Exam only
... Hydrogen bonding is the force that is often responsible for many of the structural aspects of proteins. Hydrogen bonding allows many very large organic molecules to be soluble in water. Sugars are an example. Hydrogen bonding is the force that allows salts like sodium chloride to dissolve in ...
... Hydrogen bonding is the force that is often responsible for many of the structural aspects of proteins. Hydrogen bonding allows many very large organic molecules to be soluble in water. Sugars are an example. Hydrogen bonding is the force that allows salts like sodium chloride to dissolve in ...
Chemistry 3719L – Week 9 Reduction of Benzil with Sodium
... The use of metal hydride reagents (e.g. NaBH4 and LiAlH4) for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones is the most widely used method for conversion to primary and secondary alcohols respectively. This experiment will give you experience in using the milder NaBH4 reagent that readily converts the dike ...
... The use of metal hydride reagents (e.g. NaBH4 and LiAlH4) for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones is the most widely used method for conversion to primary and secondary alcohols respectively. This experiment will give you experience in using the milder NaBH4 reagent that readily converts the dike ...
Chemistry - Target Publications
... Molarity of the solution. [Given: Density of solution is 1.20 g mL−1 and molar mass of glucose is 180 g mol−1] iii. Resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 ohms. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductiv ...
... Molarity of the solution. [Given: Density of solution is 1.20 g mL−1 and molar mass of glucose is 180 g mol−1] iii. Resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 ohms. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductiv ...
orgchem rev integ odd numbers
... t-BuOK, t-BuOH – Bulky bases Bulky bases as catalysts follows Anti-Zaitsev’s Rule Anti-Zaitsev’s Rule – is an empirical rule for predicting the favored alkene products in elimination reactions. Attachment to the least substituted Carbon ...
... t-BuOK, t-BuOH – Bulky bases Bulky bases as catalysts follows Anti-Zaitsev’s Rule Anti-Zaitsev’s Rule – is an empirical rule for predicting the favored alkene products in elimination reactions. Attachment to the least substituted Carbon ...
Answer Key to Assignment #7
... i) Both hydrogens of acetylene can be removed by reaction with n-butyllithium to give dilithium acetylide – an ambident nucleophile. With this in mind, show how you would make the following molecule from acetylene and benzaldehyde. ...
... i) Both hydrogens of acetylene can be removed by reaction with n-butyllithium to give dilithium acetylide – an ambident nucleophile. With this in mind, show how you would make the following molecule from acetylene and benzaldehyde. ...
Functional Groups (13 Questions) File
... The compound with the formula CH3CH2OOCH2CH3 is a member of the _______ family of hydrocarbon derivatives. a) c) ...
... The compound with the formula CH3CH2OOCH2CH3 is a member of the _______ family of hydrocarbon derivatives. a) c) ...
Octenes from E1 versus E2 Eliminations
... Fill a 10 x 100 mm reaction tube to the 0.5 mL mark with 1-octanol (n-octyl alcohol) and insert a 1/2-inch stir bar. Add 5 drops of conc. sulfuric acid. While stirring, heat the reaction for 20 to 30 minutes. At first you will see water droplets and a cloudy liquid condensing on the walls of the rea ...
... Fill a 10 x 100 mm reaction tube to the 0.5 mL mark with 1-octanol (n-octyl alcohol) and insert a 1/2-inch stir bar. Add 5 drops of conc. sulfuric acid. While stirring, heat the reaction for 20 to 30 minutes. At first you will see water droplets and a cloudy liquid condensing on the walls of the rea ...
Organic Pathways
... liquids are separated by what can be considered to be a succession of simple distillations. • When the mixture of liquids is heated in the distillation flask, the vapours rise up the fractioning column. • These vapours contain a higher concentration of the more volatile component than the liquid in ...
... liquids are separated by what can be considered to be a succession of simple distillations. • When the mixture of liquids is heated in the distillation flask, the vapours rise up the fractioning column. • These vapours contain a higher concentration of the more volatile component than the liquid in ...
Ester
... You do not have to write a ‘purpose’ for this reaction—the reaction equation is considered the ‘purpose’. (you do not need to write the arrow pushing mechanism-just the reactants and products). Use the acid and alcohol that you chose in the reaction equation and clearly show the ester that they will ...
... You do not have to write a ‘purpose’ for this reaction—the reaction equation is considered the ‘purpose’. (you do not need to write the arrow pushing mechanism-just the reactants and products). Use the acid and alcohol that you chose in the reaction equation and clearly show the ester that they will ...
Chem 341 Review for Finals Key Reactions Mechanisms
... Chem 341 Review for Finals Reaction Types • RMgBr (Grignard Reagents) –Preparation from alkyl halides –Reactions with aldehydes, ketones, and esters • Nucleophilic Addition to Ketones – Irreversible additions: LiAlH4 RMgBr – Reversible additions: alcohols => hemiacetal & acetal – Addition-Eliminati ...
... Chem 341 Review for Finals Reaction Types • RMgBr (Grignard Reagents) –Preparation from alkyl halides –Reactions with aldehydes, ketones, and esters • Nucleophilic Addition to Ketones – Irreversible additions: LiAlH4 RMgBr – Reversible additions: alcohols => hemiacetal & acetal – Addition-Eliminati ...
CHEM 2412
... Nomenclature and drawing of alkynes; Physical properties of alkynes; Hybridization and bond lengths, scharacter; Acidity of terminal alkynes; Acetylide formation and reactions with alkyl halides and carbonyl compounds; Elimination reactions used to form alkynes (terminal/internal isomerization); Add ...
... Nomenclature and drawing of alkynes; Physical properties of alkynes; Hybridization and bond lengths, scharacter; Acidity of terminal alkynes; Acetylide formation and reactions with alkyl halides and carbonyl compounds; Elimination reactions used to form alkynes (terminal/internal isomerization); Add ...
4.6, 4.7 test - A
... The following reaction scheme shows the formation of two amines, K and L, from ...
... The following reaction scheme shows the formation of two amines, K and L, from ...
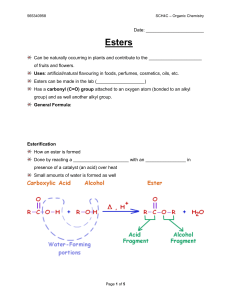
Esters - Mr. Lee`s Science
... Uses: artificial/natural flavouring in foods, perfumes, cosmetics, oils, etc. Esters can be made in the lab (___________________) Has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached to an oxygen atom (bonded to an alkyl group) and as well another alkyl group. General Formula: ...
... Uses: artificial/natural flavouring in foods, perfumes, cosmetics, oils, etc. Esters can be made in the lab (___________________) Has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached to an oxygen atom (bonded to an alkyl group) and as well another alkyl group. General Formula: ...
handout alkenes from alcohols
... This procedure has been adapted from the microscale procedure described in the third edition of Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments by Kenneth L. Williamson (Houghton Mifflin, Boston, 1999). ...
... This procedure has been adapted from the microscale procedure described in the third edition of Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments by Kenneth L. Williamson (Houghton Mifflin, Boston, 1999). ...
Amino acids - Boardworks
... Amino acids contain both amine (NH2) and carboxyl (COOH) functional groups. In alpha amino acids, these groups are attached to the same carbon atom. ...
... Amino acids contain both amine (NH2) and carboxyl (COOH) functional groups. In alpha amino acids, these groups are attached to the same carbon atom. ...
Chem 30CL - Lecture 1d - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • Chiral carboxylic acids and chiral amines are converted into diastereomeric salts that are separated by fractionated crystallization in a suitable solvent i.e., water, methanol, etc. • Chiral alcohols are resolved by converting them to (half) esters • Chiral aldehyde and ketones are converted into ...
... • Chiral carboxylic acids and chiral amines are converted into diastereomeric salts that are separated by fractionated crystallization in a suitable solvent i.e., water, methanol, etc. • Chiral alcohols are resolved by converting them to (half) esters • Chiral aldehyde and ketones are converted into ...
twelve important naval substances – bonding
... as fuels or solvents. Most organic molecules consist of a structural backbone of C-C single bonds and one or more functional groups. Functional groups are portions of an organic molecule where carbon has bonds to atoms other than carbon or hydrogen. ...
... as fuels or solvents. Most organic molecules consist of a structural backbone of C-C single bonds and one or more functional groups. Functional groups are portions of an organic molecule where carbon has bonds to atoms other than carbon or hydrogen. ...
File - TGHS Level 3 Chemistry
... pans, chloroform – CHCl3 – used as a solvent and in movies as an anaesthetic, CCl4 – solvent used in drycleaning fluid until it was found to ...
... pans, chloroform – CHCl3 – used as a solvent and in movies as an anaesthetic, CCl4 – solvent used in drycleaning fluid until it was found to ...
Organic Notes #5 - RX`ns - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... Dehydration of alcohols are also possible. The removal of the hydroxyl from one carbon and the hydrogen from another carbon creates an alkene and water. Oxidation -the conversion of an alcohol to a carboxylic acid or a ketone. Primary alcohols are converted to carboxylic acids because the hydroxide ...
... Dehydration of alcohols are also possible. The removal of the hydroxyl from one carbon and the hydrogen from another carbon creates an alkene and water. Oxidation -the conversion of an alcohol to a carboxylic acid or a ketone. Primary alcohols are converted to carboxylic acids because the hydroxide ...
General Chemistry (II) Chapter 1: Chemical Kinetic 1
... 4-1-2 Trend s in Radius, Density, Oxidation Number and Electronegativity of Transition Metals, 4-2 Study of Properties first series of Transiton Metals 4-3 Coordination Chemistry 4-3-1 Nomenclature of Coordination compounds 4-3-2 -1 Structural Isomerism 4-3-2-2 Stereoisomers 4-4 Bonding in Coordina ...
... 4-1-2 Trend s in Radius, Density, Oxidation Number and Electronegativity of Transition Metals, 4-2 Study of Properties first series of Transiton Metals 4-3 Coordination Chemistry 4-3-1 Nomenclature of Coordination compounds 4-3-2 -1 Structural Isomerism 4-3-2-2 Stereoisomers 4-4 Bonding in Coordina ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.