10 Introduction to organic chemistry
... ethane, all the bonds are σ-bonds, so there is no centre of high-electron density. The propagation step of the photochemical substitution reaction with ethane involves the reaction of a bromine radical with an ethane molecule. This is a slow reaction. It is energetically unfavourable because of the ...
... ethane, all the bonds are σ-bonds, so there is no centre of high-electron density. The propagation step of the photochemical substitution reaction with ethane involves the reaction of a bromine radical with an ethane molecule. This is a slow reaction. It is energetically unfavourable because of the ...
Chapter 3 Properties of organic compounds
... substitution of alcohols is increased by heating the reaction mixture under reflux – this way the reaction mixture can be heated for a period of time without material (reactant, product or solvent) evaporating and being lost from the flask. Oxidation – using acidified KMnO4 or acidified K2Cr2O7. Pri ...
... substitution of alcohols is increased by heating the reaction mixture under reflux – this way the reaction mixture can be heated for a period of time without material (reactant, product or solvent) evaporating and being lost from the flask. Oxidation – using acidified KMnO4 or acidified K2Cr2O7. Pri ...
CHM 260 – Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
... 5. Understand the difference between elimination vs nucleophilic substitution reactions. Predict whether an alkyl halide will undergo elimination or substitution. 6. Name aldehydes/ketones based on their structures; draw aldehydes/ketones from their names. 7. Predict the products of reduction of ald ...
... 5. Understand the difference between elimination vs nucleophilic substitution reactions. Predict whether an alkyl halide will undergo elimination or substitution. 6. Name aldehydes/ketones based on their structures; draw aldehydes/ketones from their names. 7. Predict the products of reduction of ald ...
fulltext $(function(){PrimeFaces.cw("Tooltip","widget_formSmash_items_resultList_20_j_idt799_0_j_idt801",{id:"formSmash:items:resultList:20:j_idt799:0:j_idt801",widgetVar:"widget_formSmash_items_resultList_20_j_idt799_0_j_idt801",showEffect:"fade",hideEffect:"fade",target:"formSmash:items:resultList:20:j_idt799:0:fullText"});});
... alcohols and the desired N-monoalkylated products were isolated in excellent yields (Table 1, entries 113). Benzyl alcohol derivatives bearing electron-donating substituents in the meta or para positions on the aromatic rings as well as 2naphthylmethanol were well-tolerated (Entries 2, 3 and 5). Mo ...
... alcohols and the desired N-monoalkylated products were isolated in excellent yields (Table 1, entries 113). Benzyl alcohol derivatives bearing electron-donating substituents in the meta or para positions on the aromatic rings as well as 2naphthylmethanol were well-tolerated (Entries 2, 3 and 5). Mo ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... Know that “saturated” means “saturated with hydrogens” and describes alkanes. Know that alkenes, alkynes, and cyclic hydrocarbons are all “unsaturated.” State why unsaturated fats are better for you (the double bond makes them easier to digest and less likely to coat the inside of your arterie ...
... Know that “saturated” means “saturated with hydrogens” and describes alkanes. Know that alkenes, alkynes, and cyclic hydrocarbons are all “unsaturated.” State why unsaturated fats are better for you (the double bond makes them easier to digest and less likely to coat the inside of your arterie ...
carboxylic acids
... • Low molecular weight carboxylic acids are liquids at room temperature and have characteristically sharp or unpleasant odors. • The –COOH group is very polar. Hydrogen bonding between –COOH groups creates dimers (two identical molecules bonded together). ...
... • Low molecular weight carboxylic acids are liquids at room temperature and have characteristically sharp or unpleasant odors. • The –COOH group is very polar. Hydrogen bonding between –COOH groups creates dimers (two identical molecules bonded together). ...
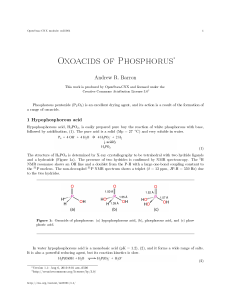
Oxoacids of Phosphorus
... spectroscopy demonstrates the presence of a single hydride by the presence of a doublet as a consequence of the phosphorous center being split by a single hydride (δ = 4 ppm, J P-H = 700 Hz). The 1 H NMR spectrum shows a doublet for the hydride and a single resonance of twice the intensity for the h ...
... spectroscopy demonstrates the presence of a single hydride by the presence of a doublet as a consequence of the phosphorous center being split by a single hydride (δ = 4 ppm, J P-H = 700 Hz). The 1 H NMR spectrum shows a doublet for the hydride and a single resonance of twice the intensity for the h ...
T. V. RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Enolates - kinetic vs thermodynamic - regiochemistry in unsymmetrical ketone enolates - how to prepare regiochemically pure enolates Other carbanions in synthesis - dithianes and corresponding sulfoxides, nitrocompound, cyanoalkanes Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for ch ...
... Enolates - kinetic vs thermodynamic - regiochemistry in unsymmetrical ketone enolates - how to prepare regiochemically pure enolates Other carbanions in synthesis - dithianes and corresponding sulfoxides, nitrocompound, cyanoalkanes Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for ch ...
730-2005 topics
... Enolates - kinetic vs thermodynamic - regiochemistry in unsymmetrical ketone enolates - how to prepare regiochemically pure enolates Other carbanions in synthesis - dithianes and corresponding sulfoxides, nitrocompound, cyanoalkanes Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for che ...
... Enolates - kinetic vs thermodynamic - regiochemistry in unsymmetrical ketone enolates - how to prepare regiochemically pure enolates Other carbanions in synthesis - dithianes and corresponding sulfoxides, nitrocompound, cyanoalkanes Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for che ...
Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions
... obtained from the addition of an unsymmetrical reagent such as H-Br, H-Cl, or H-OH to an alkene or alkyne is the one obtained when the H atom of the reagent is added to the C atom of the multiple bond that already has the greater number of H atoms. “The rich get richer” ...
... obtained from the addition of an unsymmetrical reagent such as H-Br, H-Cl, or H-OH to an alkene or alkyne is the one obtained when the H atom of the reagent is added to the C atom of the multiple bond that already has the greater number of H atoms. “The rich get richer” ...
Organic Reactions Summary
... Alkynes: Same as alkenes, but require 2 moles of the 2 column to fully saturate the triple bond. ...
... Alkynes: Same as alkenes, but require 2 moles of the 2 column to fully saturate the triple bond. ...
ppt
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
22 Acyl Substn
... e) Nitriles are different, as no leaving group is attached to electrophilic C. Nitriles do addition reactions that are analogous to the addition reactions of aldehydes and ketones. After protonation, an imine is obtained. This initial product is usually converted to other compounds by tautomerizatio ...
... e) Nitriles are different, as no leaving group is attached to electrophilic C. Nitriles do addition reactions that are analogous to the addition reactions of aldehydes and ketones. After protonation, an imine is obtained. This initial product is usually converted to other compounds by tautomerizatio ...
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... Hydrolysis of Nitriles • Hot acid or base yields carboxylic acids • Conversion of an alkyl halide to a nitrile (with cyanide ion) followed by hydrolysis produces a carboxylic acid with one more carbon (RBr RCN RCO2H) • Best with primary halides because elimination reactions occur with secondar ...
... Hydrolysis of Nitriles • Hot acid or base yields carboxylic acids • Conversion of an alkyl halide to a nitrile (with cyanide ion) followed by hydrolysis produces a carboxylic acid with one more carbon (RBr RCN RCO2H) • Best with primary halides because elimination reactions occur with secondar ...
Handout
... 16. What is the name of the bond indicated by the arrow in the lipid above? 17. What type of fatty acid is shown in the lipid above? 18. How would a polyunsaturated fatty acid differ? 19. How would a saturated fatty acid differ? 20. If the lipid above was a triglyceride, how many fatty acids would b ...
... 16. What is the name of the bond indicated by the arrow in the lipid above? 17. What type of fatty acid is shown in the lipid above? 18. How would a polyunsaturated fatty acid differ? 19. How would a saturated fatty acid differ? 20. If the lipid above was a triglyceride, how many fatty acids would b ...
Oxidation of Cyclohexanol to Cyclohexanone
... You are required to calculate a theoretical and a percent yield for this experiment. For instructions and examples on how to do this, see the examples in the Percent Yield Instruction sheet. Note that one of the starting materials was added as a neat liquid, the other material was added as an aqueou ...
... You are required to calculate a theoretical and a percent yield for this experiment. For instructions and examples on how to do this, see the examples in the Percent Yield Instruction sheet. Note that one of the starting materials was added as a neat liquid, the other material was added as an aqueou ...
Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Subst’n Acid Derivatives and their Names - Acid Halides have a Cl or Br instead of OH. Replace “ic acid” with “yl halide”, such as propionyl chloride (a common name) and propanoyl bromide (a systematic name). Replace “carboxylic acid” with “carbonyl hali ...
... Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Subst’n Acid Derivatives and their Names - Acid Halides have a Cl or Br instead of OH. Replace “ic acid” with “yl halide”, such as propionyl chloride (a common name) and propanoyl bromide (a systematic name). Replace “carboxylic acid” with “carbonyl hali ...
File
... • Soaps are salts of carboxylic acids that have many C atoms in a long hydrocarbon chain. • A soap molecule has two parts: 1. The ionic end is called the polar head. ...
... • Soaps are salts of carboxylic acids that have many C atoms in a long hydrocarbon chain. • A soap molecule has two parts: 1. The ionic end is called the polar head. ...
Chapter 6- Proteins FON 241 Principles of Human Nutrition What
... Hydrolysis reactions Peptidase enzymes Protein Quality Digestibility/Score – amino acid composition High quality proteins Roles of Proteins Growth and maintenance Enzymes Hormones Regulators of fluid balance Acid-base regulators Revised August 2015 ...
... Hydrolysis reactions Peptidase enzymes Protein Quality Digestibility/Score – amino acid composition High quality proteins Roles of Proteins Growth and maintenance Enzymes Hormones Regulators of fluid balance Acid-base regulators Revised August 2015 ...
Ch 26 C-C bond formation
... carbon double bond, are prepared by hydroboration using catecholborane, a commercially available reagent. • Hydroboration adds H and B in a syn fashion to form a trans vinylborane. • With terminal alkynes, hydroboration always places the boron atom on the less substituted terminal carbon. ...
... carbon double bond, are prepared by hydroboration using catecholborane, a commercially available reagent. • Hydroboration adds H and B in a syn fashion to form a trans vinylborane. • With terminal alkynes, hydroboration always places the boron atom on the less substituted terminal carbon. ...
Test 3 Test Skills/Competencies
... f. Amines (reversible aminol and imine formation, including cyclic aminols and imines, and the reverse reaction involving imine hydrolysis) Mechanisms: Be able to draw mechanisms for carbonyl reactions listed above, including the reverse reaction, including those involving rings. Major mechanisms in ...
... f. Amines (reversible aminol and imine formation, including cyclic aminols and imines, and the reverse reaction involving imine hydrolysis) Mechanisms: Be able to draw mechanisms for carbonyl reactions listed above, including the reverse reaction, including those involving rings. Major mechanisms in ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.