Study Guide
... bonds. 1 carbon with hydrogens on each of the 4 valance sites is called methane: METH=1 and alkANE = single bonds. 2 carbons with a double bond is ethane: ETH=2, alkENE = double bonds. See the table in the TeacherNotes. Each compound has different characteristics. Propane (3 carbons, single bonds) i ...
... bonds. 1 carbon with hydrogens on each of the 4 valance sites is called methane: METH=1 and alkANE = single bonds. 2 carbons with a double bond is ethane: ETH=2, alkENE = double bonds. See the table in the TeacherNotes. Each compound has different characteristics. Propane (3 carbons, single bonds) i ...
Chapter 16. Biological Reagents
... The synthesis of organic compounds in the laboratory requires methods that form new carbon-carbon bonds. Many of these reactions involve the formation of an enolate, a carbanion stabilized by an adjacent carbonyl group, and subsequent addition of the enolate nucleophile to the carbonyl function of a ...
... The synthesis of organic compounds in the laboratory requires methods that form new carbon-carbon bonds. Many of these reactions involve the formation of an enolate, a carbanion stabilized by an adjacent carbonyl group, and subsequent addition of the enolate nucleophile to the carbonyl function of a ...
Chapter 7
... Acid Catalyzed Dehydration of Alcohols • Heating most alcohols with a strong Acid causes the alcohol to lose the equivalent of a molecule of water (dehydrate) and form an alkene • Generic Reaction: • This reaction is an elimination and is favored at high temps • The most commonly used acids in labs ...
... Acid Catalyzed Dehydration of Alcohols • Heating most alcohols with a strong Acid causes the alcohol to lose the equivalent of a molecule of water (dehydrate) and form an alkene • Generic Reaction: • This reaction is an elimination and is favored at high temps • The most commonly used acids in labs ...
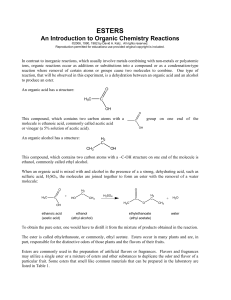
Esters - chymist.com
... An Introduction to Organic Chemistry Reactions ©2006, 1990, 1982 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Reproduction permitted for educationa use provided original copyright is included. ...
... An Introduction to Organic Chemistry Reactions ©2006, 1990, 1982 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Reproduction permitted for educationa use provided original copyright is included. ...
CHEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 4 April 15, 2003 Name
... (9 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following statements. Do not explain! • Fischer esterification occurs only in strongly basic conditions; • Amides are less reactive than acid chlorides but more reactive than esters; • Saponification is the process of base-catalyzed hydrolysis of esters; • L ...
... (9 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following statements. Do not explain! • Fischer esterification occurs only in strongly basic conditions; • Amides are less reactive than acid chlorides but more reactive than esters; • Saponification is the process of base-catalyzed hydrolysis of esters; • L ...
Chemistry 212 — Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2
... (b) Free phosphatidic acids are rare. Instead, the phosphoric acid moiety is usually esterified with another alcohol. The ester formed with the phosphatidic acid are the phosphatidyl derivatives. We learned about phosphatidylcholine, the ester of phosphatidic acid and choline. Now let’s look at a si ...
... (b) Free phosphatidic acids are rare. Instead, the phosphoric acid moiety is usually esterified with another alcohol. The ester formed with the phosphatidic acid are the phosphatidyl derivatives. We learned about phosphatidylcholine, the ester of phosphatidic acid and choline. Now let’s look at a si ...
Microsoft Word
... alcohol 33, which was then converted to the ketone-1,3-dithio acetal 34 (Scheme8). However, further oxidation of the dithio acetal 34 yielded the acid 35 in low yields and hence an alterate synthetic route was adopted. (Scheme-9) Figure In the scheme-9, allylic secondary alcohol 38, was prepared by ...
... alcohol 33, which was then converted to the ketone-1,3-dithio acetal 34 (Scheme8). However, further oxidation of the dithio acetal 34 yielded the acid 35 in low yields and hence an alterate synthetic route was adopted. (Scheme-9) Figure In the scheme-9, allylic secondary alcohol 38, was prepared by ...
Part B: Short Written Response - bourre-chem-11
... number of carbons. Use the data in the table below to state the pattern between the molecular formula and the boiling point of alcohols. (2 marks) ...
... number of carbons. Use the data in the table below to state the pattern between the molecular formula and the boiling point of alcohols. (2 marks) ...
Carboxylic Acid Structure and Chemistry
... conditions" nucleophiles can attack the acids carbonyl and displace the acid OH as water, or another good leaving group. Such is the case in esterification reactions performed under acidic conditions. In these reactions an acid is treated with an alcohol which serves as the nucleophile, and an acid ...
... conditions" nucleophiles can attack the acids carbonyl and displace the acid OH as water, or another good leaving group. Such is the case in esterification reactions performed under acidic conditions. In these reactions an acid is treated with an alcohol which serves as the nucleophile, and an acid ...
Topic 19 Assessed Homework - A
... State a reagent which could produce X from H2N(CH2)6NH2 and give a necessary condition to ensure that X is the major product. Reagent ............................................................................................. Condition .............................................................. ...
... State a reagent which could produce X from H2N(CH2)6NH2 and give a necessary condition to ensure that X is the major product. Reagent ............................................................................................. Condition .............................................................. ...
Chapter 9 Acids and Bases
... Acids react with metals for form H2 and a metal compound. The acid corrodes the metal and produces a residue. All acids contain hydrogen, but not everything that contains hydrogen is an acid. When an acid is mixed with water, acids ionize to produce hydrogen ions (H+). This ion is rapidly surrou ...
... Acids react with metals for form H2 and a metal compound. The acid corrodes the metal and produces a residue. All acids contain hydrogen, but not everything that contains hydrogen is an acid. When an acid is mixed with water, acids ionize to produce hydrogen ions (H+). This ion is rapidly surrou ...
1 - contentextra
... Pi (π) bond A bond formed by the sideways overlap of two p-orbitals. In a π bond the electron density is concentrated on either side of the internuclear axis. A π bond is weaker than a σ bond. Polyamide A polymer in which the monomer molecules are linked by amide bonds. Polydentate ligand A ligand t ...
... Pi (π) bond A bond formed by the sideways overlap of two p-orbitals. In a π bond the electron density is concentrated on either side of the internuclear axis. A π bond is weaker than a σ bond. Polyamide A polymer in which the monomer molecules are linked by amide bonds. Polydentate ligand A ligand t ...
Lab Reports File
... Scientific writing should be clear and organized. Say exactly what you mean as simply and accurately as you can. Be brief. Don't be verbose or stilted. However, do get used to the scientific terms commonly used to describe certain operations, e.g., refluxed, filtered, recrystallized, distilled, etc. ...
... Scientific writing should be clear and organized. Say exactly what you mean as simply and accurately as you can. Be brief. Don't be verbose or stilted. However, do get used to the scientific terms commonly used to describe certain operations, e.g., refluxed, filtered, recrystallized, distilled, etc. ...
From carb acid till end ch 4
... The production of an ester from the reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid is slow at 25°C. ...
... The production of an ester from the reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid is slow at 25°C. ...
Exp`t 70
... Guide. DO NOT ADD DICHLOROMETHANE, but instead analyze the pure liquid as a “neat” sample on the gas chromatograph. (Check the GC compendium in 206 W for GC conditions). In analyzing your results, consider that the carbocation can lose any of 6 primary hydrogen atoms, but only 2 secondary hydrogen a ...
... Guide. DO NOT ADD DICHLOROMETHANE, but instead analyze the pure liquid as a “neat” sample on the gas chromatograph. (Check the GC compendium in 206 W for GC conditions). In analyzing your results, consider that the carbocation can lose any of 6 primary hydrogen atoms, but only 2 secondary hydrogen a ...
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Epoxides
... • In this chapter, we will use HCl, HBr, HI, ZnCl2, PBr2, SOCl2, and R’SO2Cl/py to convert OH to a better LG. ...
... • In this chapter, we will use HCl, HBr, HI, ZnCl2, PBr2, SOCl2, and R’SO2Cl/py to convert OH to a better LG. ...
Synthesis and reactions of silicon containing cyclic a
... 19 and 20 were contaminated with the starting material and chromatographic methods were not suitable for separation. The yield of the reactions was determined by NMR spectral data. It may be worth noting that the halogen derivatives 17 and 18 can serve as useful substrates for metal mediated cross-c ...
... 19 and 20 were contaminated with the starting material and chromatographic methods were not suitable for separation. The yield of the reactions was determined by NMR spectral data. It may be worth noting that the halogen derivatives 17 and 18 can serve as useful substrates for metal mediated cross-c ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
... All acid derivatives absorb in the same range so NMR does not distinguish them from each other ...
... All acid derivatives absorb in the same range so NMR does not distinguish them from each other ...
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes – Properties and Synthesis
... The formation of the more stable alkene is the general rule (Zaitsev's rule) in the acid-catalyzed dehydration reactions of alcohols. ...
... The formation of the more stable alkene is the general rule (Zaitsev's rule) in the acid-catalyzed dehydration reactions of alcohols. ...
Ch 20 review - Organic Chemistry at CU Boulder
... Note that whatever R was, we’ve just added one carbon to it overall. This is a useful way of extending chains one carbon at a time. The only limitation is that R has to be compatible with Grignards – no alcohols or unprotected carbonyls, etc. 5) SN2 with a cyano group, followed by hydrolysis: This o ...
... Note that whatever R was, we’ve just added one carbon to it overall. This is a useful way of extending chains one carbon at a time. The only limitation is that R has to be compatible with Grignards – no alcohols or unprotected carbonyls, etc. 5) SN2 with a cyano group, followed by hydrolysis: This o ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.