chelating agents, such as titanium tetrachloride, and with nonchelating agents, such as cerium trichloride, proceed through a cyclic or a Felkin-Ahn transition state respectively, leading to opposite stereochemical outcomes. Prof. Bartoli found that the complex formed ...
Molecular structure–reactivity relationships for the oxidation of sulfur
... sorbed onto a V2 O5 /CeO2 /Mg2 Al2 O5 spinel where it is later regenerated to produce concentrated H2 S and SO2 , which is recycled to the Claus plant for further processing [16]. In spite of the industrial importance and environmental consequences of the above catalytic oxidation processes involvin ...
... sorbed onto a V2 O5 /CeO2 /Mg2 Al2 O5 spinel where it is later regenerated to produce concentrated H2 S and SO2 , which is recycled to the Claus plant for further processing [16]. In spite of the industrial importance and environmental consequences of the above catalytic oxidation processes involvin ...
Rh(acac)(CO)(PR1R2R3) - University of the Free State
... catalyst metal. This led to the development of processes which operate under milder reaction conditions and used highly active catalysts with excellent selectivity for the formation of the desired products.4 ...
... catalyst metal. This led to the development of processes which operate under milder reaction conditions and used highly active catalysts with excellent selectivity for the formation of the desired products.4 ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.