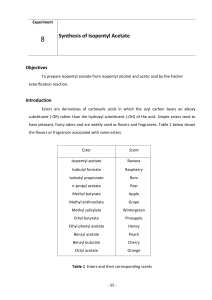
PowerPoint **
... Claisen condensation: An ester enolate is condensed with a ketone, aldehyde, or ester. ...
... Claisen condensation: An ester enolate is condensed with a ketone, aldehyde, or ester. ...
Weekly Review Lecture
... 1) Is each of the compounds below aromatic, antiaromatic, or non-aromatic? ...
... 1) Is each of the compounds below aromatic, antiaromatic, or non-aromatic? ...
Chapter 11: Reactions at an sp3 Hybridized Carbon III
... • In this case, however, the stability of tertiary carbocation which results from H– shifting and substituting for CH3OH makes this reaction work with HCl • If tertiary carbocations can be formed then HCl is strong enough to cleave ethers ...
... • In this case, however, the stability of tertiary carbocation which results from H– shifting and substituting for CH3OH makes this reaction work with HCl • If tertiary carbocations can be formed then HCl is strong enough to cleave ethers ...
Document
... acid is transferred to the alcohol. Acid chlorides and anhydrides also serve as acylating agents. Because acid chlorides and anhydrides contain good leaving groups, these compounds are very reactive toward nucleophilic substitution by an alcohol, as shown in Equations 7-8. ...
... acid is transferred to the alcohol. Acid chlorides and anhydrides also serve as acylating agents. Because acid chlorides and anhydrides contain good leaving groups, these compounds are very reactive toward nucleophilic substitution by an alcohol, as shown in Equations 7-8. ...
Catalysis Web Pages for Pre-University
... The traditional example of catalysis in the manufacture of another of the world’s bulk chemicals is the Contact process for the manufacture of sulfuric acid. It used to be said that one measure of a country’s wealth was its output of sulfuric acid. In the three step process sulfur, or a sulfide is r ...
... The traditional example of catalysis in the manufacture of another of the world’s bulk chemicals is the Contact process for the manufacture of sulfuric acid. It used to be said that one measure of a country’s wealth was its output of sulfuric acid. In the three step process sulfur, or a sulfide is r ...
Slide 1
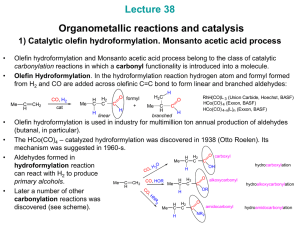
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
U. of Kentucky Chemistry 535 Synthetic Organic Chemistry Spring
... reduction of propargyl alcohols, C-C bond formation with alkyne anions. trans-selectivity with dissolving metal reduction. Now put it all together or devise your own approach. Remember, retrosyntheses use synthons. ...
... reduction of propargyl alcohols, C-C bond formation with alkyne anions. trans-selectivity with dissolving metal reduction. Now put it all together or devise your own approach. Remember, retrosyntheses use synthons. ...
Dehydration notes
... Dehydration of alcohols is … Acid catalyzed – creates a good leaving group (i.e. water) Carbocation intermediate formation. First two steps of the mechanism at the same as for SN1. Carbocation will rearrange for increased stability, if possible. 5. Protons can be removed from any adjacent position ...
... Dehydration of alcohols is … Acid catalyzed – creates a good leaving group (i.e. water) Carbocation intermediate formation. First two steps of the mechanism at the same as for SN1. Carbocation will rearrange for increased stability, if possible. 5. Protons can be removed from any adjacent position ...
chapter 8 lecture
... • Because conformation B has two different axial hydrogens, labeled Ha and Hb, E2 reaction occurs in two different directions to afford two alkenes. • The major product contains the more stable trisubstituted double bond, as predicted by the Zaitsev ...
... • Because conformation B has two different axial hydrogens, labeled Ha and Hb, E2 reaction occurs in two different directions to afford two alkenes. • The major product contains the more stable trisubstituted double bond, as predicted by the Zaitsev ...
Chapter 20 Amines-part 2
... è Primary and secondary amines undergo N-oxidation, but useful products are not obtained because of side-reactions è Tertiary amines undergo clean N-oxidation ...
... è Primary and secondary amines undergo N-oxidation, but useful products are not obtained because of side-reactions è Tertiary amines undergo clean N-oxidation ...
Chapter 16. Biological Reagents
... carboxylic acids is the reaction of an alcohol with an anhydride to form an ester. Acetic anhydride, which is a dehydrated form of acetic acid, is considered a high energy molecule because it is ready to react with hydroxyl functions and return to acetic acid. Thus the reaction occurs readily in the ...
... carboxylic acids is the reaction of an alcohol with an anhydride to form an ester. Acetic anhydride, which is a dehydrated form of acetic acid, is considered a high energy molecule because it is ready to react with hydroxyl functions and return to acetic acid. Thus the reaction occurs readily in the ...
Lab B
... the same phase, and although there are common examples of such processes in organic chemistry (e.g. acid catalysis), this experiment introduces transition-metal-catalyzed reactions. Transition-metal based homogeneous catalysts are often inorganic or organometallic compounds that can coordinate to th ...
... the same phase, and although there are common examples of such processes in organic chemistry (e.g. acid catalysis), this experiment introduces transition-metal-catalyzed reactions. Transition-metal based homogeneous catalysts are often inorganic or organometallic compounds that can coordinate to th ...
CH402 Asymmetric catalytic reactions Prof M. Wills
... reaction to one face of a substrate and release the product: Catalyst recycled ...
... reaction to one face of a substrate and release the product: Catalyst recycled ...
Organic Reactions
... b. Diatomic gas has two atoms – both add to opposite sides of the double bond (and opposite sides of the molecule) c. Uses: Chlorine + ethane 1,2-dichloroethane: used as starting material for PVC d. Uses: Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddi ...
... b. Diatomic gas has two atoms – both add to opposite sides of the double bond (and opposite sides of the molecule) c. Uses: Chlorine + ethane 1,2-dichloroethane: used as starting material for PVC d. Uses: Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddi ...
cycloadditions with singlet oxygen
... reaction pathway. Proceeding from the diradical to the dioxetane product was predicted to be lower in energy. However, these calculations have only been performed on simple systems and might not be representative of the reactivity of larger compounds. Thus far, mechanistic experiments have not been ...
... reaction pathway. Proceeding from the diradical to the dioxetane product was predicted to be lower in energy. However, these calculations have only been performed on simple systems and might not be representative of the reactivity of larger compounds. Thus far, mechanistic experiments have not been ...
Combining transition metal catalysis and organocatalysis
... a novel class of metal Lewis acid-enamine bifunctional catalysts with the intention to bridge more traditional transition-metal catalysis with the newly established prosperous area of organocatalysis the Challenging Problem the acid-base self-quenching reaction leading to catalyst inactivation •fine ...
... a novel class of metal Lewis acid-enamine bifunctional catalysts with the intention to bridge more traditional transition-metal catalysis with the newly established prosperous area of organocatalysis the Challenging Problem the acid-base self-quenching reaction leading to catalyst inactivation •fine ...
CH 3 Br + Nu
... A) it is a two-step process and has the same first step as a SN1 mechanism B) it involves the formation of the carbocation from elimination of a good leaving group C) a common competing reaction is rearrangement of a less stable carbocation to a more stable carbocation D) the loss of a proton by the ...
... A) it is a two-step process and has the same first step as a SN1 mechanism B) it involves the formation of the carbocation from elimination of a good leaving group C) a common competing reaction is rearrangement of a less stable carbocation to a more stable carbocation D) the loss of a proton by the ...
AlCl3 in modern chemistry of polyfluoroarenes
... proceeds in a different way in comparison with above mentioned examples [17,18]. The substitution of hydrogen atoms for fluorine excludes the reaction of polychloroalkylation of the aromatic ring. Obviously, the transformation scheme includes the attack of donor heteroatom of the functional group by ...
... proceeds in a different way in comparison with above mentioned examples [17,18]. The substitution of hydrogen atoms for fluorine excludes the reaction of polychloroalkylation of the aromatic ring. Obviously, the transformation scheme includes the attack of donor heteroatom of the functional group by ...
Study Guide for Exam 4 Chapter 17
... Know the basic terms, especially those discussed in class and in bold face print in the text From their structural or line-angle formulas, write IUPAC names for aldehydes and ketones. Describe the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones in terms of how their intermolecular forces determin ...
... Know the basic terms, especially those discussed in class and in bold face print in the text From their structural or line-angle formulas, write IUPAC names for aldehydes and ketones. Describe the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones in terms of how their intermolecular forces determin ...
CHM 222 Organic Chemistry II
... NACC and the Alabama State Board of Education are committed to providing both employment and educational environments free of harassment or discrimination related to an individual’s race, color, gender, religion, national origin, age, or disability. Such harassment is a violation of State Board of E ...
... NACC and the Alabama State Board of Education are committed to providing both employment and educational environments free of harassment or discrimination related to an individual’s race, color, gender, religion, national origin, age, or disability. Such harassment is a violation of State Board of E ...
N-METAL COMPOUNDS
... than the notion that, with a "few" exceptions, compounds with bonds between carbon and transition metals (Fe, Co, Ni, Ti, and so on) are inherently unstable. This idea was swept away in 1951 with the discovery of ferrocene, (C,H,),Fe, by P. L. Pauson. Ferrocene has unheard of properties for an organ ...
... than the notion that, with a "few" exceptions, compounds with bonds between carbon and transition metals (Fe, Co, Ni, Ti, and so on) are inherently unstable. This idea was swept away in 1951 with the discovery of ferrocene, (C,H,),Fe, by P. L. Pauson. Ferrocene has unheard of properties for an organ ...
General properties of urea : It is water
... Classically it was the first naturally occurring “organic” compound to be prepared from inorganic compounds traversing for the first time the great divide that appeared to classify all substances known at the time. Evaporation of an aqueous solution of ammonium cyanate to dryness was observed to giv ...
... Classically it was the first naturally occurring “organic” compound to be prepared from inorganic compounds traversing for the first time the great divide that appeared to classify all substances known at the time. Evaporation of an aqueous solution of ammonium cyanate to dryness was observed to giv ...
Ene reaction

The ene reaction (also known as the Alder-ene reaction) is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen (the ene) and a compound containing a multiple bond (the enophile), in order to form a new σ-bond with migration of the ene double bond and 1,5 hydrogen shift. The product is a substituted alkene with the double bond shifted to the allylic position.This transformation is a group transfer pericyclic reaction, and therefore, usually requires highly activated substrates and/or high temperatures. Nonetheless, the reaction is compatible with a wide variety of functional groups that can be appended to the ene and enophile moieties. Also,many useful Lewis acid-catalyzed ene reactions have been developed which can afford high yields and selectivities at significantly lower temperatures, making the ene reaction a useful C–C forming tool for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products.