ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: The chemistry of carbon compounds
... 18. This German chemist proposed a cyclic structure for benzene: 19. The common name for methylbenzene is: 20. When benzene is not the parent chain it is called a ________________ group. 21. The OH group is called a_____________________________________ group. 22. When a halide such as chlorine is at ...
... 18. This German chemist proposed a cyclic structure for benzene: 19. The common name for methylbenzene is: 20. When benzene is not the parent chain it is called a ________________ group. 21. The OH group is called a_____________________________________ group. 22. When a halide such as chlorine is at ...
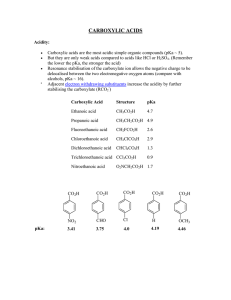
carboxylic acids - La Salle University
... 1o and 2o alkyl halides (X = Cl, Br, I) or tosylates undergo SN2 substitution with cyanide salts to give nitriles. Nitriles can be hydrolysed to carboxylic acids without the isolation of the amide intermediate. Note that the carbon skeleton is extended by 1 C atom during this reaction sequence. Alth ...
... 1o and 2o alkyl halides (X = Cl, Br, I) or tosylates undergo SN2 substitution with cyanide salts to give nitriles. Nitriles can be hydrolysed to carboxylic acids without the isolation of the amide intermediate. Note that the carbon skeleton is extended by 1 C atom during this reaction sequence. Alth ...
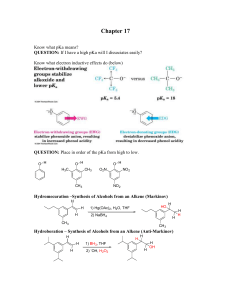
Chapter 17 - Ellis Benjamin
... Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
... Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
Chap20 Grignard reagents
... 1) Grignard reagents are nucleophiles that add to the specific types of electrophiles shown in this handout (ie. that are not generally used for SN 2 reactions on alkyl halides). 2) Alkyl Na, Li, and K reagents (i.e. H 3CC CNa ) react very similarly to Grignard reagents. 3) An R – addition to a carb ...
... 1) Grignard reagents are nucleophiles that add to the specific types of electrophiles shown in this handout (ie. that are not generally used for SN 2 reactions on alkyl halides). 2) Alkyl Na, Li, and K reagents (i.e. H 3CC CNa ) react very similarly to Grignard reagents. 3) An R – addition to a carb ...
Final-01 - Yale Department of Chemistry
... moments to look over the exam. Do problems first with which you are most comfortable. Important points and unknowns are in bold type. Do all preliminary work on the worksheets. The worksheets will not be graded. The exam is the length of two hour exams with an additional one hour for review. STOP wr ...
... moments to look over the exam. Do problems first with which you are most comfortable. Important points and unknowns are in bold type. Do all preliminary work on the worksheets. The worksheets will not be graded. The exam is the length of two hour exams with an additional one hour for review. STOP wr ...
Lecture 14a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Solvent: DMSO (cannot be used in Chem 30CL), PTC conditions, solid state reaction An one-pot reaction is not advisable here because the reactants, the intermediate and the product are very difficult to separate from each other (anhydrous ZnI2 is not available!) The Corey-Chaykovsky reagent can ...
... Solvent: DMSO (cannot be used in Chem 30CL), PTC conditions, solid state reaction An one-pot reaction is not advisable here because the reactants, the intermediate and the product are very difficult to separate from each other (anhydrous ZnI2 is not available!) The Corey-Chaykovsky reagent can ...
Introduction to Organic Synthesis 2011
... The formation of new C-C bond(s) Having looked at radical reactions in previous lectures we now going to go back to reactions involving the transfer of electron pairs. Hence these are reactions that involve the use of nucleophiles. Nucleophiles donates electrons, but can often react as bases as wel ...
... The formation of new C-C bond(s) Having looked at radical reactions in previous lectures we now going to go back to reactions involving the transfer of electron pairs. Hence these are reactions that involve the use of nucleophiles. Nucleophiles donates electrons, but can often react as bases as wel ...
Chapter 12- Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds, Redox Reactions
... to being a strong nucleophile, they are also a very strong base • It is not possible to prepare a Grignard from an organic compound that contains an acidic hydrogen • By acidic Hydrogen, we mean any hydrogen that is more acidic than the hydrogens on an alkane or ...
... to being a strong nucleophile, they are also a very strong base • It is not possible to prepare a Grignard from an organic compound that contains an acidic hydrogen • By acidic Hydrogen, we mean any hydrogen that is more acidic than the hydrogens on an alkane or ...
Export To Word
... Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeating (periodic) patterns of physical and chemical properties occur among elements that define groups of elements with ...
... Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeating (periodic) patterns of physical and chemical properties occur among elements that define groups of elements with ...
Demonstrate skill in organic chemistry techniques.
... Analyze and examine the structure, properties, and reactions of carboxylic acids. Learning Objectives Draw and name carboxylic acids and dicarboxylic acids; describe trends in acidity and physical properties and explain variations in their acidity. Predict products and propose mechanisms for reactio ...
... Analyze and examine the structure, properties, and reactions of carboxylic acids. Learning Objectives Draw and name carboxylic acids and dicarboxylic acids; describe trends in acidity and physical properties and explain variations in their acidity. Predict products and propose mechanisms for reactio ...
2 - My CCSD
... For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
... For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes
... Nucleophilic Addition • A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated. • A weak nucleophile will attack a carbonyl if it has been protonated, thus increasing its reactivity. • Aldehydes are more reactive than ...
... Nucleophilic Addition • A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated. • A weak nucleophile will attack a carbonyl if it has been protonated, thus increasing its reactivity. • Aldehydes are more reactive than ...
Faculteit der Natuurwetenschappen, Wiskunde en Informatica
... was observed at all. A plausible explanation for the low reactivity of n-BuLi and t-BuLi is that they are too bulky. In order to test this theory the less sterically encumbered MeLi was used. Suprisingly another product formed. The proposed reaction using MeLi as lithiating agent is most likely the ...
... was observed at all. A plausible explanation for the low reactivity of n-BuLi and t-BuLi is that they are too bulky. In order to test this theory the less sterically encumbered MeLi was used. Suprisingly another product formed. The proposed reaction using MeLi as lithiating agent is most likely the ...
Demonstrate skill in organic chemistry techniques.
... Analyze and examine the structure, properties, and reactions of carboxylic acids. Learning Objectives Draw and name carboxylic acids and dicarboxylic acids; describe trends in acidity and physical properties and explain variations in their acidity. Predict products and propose mechanisms for reactio ...
... Analyze and examine the structure, properties, and reactions of carboxylic acids. Learning Objectives Draw and name carboxylic acids and dicarboxylic acids; describe trends in acidity and physical properties and explain variations in their acidity. Predict products and propose mechanisms for reactio ...
Test: "Chemical Equations" (General Chemistry)
... d. Looking at the solubility chart below, list any pair(s) of ions that form a solid precipitate. e. Looking at the solubility chart below, list any pair(s) of ions that remain in solution. ...
... d. Looking at the solubility chart below, list any pair(s) of ions that form a solid precipitate. e. Looking at the solubility chart below, list any pair(s) of ions that remain in solution. ...
Organic Reactions
... – Diatomic gas has two atoms – both add to opposite sides of the double bond (and opposite sides of the molecule) – Uses: Chlorine + ethane 1,2-dichloroethane: used as starting material for PVC – Uses: Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddish- ...
... – Diatomic gas has two atoms – both add to opposite sides of the double bond (and opposite sides of the molecule) – Uses: Chlorine + ethane 1,2-dichloroethane: used as starting material for PVC – Uses: Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddish- ...
Alcohols/Wade: Reactions
... 10. Compound A is an optically active alcohol. Treatment with chromic acid converts A to a ketone B. In a separate reaction A is treated with PBr3, converting A to C. Compound D is purified and reacted with magnesium and ether. Compound B is added to the resulting solution of the Grignard reagent. ...
... 10. Compound A is an optically active alcohol. Treatment with chromic acid converts A to a ketone B. In a separate reaction A is treated with PBr3, converting A to C. Compound D is purified and reacted with magnesium and ether. Compound B is added to the resulting solution of the Grignard reagent. ...
Chemistry
... 2. Explain the difference between 10, 20 and 30 alkyl halides, with suitable examples. 3. Allyl halides are more reactive than alkyl halides. Why? 4. What are the reagents required prepare alkyl halide from the following (i) alcohol (ii) alkene (iv) alkanes 5. Explain the reactions used to convert b ...
... 2. Explain the difference between 10, 20 and 30 alkyl halides, with suitable examples. 3. Allyl halides are more reactive than alkyl halides. Why? 4. What are the reagents required prepare alkyl halide from the following (i) alcohol (ii) alkene (iv) alkanes 5. Explain the reactions used to convert b ...
PREPARATION OF ALDEHYDES
... 2. Reduction of acyl chlorides: RCOCl → RCHO Lithium tri-t-butoxyaluminum hydride is often used for this reduction. CH3 H3C C O ...
... 2. Reduction of acyl chlorides: RCOCl → RCHO Lithium tri-t-butoxyaluminum hydride is often used for this reduction. CH3 H3C C O ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.