Organic Chemistry
... Fats are important to our body, they provide padding, energy storage, and are essential for our nervous system; there are also several essential vitamins that are fat soluble (vit. A, D, E, and K) Fats are known as triglycerides which are made up of 3 fatty acids and a glycerol molecule. They’re cal ...
... Fats are important to our body, they provide padding, energy storage, and are essential for our nervous system; there are also several essential vitamins that are fat soluble (vit. A, D, E, and K) Fats are known as triglycerides which are made up of 3 fatty acids and a glycerol molecule. They’re cal ...
Physical Properties and Acidity of Carboxylic Acids
... ten times weaker an acid than formic acid (first two entries in the second row), confirming the electron donating character of an alkyl group relative to hydrogen, as noted earlier in a discussion of carbocation stability. Electronegative substituents increase acidity by inductive electron withdrawa ...
... ten times weaker an acid than formic acid (first two entries in the second row), confirming the electron donating character of an alkyl group relative to hydrogen, as noted earlier in a discussion of carbocation stability. Electronegative substituents increase acidity by inductive electron withdrawa ...
Derivatives of carboxylic acids - amides, acid anhydrides and nitriles
... In every example of this kind, the -OH group will be on the number 2 carbon atom - the one next to the CN group. The reaction isn't normally done using hydrogen cyanide itself, because this is an extremely poisonous gas. Instead, the aldehyde or ketone is mixed with a solution of sodium or potassium ...
... In every example of this kind, the -OH group will be on the number 2 carbon atom - the one next to the CN group. The reaction isn't normally done using hydrogen cyanide itself, because this is an extremely poisonous gas. Instead, the aldehyde or ketone is mixed with a solution of sodium or potassium ...
reduction of ketones and imines with CaH2/ZnX2 in the presence of
... meso-hydrobenzoin exclusively (eq ...
... meso-hydrobenzoin exclusively (eq ...
Carboxylic Acid Nomenclature
... NMR: The -CO2H proton is a broad singlet near ~12. When D2O is added to the sample the -CO2H proton is replaced by D causing the resonance to disappear (same for alcohols). The -CO2H proton is often not observed. 1H ...
... NMR: The -CO2H proton is a broad singlet near ~12. When D2O is added to the sample the -CO2H proton is replaced by D causing the resonance to disappear (same for alcohols). The -CO2H proton is often not observed. 1H ...
Honors Biology - LangdonBiology.org
... amino acids. Humans have lost the ability to make these amino acids themselves, and must eat other life forms to get them. List the essential amino acids. You may have to use other resources to find the answer to this question. The essential amino acids for humans are tryptophan, methionine, threoni ...
... amino acids. Humans have lost the ability to make these amino acids themselves, and must eat other life forms to get them. List the essential amino acids. You may have to use other resources to find the answer to this question. The essential amino acids for humans are tryptophan, methionine, threoni ...
Regiochemistry of Eliminations
... Regiochemistry of Eliminations: Formation of a Cycloalkene Mixture Study Questions 1) Show the mechanism for the formation of each of the three products expected in this experiment. Answer: ...
... Regiochemistry of Eliminations: Formation of a Cycloalkene Mixture Study Questions 1) Show the mechanism for the formation of each of the three products expected in this experiment. Answer: ...
The Formation of 2,2,4-Trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,5
... Scheme 2 shows the proposed reaction mechanism for the formation of the benzodiazepine. It is proposed that the initial step is the attack of the carbonyl carbon of acetone by the lone pair of electrons on the amino group. Due to the difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the ox ...
... Scheme 2 shows the proposed reaction mechanism for the formation of the benzodiazepine. It is proposed that the initial step is the attack of the carbonyl carbon of acetone by the lone pair of electrons on the amino group. Due to the difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the ox ...
Chapter 07
... • The functional group of carboxylic acids consists of a C=O with -OH bonded to the same carbon. • Carboxyl group is usually written -COOH. • Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to COOH. • Aromatic acids have an aryl group. • Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids. ...
... • The functional group of carboxylic acids consists of a C=O with -OH bonded to the same carbon. • Carboxyl group is usually written -COOH. • Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to COOH. • Aromatic acids have an aryl group. • Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids. ...
Part I Power generation in fuel cells
... feasibility of the corrosion process. The iron half reaction coupled to a half reaction such as described above produces what is known as a corrosion cell, with the corrosion process being the cell reaction. Seeing corrosion in electrolytic terms allows the understanding of the inhibition of corrosi ...
... feasibility of the corrosion process. The iron half reaction coupled to a half reaction such as described above produces what is known as a corrosion cell, with the corrosion process being the cell reaction. Seeing corrosion in electrolytic terms allows the understanding of the inhibition of corrosi ...
Spring 2008 Final Exam Key
... 7. Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. 8. A(n) mole is the amount of substance that contains the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 g of carbon-12. 9. A(n) combustion reaction is a rapid oxidation accompanied by heat and usual ...
... 7. Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. 8. A(n) mole is the amount of substance that contains the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 g of carbon-12. 9. A(n) combustion reaction is a rapid oxidation accompanied by heat and usual ...
1. 4-methyl-4-octanol oxidizes to form a) 4-methyl-4
... 20. Aldehydes ____ soluble in water. Carboxylic acids ______ soluble in water a) are, are not b) are not, are not c) are, are d) are not, are 21.Of the following, which would have the highest boiling point? a) propane b) propanal c) propanoic acid d) methyl ethyl ether. 22. Of the following aldehyd ...
... 20. Aldehydes ____ soluble in water. Carboxylic acids ______ soluble in water a) are, are not b) are not, are not c) are, are d) are not, are 21.Of the following, which would have the highest boiling point? a) propane b) propanal c) propanoic acid d) methyl ethyl ether. 22. Of the following aldehyd ...
O V O O RO OH t-BuOOH, CH2Cl2, Ti(OPr-i)4(cat), 20 oC (L)
... See Kolb, H.C.; VanNieuwenzhe, M. S; Sharpless, K. B. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2483. Recall that alkenes can be converted to 1,2- (vic-) diols by the use of OsO4, followed by a workup that breaks up the osmate ester. It has been known for many years that pyridine accelerates the rate of this reaction; s ...
... See Kolb, H.C.; VanNieuwenzhe, M. S; Sharpless, K. B. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2483. Recall that alkenes can be converted to 1,2- (vic-) diols by the use of OsO4, followed by a workup that breaks up the osmate ester. It has been known for many years that pyridine accelerates the rate of this reaction; s ...
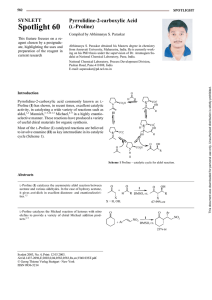
Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid (l
... catalyzes asymmetric the three component coupling involving Mannich reaction of acetone aldehydes and aryl amines to give β-amino ketones. In case of hydoxyacetone it gives α-hydroxy β-amino ketones in good to excellent ee. This reaction complements the Sharpless asymmetric aminohydroxylation.3–5,10 ...
... catalyzes asymmetric the three component coupling involving Mannich reaction of acetone aldehydes and aryl amines to give β-amino ketones. In case of hydoxyacetone it gives α-hydroxy β-amino ketones in good to excellent ee. This reaction complements the Sharpless asymmetric aminohydroxylation.3–5,10 ...
Reductive etherification of substituted cyclohexanones with
... remarkably shape selective reductive etherification of cyclohexanones with bulky substituents at the 4-position, employing secondary alcohols as reductants. Zeolite MCM-22 has recently been introduced as a unique biporous zeolite.1 It has been shown that it contains two independent pore systems,2,3 ...
... remarkably shape selective reductive etherification of cyclohexanones with bulky substituents at the 4-position, employing secondary alcohols as reductants. Zeolite MCM-22 has recently been introduced as a unique biporous zeolite.1 It has been shown that it contains two independent pore systems,2,3 ...
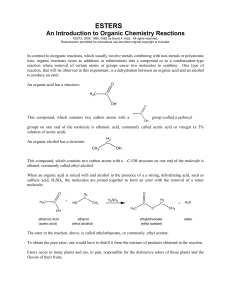
Slide 1
... the acid group modified to end in –oate or -ate Esters have strong, fragrant aromas and are the cause of the odors and flavors of pineapple, banana, wintergreen and oranges. Ex. The smell of pineapples is due to ethyl butyrate ethanol + butanoic acid water (alcohol) ...
... the acid group modified to end in –oate or -ate Esters have strong, fragrant aromas and are the cause of the odors and flavors of pineapple, banana, wintergreen and oranges. Ex. The smell of pineapples is due to ethyl butyrate ethanol + butanoic acid water (alcohol) ...
SPRING 2002 Test 2 1. Which of the following statements is
... CH3COOC2H5 + H2O => CH3C(OH)OC2H5+ + OHCH3C(OH)OC2H5+ => CH3COOH + C2H5+ C2H5+ + OH- => C2H5OH A.Rate = k[CH3COOC2H5][H2O]2 B.Rate = k[C2H5OH] C.Rate = k[CH3COOH] D.Rate = k[CH3COOC2H5] E.Rate = k[CH3COOC2H5][H2O] Ans. E ...
... CH3COOC2H5 + H2O => CH3C(OH)OC2H5+ + OHCH3C(OH)OC2H5+ => CH3COOH + C2H5+ C2H5+ + OH- => C2H5OH A.Rate = k[CH3COOC2H5][H2O]2 B.Rate = k[C2H5OH] C.Rate = k[CH3COOH] D.Rate = k[CH3COOC2H5] E.Rate = k[CH3COOC2H5][H2O] Ans. E ...
Esters - chymist.com
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.