CHE 101– Chapter 8 – Study Guide Terms: Products, reactants
... Terms: Products, reactants, chemical equation vs. balanced equation, activation energy, combination reaction, displacement reactions (single and double), decomposition reactions, exothermic vs. endothermic, heat of reaction, activation energy. 1. Things you should know/memorize for the exam. They wi ...
... Terms: Products, reactants, chemical equation vs. balanced equation, activation energy, combination reaction, displacement reactions (single and double), decomposition reactions, exothermic vs. endothermic, heat of reaction, activation energy. 1. Things you should know/memorize for the exam. They wi ...
lec-2- 211(ES +Add)
... HX which can donate a proton, H2O should be able to add to alkenes in the same way as HBr, for example, resulting in the hydration of an alkene. However, for the addition of H2O to alkenes to occur acid catalysts are required. ...
... HX which can donate a proton, H2O should be able to add to alkenes in the same way as HBr, for example, resulting in the hydration of an alkene. However, for the addition of H2O to alkenes to occur acid catalysts are required. ...
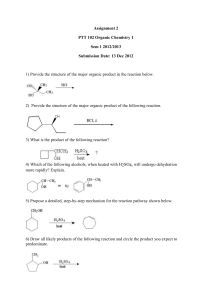
Assignment 2 Group A and B
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
10.4b Organic Practice Test Version 2
... 11. When Reactions A, B, and C are classified according to the key given in Chart 1, the number sequence that would correspond to ABC is ___, ___, ___. 12. When Reactions D, E, and F are classified according to the key given in Chart 1, the number sequence that would correspond to DEF is ___, ___, _ ...
... 11. When Reactions A, B, and C are classified according to the key given in Chart 1, the number sequence that would correspond to ABC is ___, ___, ___. 12. When Reactions D, E, and F are classified according to the key given in Chart 1, the number sequence that would correspond to DEF is ___, ___, _ ...
CHE 312 Exam III Review Sheet - Saint Leo University Faculty
... Explain why an aromatic molecule like benzene reacts differently than the corresponding alkene (actually a –triene)? ...
... Explain why an aromatic molecule like benzene reacts differently than the corresponding alkene (actually a –triene)? ...
슬라이드 1
... When secondary Grignard reagents are used, the coupling product sometimes is derived from the corresponding primary alkyl group. This transformation can occur by reversible formation. ...
... When secondary Grignard reagents are used, the coupling product sometimes is derived from the corresponding primary alkyl group. This transformation can occur by reversible formation. ...
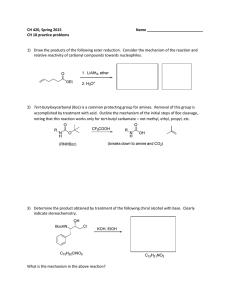
CH 420, Spring 2015 Name ___________________________ CH 18 practice problems
... 7) Rank the following compounds according to their relative acidity: cyclohexanol, phenol, pmethoxyphenol, p-nitrophenol. ...
... 7) Rank the following compounds according to their relative acidity: cyclohexanol, phenol, pmethoxyphenol, p-nitrophenol. ...
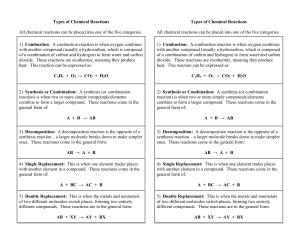
PowerPoint - Types of Chemical Reactions
... Pb(NO3)2(aq) + BaCl2(aq) FeCl3(aq) + NaOH(aq) H2SO4(aq) + NaOH(aq) ...
... Pb(NO3)2(aq) + BaCl2(aq) FeCl3(aq) + NaOH(aq) H2SO4(aq) + NaOH(aq) ...
CHE 322
... conditions, to make the indicated large compound? In each case show the reaction that makes the C-C or C-O bond that links the pieces. All three must be different kinds of reactions. [Caution: parts of some reaction partners are missing in the given products due to replacement or subsequent reaction ...
... conditions, to make the indicated large compound? In each case show the reaction that makes the C-C or C-O bond that links the pieces. All three must be different kinds of reactions. [Caution: parts of some reaction partners are missing in the given products due to replacement or subsequent reaction ...
Organic Reactions 2.1- 2.3 - mccormack-sch4u-2013
... 4) OXIDATION & 5) REDUCTION REACTIONS • Change in the number of H or O atoms bonded to C • Always occur together • One reactant is oxidized while the other is reduced • For now, lets focus on reactant only… ...
... 4) OXIDATION & 5) REDUCTION REACTIONS • Change in the number of H or O atoms bonded to C • Always occur together • One reactant is oxidized while the other is reduced • For now, lets focus on reactant only… ...
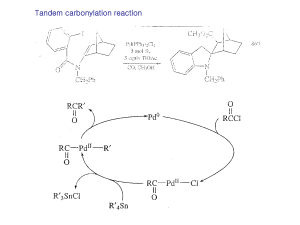
... Johnson Matthey have published an informative 82-page brochure, “The Catalyst Technical Handbook”, which covers the use of catalysts for chemical reactions important in industrial synthesis. The handbook recommends platinum group metal homogeneous, heterogeneous and FibreCatm anchored homogeneous ca ...
chapter 2: reactions of organic compounds
... 4) OXIDATION & 5) REDUCTION REACTIONS • Change in the number of H or O atoms bonded to C • Always occur together • One reactant is oxidized while the other is reduced • For now, lets focus on reactant only… ...
... 4) OXIDATION & 5) REDUCTION REACTIONS • Change in the number of H or O atoms bonded to C • Always occur together • One reactant is oxidized while the other is reduced • For now, lets focus on reactant only… ...
Syllabus
... There will be 12 homework assignments, a midterm and a final. All are given on a take-home basis. If you have any question about a problem before starting to work, you are strongly encouraged to discuss the matter with the professor or fellow students. That is, students are encouraged to discuss and ...
... There will be 12 homework assignments, a midterm and a final. All are given on a take-home basis. If you have any question about a problem before starting to work, you are strongly encouraged to discuss the matter with the professor or fellow students. That is, students are encouraged to discuss and ...
Nugget
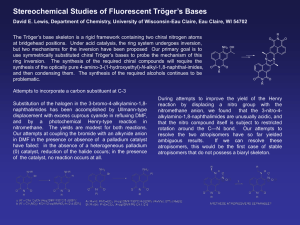
... The Tröger’s base skeleton is a rigid framework containing two chiral nitrogen atoms at bridgehead positions. Under acid catalysis, the ring system undergoes inversion, but two mechanisms for the inversion have been proposed Our primary goal is to use symmetrically substituted chiral Tröger’s bases ...
... The Tröger’s base skeleton is a rigid framework containing two chiral nitrogen atoms at bridgehead positions. Under acid catalysis, the ring system undergoes inversion, but two mechanisms for the inversion have been proposed Our primary goal is to use symmetrically substituted chiral Tröger’s bases ...
Organic Reactions 1
... C3H4 + 2H-H => C3H8 propyne + 2H-H => propane b) Halogenation (with Br2 or Cl2) Halides also have the ability to add halogens to the carbons of double or triple bonds creating organic halides. Example: H H H H ...
... C3H4 + 2H-H => C3H8 propyne + 2H-H => propane b) Halogenation (with Br2 or Cl2) Halides also have the ability to add halogens to the carbons of double or triple bonds creating organic halides. Example: H H H H ...
+ Y
... cis addition – both groups attach to the same side of the double bond trans addition –groups attach to the opposite side of the double bond ...
... cis addition – both groups attach to the same side of the double bond trans addition –groups attach to the opposite side of the double bond ...
Chem 2641 Chapter 5 Understanding Organic Reactions I. Writing
... A. A radical is a neutral but highly reactive species because it requires another electron to fulfill its octet. B. Examples ...
... A. A radical is a neutral but highly reactive species because it requires another electron to fulfill its octet. B. Examples ...
Unit 3 Goals - kimscience.com
... o complete and balance combustion reactions of organic molecules containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and explain the reaction in terms of bonds breaking and forming, enthalpy, and entropy change. o distinguish between complete and incomplete combustion in terms of reaction conditions, resulting ...
... o complete and balance combustion reactions of organic molecules containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and explain the reaction in terms of bonds breaking and forming, enthalpy, and entropy change. o distinguish between complete and incomplete combustion in terms of reaction conditions, resulting ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
Combustion, Addition and Elimination Objective Combustion Example
... is weaker than the single bond, this bond can break and then we have free bonding electrons where another element or functional group can be added. In general: ...
... is weaker than the single bond, this bond can break and then we have free bonding electrons where another element or functional group can be added. In general: ...
Ene reaction

The ene reaction (also known as the Alder-ene reaction) is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen (the ene) and a compound containing a multiple bond (the enophile), in order to form a new σ-bond with migration of the ene double bond and 1,5 hydrogen shift. The product is a substituted alkene with the double bond shifted to the allylic position.This transformation is a group transfer pericyclic reaction, and therefore, usually requires highly activated substrates and/or high temperatures. Nonetheless, the reaction is compatible with a wide variety of functional groups that can be appended to the ene and enophile moieties. Also,many useful Lewis acid-catalyzed ene reactions have been developed which can afford high yields and selectivities at significantly lower temperatures, making the ene reaction a useful C–C forming tool for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products.