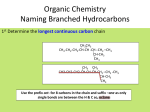
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry 2100 - Bonham Chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Chemistry 2100 Lecture 6 Carboxyl Derivatives In this chapter, we study three classes of compounds derived from carboxylic acids; anhydrides, esters, and amides. – Each is related to a carboxyl group by loss of H2O. O RCOH A carboxylic acid O O RCOCR' An anhydride -H2 O O O RC- OH H- OCR' O RCOR' An ester -H2 O O RCNH2 An amide -H2 O O O RC- OH H- OR' RC- OH H- NH 2 O R [ C Y acyl acetyl = Ac: R = CH3 ] Y = OH Cl O CO R' O R' NR2 carboxyl i c aci d aci d chloride anhydri de e ste r ami de Esters The functional group of an ester is a carbonyl group bonded to an -OR group. R may be alkyl or aryl. – Both IUPAC and common names of esters are derived from the names of the parent carboxylic acids. – Name the alkyl or aryl group bonded to oxygen first, followed by the name of the acid; replace the suffix -ic acid by -ate. – A cyclic ester is called a lactone. O CH3 COCH2 CH3 Ethyl ethanoate (Ethyl acetate) O O O O O Diethyl pentanedioate (Diethyl glutarate) O A five-membered lactone O R C O Y + H Z R C Z + H Y O R C O Y + H Z R C Z + H Y O R C O Y + H Z R C Z + H Y O R C O Y + H Z R C Z + H Y O R C O Y + H Z R C Z OR' + H Y O R C O Y + H Z OR' R C Z OR' + H Y O R C O OH Y + H Z OR' R C Z OR' + H Y O R C O OH Y + H Z OR' R C Z OR' + H OH Y Fischer esterification O R C O OH Y + H Z OR' H+ R C Z OR' + H OH Y Hydrolysis of Esters O CH3 COCH2 CH3 Eth yl acetate + H2 O H + O CH3 COH + CH3 CH2 OH Acetic acid Ethanol Saponification O H2 O CH3 COCH2 CH3+ N aOH heat Ethyl acetate Sodium hydroxide O CH3 CO - N a++ CH3 CH2 OH Sodium Ethanol acetate Properties of Esters ethyl butyrate pineapple octyl acetate orange O C OCH3 OH coumarin clover methyl salicylate methyl anthranilate NH NH22 wintergreen grape methyl anthranilate grape Triglycerides & Waxess O O CH 2 O C O CH (oleic) CH 2 O C O (myristic) C (linoleic) waxes Reaction with Amines • Esters react with ammonia and with 1° and 2° amines to form amides. O O OCH2 CH3 + N H3 Ethyl 2-phenyl acetate N H2 + CH3 CH2 OH 2-Phenylacetamide Amides The functional group of an amide is a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom. – To name an amide, drop the suffix -oic acid from the IUPAC name of the parent acid, or -ic acid from its common name, and add -amide. – If the amide nitrogen is also bonded to an alkyl or aryl group, name the group and show its location on nitrogen by N- ; two alkyl or aryl groups by N,N-di-. O CH3 CNH2 Acetamide (a 1° amide) O CH3 CNHCH3 N -Methylacetamide (a 2° amide) O HCN(CH3 ) 2 N ,N-D imethylformamide (a 3° amide) •• •• O R C • • R' •• R N R" •• O •• C R' N R" •• •• O R C • • R' •• R N R" •• O •• C R' N R" •• •• O R C • • R' •• R N R" •• O •• C R' N R" •• •• O R C • • R' •• R N R" •• O •• C R' N R" •• •• O R C • • R' •• R N R" •• O •• C R' N R" Amides A cyclic amide is called a lactam. O O b NH A four-membered lactam (a b-lactam) NH A seven-memb ered lactam – The penicillins are referred to as b-lactam antibiotics. HO The p enicillins differ in th e group bond ed to th e carbonyl carbon Theb-lactam rin g O N NH2 H O A moxicillin S N CH3 CH3 COOH Preparation of Amides • In principle, we can form an amide by treating a carboxylic acid with an amine and removing -OH from the acid and an -H from the amine. – In practice what occurs if the two are mixed is an acid-base reaction to form an ammonium salt. – If this salt is heated to a high enough temperature, water is eliminated and an amide forms. O CH 3 C-OH + H2 NCH2 CH 3 Acetic Ethanamine acid (Ethylamine) O + CH3 C-O H3 NCH2 CH3 An ammonium s alt h eat O CH 3 C-NHCH2 CH3 + H2 O An amid e Preparation of Amides • It is much more common, however, to prepare amides by treating an anhydride with an amine. O O CH3 C-O-CCH3 + H2 NCH2 CH3 Acetic anhdyride O O CH3 C-NHCH2 CH3 + CH3 COH An amide Anhydrides The functional group of an anhydride is two carbonyl groups bonded to the same oxygen. – The anhydride may be symmetrical (from two identical acyl groups), or mixed (from two different acyl groups). – To name an anhydride, drop the word "acid" from the name of the carboxylic acid from which the anhydride is derived and add the word "anhydride”. O O CH3 C-O-CCH3 Acetic an hydrid e Reaction with Alcohols Anhydrides react with alcohols and phenols to give an ester and a carboxylic acid. O O CH3 COCCH3 + HOCH2 CH3 Acetic anhydride Ethanol O O CH3 COCH 2 CH 3 + HOCCH3 Ethyl acetate Acetic acid Aspirin is prepared by the reaction of salicylic acid with acetic anhydride. COOH OH Salicylic acid + O O CH3 C- O-CCH3 Acetic anhyd rid e COOH OCCH 3 O Acetylsalicylic acid (Asp irin) + O CH3 C- OH Acetic acid Phosphoric Anhydrides The functional group of a phosphoric anhydride is two phosphoryl (P=O) groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. O O HO-P-O-P-OH OH OH D iphosph oric acid (Pyroph os phoric acid) O O O-P-O-P-OO- OD iphosph ate ion (Pyroph os phate ion) O O O HO-P-O-P-O-P-OH OH OH OH Triphosp horic acid O O O O-P-O-P-O-P-OO- O- OTriph os phate ion ATP Adenosine Triphosphate Polyamides Nylon-66 was the first purely synthetic fiber. – It is synthesized from two six-carbon monomers. remove H 2O H N O H N H OH + O H Hexanedioic acid 1,6-Hexanediamine (Adipic acid) (Hexamethyle nediami ne) HO heat - H2 O O O N H Nylon-66 (a polyamide) H N n Polyamides The polyaromatic amide known as Kevlar is made from an aromatic dicarboxylic acid and an aromatic diamine. remove H 2O O nHOC O COH H H heat + N N -H2 O H H 1,4-Benzen edicarboxylic 1,4-Benzen ediamine acid (p-Phen ylened iamin e) (Terep hthalic acid) O C O CNH NH Kevlar (a p olyaromatic amide) n Polyesters The first polyester involved polymerization of this diester and diol. remove CH 3 OH O OCH3 HO + CH3 O O Dimethyl terephthalate OH 1,2-Ethaned iol (Ethylene glycol) O heat -CH3 OH O O O n Poly(eth ylene tereph thalate) (D acron , Mylar) Polycarbonates Lexan, the most familiar polycarbonate, is formed by reaction between the disodium salt of bisphenol A and phosgene. remove N a+ ClO CH3 + Na-O O- Na+ + Cl CH3 D isodium salt of Bis phenol A Cl -NaCl Phosgen e O CH3 O CH3 Lexan (a p olycarbonate) O n