Bifunctional Asymmetric Catalysis: Cooperative Lewis Acid/Base
... instead of activating the imine.9 They use a cinchona alkaloid nucleophile in conjunction with a Lewis acid to form β-lactams from aryl imines and phenoxyacetyl chloride. In this system, bidentate metal-enolate binding is preferred to monodentate metal-imine binding for hard Lewis acids. We had prev ...
... instead of activating the imine.9 They use a cinchona alkaloid nucleophile in conjunction with a Lewis acid to form β-lactams from aryl imines and phenoxyacetyl chloride. In this system, bidentate metal-enolate binding is preferred to monodentate metal-imine binding for hard Lewis acids. We had prev ...
synthesis in industry
... used to prepare allylic primary amines. Unfortunately, the unsubstituted metal imides with M=NH functions are not sufficiently tractable to be useful as reagents. The desired synthesis can be achieved, however, by an indirect route. The silylimide complex 3 serves as a reagent for synthesis of the d ...
... used to prepare allylic primary amines. Unfortunately, the unsubstituted metal imides with M=NH functions are not sufficiently tractable to be useful as reagents. The desired synthesis can be achieved, however, by an indirect route. The silylimide complex 3 serves as a reagent for synthesis of the d ...
Cooperative Lewis Acid/Base Systems
... instead of activating the imine.9 They use a cinchona alkaloid nucleophile in conjunction with a Lewis acid to form β-lactams from aryl imines and phenoxyacetyl chloride. In this system, bidentate metal-enolate binding is preferred to monodentate metal-imine binding for hard Lewis acids. We had prev ...
... instead of activating the imine.9 They use a cinchona alkaloid nucleophile in conjunction with a Lewis acid to form β-lactams from aryl imines and phenoxyacetyl chloride. In this system, bidentate metal-enolate binding is preferred to monodentate metal-imine binding for hard Lewis acids. We had prev ...
File
... monochromatic light in molecules containing a single chiral centre and understand the nature of a racemic mixture d. use data on optical activity of reactants and products as evidence for proposed mechanisms, as in S N1 and SN2 and addition to carbonyl compounds. ...
... monochromatic light in molecules containing a single chiral centre and understand the nature of a racemic mixture d. use data on optical activity of reactants and products as evidence for proposed mechanisms, as in S N1 and SN2 and addition to carbonyl compounds. ...
2.10 Reactions of alcohols
... iii. substitution reactions to form halogenoalkanes, including reaction with PCl5 and its use as a qualitative test for the presence of the –OH group iv. oxidation using potassium dichromate (VI) in dilute sulfuric acid on primary alcohols to produce aldehydes and carboxylic acids and on secondary a ...
... iii. substitution reactions to form halogenoalkanes, including reaction with PCl5 and its use as a qualitative test for the presence of the –OH group iv. oxidation using potassium dichromate (VI) in dilute sulfuric acid on primary alcohols to produce aldehydes and carboxylic acids and on secondary a ...
CHEM 202_ Part 2
... Aldehydes and ketones can be used to synthesis of many organic compounds. In all these reactions, carbonyl group can be retained (halogenation), or extended to more carbon skeleton (Grignard and Witting reaction), or converted to another functional group (reduction) ...
... Aldehydes and ketones can be used to synthesis of many organic compounds. In all these reactions, carbonyl group can be retained (halogenation), or extended to more carbon skeleton (Grignard and Witting reaction), or converted to another functional group (reduction) ...
Date - Chaminade University`s syllabus repository
... This is the first part of a two-semester course in organic chemistry, where carbon compounds are studied on the basis of their functional groups. Following a review of the basic principles in general chemistry, acid-base reactions will be investigated with an emphasis on electron pair transfers and ...
... This is the first part of a two-semester course in organic chemistry, where carbon compounds are studied on the basis of their functional groups. Following a review of the basic principles in general chemistry, acid-base reactions will be investigated with an emphasis on electron pair transfers and ...
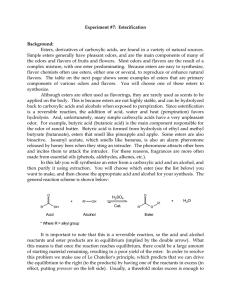
102 Lab 7 Esters Fall05
... Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, you need to use only a small amount of sulfuric acid in order for it to be effective. Heating is another way ...
... Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, you need to use only a small amount of sulfuric acid in order for it to be effective. Heating is another way ...
10. Alkyl Halides - Clayton State University
... An organic compound containing at least one carbon-halogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant solvents Refrigerants Pharmaceuticals and precursors ...
... An organic compound containing at least one carbon-halogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant solvents Refrigerants Pharmaceuticals and precursors ...
Final-01 - Yale Department of Chemistry
... E2 is kinetically-controlled. No mechanism (too high an energy barrier) with base to equilibrate isomers. The distribution of alkene products is determined by the difference in activation energy of the two transition states (e.g.; Zaitsev vs. Hofmann products. In E1 eliminations, acid is formed as a ...
... E2 is kinetically-controlled. No mechanism (too high an energy barrier) with base to equilibrate isomers. The distribution of alkene products is determined by the difference in activation energy of the two transition states (e.g.; Zaitsev vs. Hofmann products. In E1 eliminations, acid is formed as a ...
Organic Chemistry III Laboratory
... During the second week’s lab period, the yeast reactions will be worked up and the products isolated by extraction and purified by filtering the mixture through a short column of silica gel. After removing the solvent, the resulting product mixtures can be characterized by GC, 1H-NMR, and COSY spec ...
... During the second week’s lab period, the yeast reactions will be worked up and the products isolated by extraction and purified by filtering the mixture through a short column of silica gel. After removing the solvent, the resulting product mixtures can be characterized by GC, 1H-NMR, and COSY spec ...
CH 12-3 Power Point
... Alkyl halides react with Mg metal in ether solvent to form the “Grignard Reagent” containing a coordinate covalent bond. The metal stabilizes the carbon-anion. ...
... Alkyl halides react with Mg metal in ether solvent to form the “Grignard Reagent” containing a coordinate covalent bond. The metal stabilizes the carbon-anion. ...
ch15 lecture 7e
... 15.2 The Structures and Classes of Hydrocarbons 15.3 Some Important Classes of Organic Reactions 15.4 Properties and Reactivities of Common Functional Groups 15.5 The Monomer-Polymer Theme I: Synthetic Macromolecules 15.6 The Monomer-Polymer Theme II: Biological Macromolecules ...
... 15.2 The Structures and Classes of Hydrocarbons 15.3 Some Important Classes of Organic Reactions 15.4 Properties and Reactivities of Common Functional Groups 15.5 The Monomer-Polymer Theme I: Synthetic Macromolecules 15.6 The Monomer-Polymer Theme II: Biological Macromolecules ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... What can happen? Reactants are the aldehyde and concentrated hydroxide. Hydroxide ion can act both as Base, but remember we have no acidic hydrogens (no a hydrogens). Nucleophile, attacking carbonyl group. ...
... What can happen? Reactants are the aldehyde and concentrated hydroxide. Hydroxide ion can act both as Base, but remember we have no acidic hydrogens (no a hydrogens). Nucleophile, attacking carbonyl group. ...
blank lecture 11
... • Because of the polarity of the C=O group, these groups can interact, but the attraction is not as strong as hydrogen bonding. • This makes the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones ___________ than alkanes, but _________ than alcohols. ...
... • Because of the polarity of the C=O group, these groups can interact, but the attraction is not as strong as hydrogen bonding. • This makes the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones ___________ than alkanes, but _________ than alcohols. ...
Chapter 3. Analysis of Environmental System 3.1 Analysis of a
... Eq.(3.1.3) may be solved without any difficulty if we follow the process as we have done so far. Especially, when discharging rate of a pollutant into the lake is constant, it is much easier because the condition is steady state, dC/dt = 0. ...
... Eq.(3.1.3) may be solved without any difficulty if we follow the process as we have done so far. Especially, when discharging rate of a pollutant into the lake is constant, it is much easier because the condition is steady state, dC/dt = 0. ...
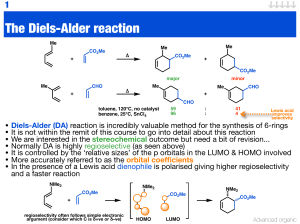
The Diels-Alder reaction
... • Another hetero-Diels-Alder reaction • It looks very similar to the previous reaction but... • It is believed that only one hydrogen bond activates the aldehyde • The other is used to form a rigid chiral environment for the reaction Advanced organic ...
... • Another hetero-Diels-Alder reaction • It looks very similar to the previous reaction but... • It is believed that only one hydrogen bond activates the aldehyde • The other is used to form a rigid chiral environment for the reaction Advanced organic ...
Carbon Bond - Rutgers Chemistry
... the structures of important pharmaceuticals, the most extensively studied have been alkenylated benzimidazoles. These compounds also undergo cyclization with satisfying generality. In addition to exploring the scope of the cyclizations, we have also investigated their mechanism.23 Through the use of ...
... the structures of important pharmaceuticals, the most extensively studied have been alkenylated benzimidazoles. These compounds also undergo cyclization with satisfying generality. In addition to exploring the scope of the cyclizations, we have also investigated their mechanism.23 Through the use of ...
Diels-Alder Reaction
... without the intervention of radicals, carbocations, or other intermediates. It is a powerful method for the construction of cyclohexene rings, and has become such a mainstay of organic synthesis that its discoverers, Otto Diels and Kurt Alder, were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950 for th ...
... without the intervention of radicals, carbocations, or other intermediates. It is a powerful method for the construction of cyclohexene rings, and has become such a mainstay of organic synthesis that its discoverers, Otto Diels and Kurt Alder, were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950 for th ...
Module - EPS School Projects - Heriot
... provide a range of methods for the interconversion of key functional groups, emphasising issues of regio- and stereocontrol discuss an extended range of reactions for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds develop the concept of retrosynthetic analysis (RSA) in a structured manner illustrate h ...
... provide a range of methods for the interconversion of key functional groups, emphasising issues of regio- and stereocontrol discuss an extended range of reactions for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds develop the concept of retrosynthetic analysis (RSA) in a structured manner illustrate h ...
Slides
... Alkylation of 1,3-Dithianes Protons on the carbon between the sulfur atoms of a 1,3-dithiane are moderately acidic l Strong bases convert the dithiane to its anion ...
... Alkylation of 1,3-Dithianes Protons on the carbon between the sulfur atoms of a 1,3-dithiane are moderately acidic l Strong bases convert the dithiane to its anion ...
ADDITION REACTIONS
... Grignard Addition - Preparation of Alcohols • Grignard reagents are prepared from the reaction of alkyl halides with magnesium in ether solvent. • The alkyl group assumes a negative character and is a nucleophile. • When presented with an aldehyde or ketone, the Grignard attacks the carbonyl carbon ...
... Grignard Addition - Preparation of Alcohols • Grignard reagents are prepared from the reaction of alkyl halides with magnesium in ether solvent. • The alkyl group assumes a negative character and is a nucleophile. • When presented with an aldehyde or ketone, the Grignard attacks the carbonyl carbon ...
Bimolecular reactions of the chromium
... ligand. This is of particular interest if the free ligand is unstable and difficult to handle under the conditions typical of synthetic chemistry. Benzyne (18-didehydrobenzene) and other arynes are very reactive intermediates3 which have to be prepared in situ during a chemical syntheeis.’ However, ...
... ligand. This is of particular interest if the free ligand is unstable and difficult to handle under the conditions typical of synthetic chemistry. Benzyne (18-didehydrobenzene) and other arynes are very reactive intermediates3 which have to be prepared in situ during a chemical syntheeis.’ However, ...
Ene reaction

The ene reaction (also known as the Alder-ene reaction) is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen (the ene) and a compound containing a multiple bond (the enophile), in order to form a new σ-bond with migration of the ene double bond and 1,5 hydrogen shift. The product is a substituted alkene with the double bond shifted to the allylic position.This transformation is a group transfer pericyclic reaction, and therefore, usually requires highly activated substrates and/or high temperatures. Nonetheless, the reaction is compatible with a wide variety of functional groups that can be appended to the ene and enophile moieties. Also,many useful Lewis acid-catalyzed ene reactions have been developed which can afford high yields and selectivities at significantly lower temperatures, making the ene reaction a useful C–C forming tool for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products.