The effect of confinement on chemical reactions
... ethanol to produce ethyl acetate, CH3COOH + C2H5OH $ C2H5OOCCH3 + H2O, is a common industrial process in the synthesis of organic solvents. There is experimental evidence [16] that when this reaction is carried out in porous materials, the selectivity towards ethyl acetate depends on the adsorbent u ...
... ethanol to produce ethyl acetate, CH3COOH + C2H5OH $ C2H5OOCCH3 + H2O, is a common industrial process in the synthesis of organic solvents. There is experimental evidence [16] that when this reaction is carried out in porous materials, the selectivity towards ethyl acetate depends on the adsorbent u ...
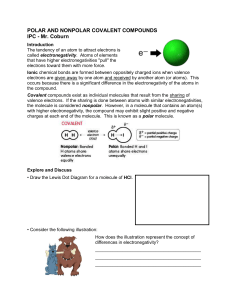
Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
... electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are given away by one atom and received by another atom (or atoms). This occurs because there is a significant difference in the electronegativity of the atoms in the compoun ...
... electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are given away by one atom and received by another atom (or atoms). This occurs because there is a significant difference in the electronegativity of the atoms in the compoun ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
... Recall the problem: If reaction occurs only at the C bearing the Cl the other should remain chiral! Hmmmm? But now notice that the intermediate sulfonium ion is achiral. It has a mirror plane of symmetry. Only optically inactive products will result. ...
... Recall the problem: If reaction occurs only at the C bearing the Cl the other should remain chiral! Hmmmm? But now notice that the intermediate sulfonium ion is achiral. It has a mirror plane of symmetry. Only optically inactive products will result. ...
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
... chain) and use the corresponding alkane name 2. Number the carbons in the parent chain starting with the one closest to the branch chain 3. Name each branch with a –yl ending and place it before the name of the parent chain 4. Use the number of the carbon to which it’s attached to indicate the branc ...
... chain) and use the corresponding alkane name 2. Number the carbons in the parent chain starting with the one closest to the branch chain 3. Name each branch with a –yl ending and place it before the name of the parent chain 4. Use the number of the carbon to which it’s attached to indicate the branc ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Alex Science Department
... - Some molecules contain branches (where a hydrogen has been replaced with carbon chains) – The carbon chain is called an ALKYL group - These are represented with an R- in the structural formula - These alkyl groups are named as follows… ...
... - Some molecules contain branches (where a hydrogen has been replaced with carbon chains) – The carbon chain is called an ALKYL group - These are represented with an R- in the structural formula - These alkyl groups are named as follows… ...
enzymatic resolution of a racemic mixture by acylation in
... The synthesis of enantiomerically pure compounds is becoming increasingly important in the pharmaceutical and the fine chemicals industries. The use of enzymes as enantioselective catalysts in kinetic resolutions has now become a common method to obtain pure enantiomers. The applicability of this ap ...
... The synthesis of enantiomerically pure compounds is becoming increasingly important in the pharmaceutical and the fine chemicals industries. The use of enzymes as enantioselective catalysts in kinetic resolutions has now become a common method to obtain pure enantiomers. The applicability of this ap ...
Thiobenzoate Photochemistry
... not significantly affect the H-abstraction pathway in O-phenethyl thiobenzoates, although the reaction is slightly slower with the nitrophenyl group.3 (d) Solvent Effects The formation of an ion pair can be controlled to some extent by solvent polarity. It is unusual to have ion pairs form in methyl ...
... not significantly affect the H-abstraction pathway in O-phenethyl thiobenzoates, although the reaction is slightly slower with the nitrophenyl group.3 (d) Solvent Effects The formation of an ion pair can be controlled to some extent by solvent polarity. It is unusual to have ion pairs form in methyl ...
Practical and selective aerobic oxidation of alcohols to
... measuring 100 mm in length (i.e. 500 mm in total). As the reaction occurred in a two-phase flow along the length of the reactor, staged injection of oxygen was used to maintain a consistent amount of gas along the reaction bed. Although characteristics of the flow system were very well-defined, the ...
... measuring 100 mm in length (i.e. 500 mm in total). As the reaction occurred in a two-phase flow along the length of the reactor, staged injection of oxygen was used to maintain a consistent amount of gas along the reaction bed. Although characteristics of the flow system were very well-defined, the ...
Reactions to know from Chapters 17, 18, 19
... the same molecule, a cyclic hemi-acetal can be formed. (shown below) O ...
... the same molecule, a cyclic hemi-acetal can be formed. (shown below) O ...
Document
... The carbonyl group is strongly polar but does not produce hydrogen bonding. As a result, the boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than the nonpolar hydrocarbons and the alkyl halides but lower than those of alcohols. Formaldehyde is a gas at room temperature (b.p. = -21 C) but heavier ...
... The carbonyl group is strongly polar but does not produce hydrogen bonding. As a result, the boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than the nonpolar hydrocarbons and the alkyl halides but lower than those of alcohols. Formaldehyde is a gas at room temperature (b.p. = -21 C) but heavier ...
Naming organic compounds
... functional group is the parent molecule or simply the longest unbranched chain for alkanes. Remember that the longest chain can go round a bend. Indicate the position of the functional group with a number, numbering from the end nearest the functional group. Name the branches and indicate the number ...
... functional group is the parent molecule or simply the longest unbranched chain for alkanes. Remember that the longest chain can go round a bend. Indicate the position of the functional group with a number, numbering from the end nearest the functional group. Name the branches and indicate the number ...
CHEMISTRY 105
... A. 2n+2 = number of hydrogens on alkane (n = # carbons) 1. If less than 2n+2 H’s, then unsaturated or cyclic B. Nomenclature 1. prefix cyclo- in front of parent chain 2. substituents numbered around ring a. such as to give lowest numbers b. 1,3 not 1,4 3. when two different groups present a. first a ...
... A. 2n+2 = number of hydrogens on alkane (n = # carbons) 1. If less than 2n+2 H’s, then unsaturated or cyclic B. Nomenclature 1. prefix cyclo- in front of parent chain 2. substituents numbered around ring a. such as to give lowest numbers b. 1,3 not 1,4 3. when two different groups present a. first a ...
Synthetic route to novel asymmetric tetradentate ligands
... Keywords: asymmetry, ligand, Schiff base, synthetic route, amino group ...
... Keywords: asymmetry, ligand, Schiff base, synthetic route, amino group ...
Chapter 5 CHEM 121
... • The amounts of SO2 that could be produced from 55.2 g of O2 reacting with excess H2S as well as from 50.8 g of H2S reacting with excess O2 will be calculated. • The reactant giving the least amount of SO2 will be the limiting reactant. • The amount of SO2 produced by the limiting reactant is the a ...
... • The amounts of SO2 that could be produced from 55.2 g of O2 reacting with excess H2S as well as from 50.8 g of H2S reacting with excess O2 will be calculated. • The reactant giving the least amount of SO2 will be the limiting reactant. • The amount of SO2 produced by the limiting reactant is the a ...
Identification of Functional Groups
... 2. In a separate, very clean test tube obtain 4mL of 5% AgNO3 solution and prepare the Tollens’ reagent as follows: --To the 4mL of 5% AgNO3 add 15 drops of 10% NaOH solution then stir thoroughly to mix. A brown precipitate should form. --Add a few drops at a time of 6M NH4OH solution to the test t ...
... 2. In a separate, very clean test tube obtain 4mL of 5% AgNO3 solution and prepare the Tollens’ reagent as follows: --To the 4mL of 5% AgNO3 add 15 drops of 10% NaOH solution then stir thoroughly to mix. A brown precipitate should form. --Add a few drops at a time of 6M NH4OH solution to the test t ...
Synthesis of enantiopure alcohols
... Previously we have reported that the enantioselectivity (E) decreased during esterifications of a range of secondary alcohols (1-4) catalyzed by immobilized lipase B from Candida antarctica (Novozym 435) and that addition of enantiopure (R)alcohols, (R)-1, (R)-2, (R)-5, (R)-6 and (R)-7, induced incr ...
... Previously we have reported that the enantioselectivity (E) decreased during esterifications of a range of secondary alcohols (1-4) catalyzed by immobilized lipase B from Candida antarctica (Novozym 435) and that addition of enantiopure (R)alcohols, (R)-1, (R)-2, (R)-5, (R)-6 and (R)-7, induced incr ...
CP Chemistry Midterm Study Guide
... oxygen, what is its empirical formula? b. What is the empirical formula for monosodium glutamate (MSG) if it is composed of 35.5% C, 4.77% H, 8.29% N,13.6% Na and 37.9% O? 44. What is the molecular formula for a compound with an empirical formula of NO2 and a molecular mass of 92.0 g? 44. The follow ...
... oxygen, what is its empirical formula? b. What is the empirical formula for monosodium glutamate (MSG) if it is composed of 35.5% C, 4.77% H, 8.29% N,13.6% Na and 37.9% O? 44. What is the molecular formula for a compound with an empirical formula of NO2 and a molecular mass of 92.0 g? 44. The follow ...
167KB - NZQA
... Carboxylic acid (butanoic acid) is obtained by reacting a mixture of butan-1ol with acidified potassium dichromate solution (under reflux conditions) until all of the reactant has been converted to butanoic acid. Observations: orange Cr2O72– to green /, purple MnO4– to colourless / aldehyde condense ...
... Carboxylic acid (butanoic acid) is obtained by reacting a mixture of butan-1ol with acidified potassium dichromate solution (under reflux conditions) until all of the reactant has been converted to butanoic acid. Observations: orange Cr2O72– to green /, purple MnO4– to colourless / aldehyde condense ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.