Development of Multi-Component Reactions using Catalytically Generated Allyl Metal Reagents
... transformations of allylboronates. The allylation of aldehydes by allylboronates leading to homoallylic alcohols is an important C-C bond forming reaction. Several attractive properties of allylboronates account for their popularity as synthetic intermediates in organic synthesis.8-62 Their high dia ...
... transformations of allylboronates. The allylation of aldehydes by allylboronates leading to homoallylic alcohols is an important C-C bond forming reaction. Several attractive properties of allylboronates account for their popularity as synthetic intermediates in organic synthesis.8-62 Their high dia ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to corresponding amines is an extensively studied organic transformation [1]. Diverse reagents and reaction conditions have been developed for this purpose. Conversion of aromatic amines to corresponding acetamides is also well documented [2]. Reduction of nitro ...
... Reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to corresponding amines is an extensively studied organic transformation [1]. Diverse reagents and reaction conditions have been developed for this purpose. Conversion of aromatic amines to corresponding acetamides is also well documented [2]. Reduction of nitro ...
Benzene, amines, amino acids and polymers File
... • The simplest and most important arene is benzene. Unfortunately, benzene is toxic and mildly carcinogenic, so it cannot be used except in research and certain industrial processes. Fortunately, the reactions of benzene are also given by many of its derivatives and in the experiments below you will ...
... • The simplest and most important arene is benzene. Unfortunately, benzene is toxic and mildly carcinogenic, so it cannot be used except in research and certain industrial processes. Fortunately, the reactions of benzene are also given by many of its derivatives and in the experiments below you will ...
Integration of chemical catalysis with extractive fermentation to
... aldehydes were observed during the reaction, suggesting that the aldehyde intermediates were present in very low concentrations and reacted rapidly with acetone and other ketones. Hence, the formation of Guerbet products was minimized, and acetone alkylation predominated. On the basis of our experim ...
... aldehydes were observed during the reaction, suggesting that the aldehyde intermediates were present in very low concentrations and reacted rapidly with acetone and other ketones. Hence, the formation of Guerbet products was minimized, and acetone alkylation predominated. On the basis of our experim ...
Chemistry 2100 - Bonham Chemistry
... The functional group of an amide is a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom. – To name an amide, drop the suffix -oic acid from the IUPAC name of the parent acid, or -ic acid from its common name, and add -amide. – If the amide nitrogen is also bonded to an alkyl or aryl group, name the group and ...
... The functional group of an amide is a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom. – To name an amide, drop the suffix -oic acid from the IUPAC name of the parent acid, or -ic acid from its common name, and add -amide. – If the amide nitrogen is also bonded to an alkyl or aryl group, name the group and ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
... Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the carbonyl ...
... Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the carbonyl ...
Selective Incorporation of Difluoromethylene
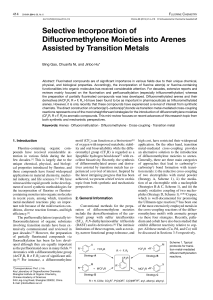
... Cy2 as dative ligand. A range of functionalities were tolerated under these reaction conditions. It is noteworthy that both aryl bromide and aryl chloride could be efficiently transformed with low catalyst loading even in large scale. Intriguingly, the base-induced cleavage of the α-aryl-α,αdifluoro ...
... Cy2 as dative ligand. A range of functionalities were tolerated under these reaction conditions. It is noteworthy that both aryl bromide and aryl chloride could be efficiently transformed with low catalyst loading even in large scale. Intriguingly, the base-induced cleavage of the α-aryl-α,αdifluoro ...
101. Alcohols as alkylating agents in heteroarene C H functionalization
... alcohols in Fig. 3b typically use methyl thioglycolate 13 as the C–H abstraction catalyst. Notably, simple aliphatic alcohols such as ethanol and propanol deliver the alkylated isoquinoline product in high yields (33 and 34, 95% and 96% yield). Steric bulk proximal to the alcohol functionality is to ...
... alcohols in Fig. 3b typically use methyl thioglycolate 13 as the C–H abstraction catalyst. Notably, simple aliphatic alcohols such as ethanol and propanol deliver the alkylated isoquinoline product in high yields (33 and 34, 95% and 96% yield). Steric bulk proximal to the alcohol functionality is to ...
Fatty Acids - dan
... • Fatty acids which can’t be synthesized by the body are essential fatty acids – Linoleic acid is an essential fatty acid required to make arachadonic acid ...
... • Fatty acids which can’t be synthesized by the body are essential fatty acids – Linoleic acid is an essential fatty acid required to make arachadonic acid ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
... Here is the crux of the matter: how can the non-reacting carbon change its configuration??? Further it does not always change but only if configuration of the reacting carbon changes!! We got a mixture of enantiomers, a racemic mixture. Something strange is happening!! Expect sulfur to attack the C- ...
... Here is the crux of the matter: how can the non-reacting carbon change its configuration??? Further it does not always change but only if configuration of the reacting carbon changes!! We got a mixture of enantiomers, a racemic mixture. Something strange is happening!! Expect sulfur to attack the C- ...
on nomenclature. compounds other than hydrocarbons%
... 7-1A Naming a Compound of Known Structure You first should decide what type of compound it is. The decision usually is straightforward for hydrocarbons, which will fall in one or the other of the categories alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, arenes, cycloalkanes, and so on. But when the compound has more th ...
... 7-1A Naming a Compound of Known Structure You first should decide what type of compound it is. The decision usually is straightforward for hydrocarbons, which will fall in one or the other of the categories alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, arenes, cycloalkanes, and so on. But when the compound has more th ...
carboxylic acids and their derivatives
... Exercise 18-1 Explain why the proton line position of the acidic hydrogen of a carboxylic acid, dissolved in a nonpolar solvent such as carbon tetrachloride, changes much less with concentration than does that of the OH proton of an alcohol under the same conditions (Section 9-1OE). ...
... Exercise 18-1 Explain why the proton line position of the acidic hydrogen of a carboxylic acid, dissolved in a nonpolar solvent such as carbon tetrachloride, changes much less with concentration than does that of the OH proton of an alcohol under the same conditions (Section 9-1OE). ...
15_01_05.html
... Most ethanol comes from fermentation Synthetic ethanol is produced by hydration of ethylene Synthetic ethanol is denatured (made unfit for drinking) by adding methanol, benzene, pyridine, castor oil, gasoline, etc. ...
... Most ethanol comes from fermentation Synthetic ethanol is produced by hydration of ethylene Synthetic ethanol is denatured (made unfit for drinking) by adding methanol, benzene, pyridine, castor oil, gasoline, etc. ...
Chapter 8 I. Nucleophilic Substitution
... rate = k [CH3Br] [HO – ] What is the reaction order of each starting material? What can you infer on a molecular level? What is the overall order of reaction? ...
... rate = k [CH3Br] [HO – ] What is the reaction order of each starting material? What can you infer on a molecular level? What is the overall order of reaction? ...
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
... • Hydrolysis in aqueous acid is the reverse of Fischer esterification – the role of the acid catalyst is to protonate the carbonyl oxygen and increase its electrophilic character toward attack by water (a weak nucleophile) to form a tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate – collapse of this inter ...
... • Hydrolysis in aqueous acid is the reverse of Fischer esterification – the role of the acid catalyst is to protonate the carbonyl oxygen and increase its electrophilic character toward attack by water (a weak nucleophile) to form a tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate – collapse of this inter ...
2nd Nine Weeks Notes
... a. An exponent of “1” is referred to as first order. b. An exponent of “2” is referred to as second order. c. I think you get the point! B. Method of Initial Rates. 1. Again, the initial rate is the instantaneous rate at t = 0. ...
... a. An exponent of “1” is referred to as first order. b. An exponent of “2” is referred to as second order. c. I think you get the point! B. Method of Initial Rates. 1. Again, the initial rate is the instantaneous rate at t = 0. ...
Get Reprint - McMaster Chemistry
... negative apparent activation energy resulting from the free energy of activation being dominated by a strongly negative entropic term (so that the rate of reaction decreases as the temperature increases).31,34 The stepwise mechanism is clearly the more consistent with the results of earlier theoreti ...
... negative apparent activation energy resulting from the free energy of activation being dominated by a strongly negative entropic term (so that the rate of reaction decreases as the temperature increases).31,34 The stepwise mechanism is clearly the more consistent with the results of earlier theoreti ...
CH 8 blackboard
... When 1 mole of C3H8 reacts with 5 moles of O2 to form 3 moles of CO2 and 4 moles of H2O, 2044 kJ of heat are emitted. These ratios can be used to construct conversion factors between amounts of reactants or products and the quantity of heat exchanged. ...
... When 1 mole of C3H8 reacts with 5 moles of O2 to form 3 moles of CO2 and 4 moles of H2O, 2044 kJ of heat are emitted. These ratios can be used to construct conversion factors between amounts of reactants or products and the quantity of heat exchanged. ...
Document
... Ozonolysis of Alkenes - oxidative cleavage of an alkene to carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones). The and -bonds of the alkene are broken and replaced with C=O double bonds. C=C of aryl rings, CN and C=O do not react with ozone, CC react very slowly with ozone ...
... Ozonolysis of Alkenes - oxidative cleavage of an alkene to carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones). The and -bonds of the alkene are broken and replaced with C=O double bonds. C=C of aryl rings, CN and C=O do not react with ozone, CC react very slowly with ozone ...
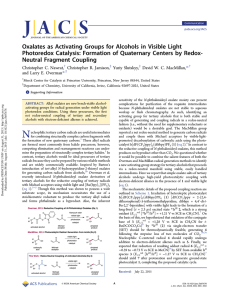
103. Oxalates as Activating Groups for Alcohols in Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis: Formation of Quaternary Centers by Redox-Neutral Fragment Coupling
... products were obtained with these substrates, and the product of trapping of the intermediate alkoxyacyl radical was also isolated (65 and 66). For more stabilized benzylic radicals, these side products were not observed; the yields remained moderate (68). ...
... products were obtained with these substrates, and the product of trapping of the intermediate alkoxyacyl radical was also isolated (65 and 66). For more stabilized benzylic radicals, these side products were not observed; the yields remained moderate (68). ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.