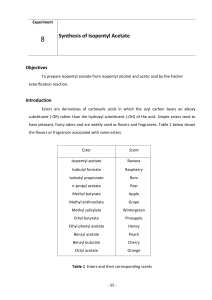
Experiment #9 – Identification of Aldehydes and Ketones
... ketones, are important in carbohydrate chemistry. Sugars are, for the most part, polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. So, a sugar has both of the functional groups that react together to form a hemiacetal. It turns out that hemiacetals can react with alcohols to give compounds known as acetals. Acetal ...
... ketones, are important in carbohydrate chemistry. Sugars are, for the most part, polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. So, a sugar has both of the functional groups that react together to form a hemiacetal. It turns out that hemiacetals can react with alcohols to give compounds known as acetals. Acetal ...
슬라이드 1
... Isotope effects indicate that the collapse of the adduct by reductive elimination is the rate determining step. The more easily reduced, the more reactive is the compound toward cuprate reagents. Compounds such as a,b-unsaturated esters and nitriles, which are not as easily reduced as the correspond ...
... Isotope effects indicate that the collapse of the adduct by reductive elimination is the rate determining step. The more easily reduced, the more reactive is the compound toward cuprate reagents. Compounds such as a,b-unsaturated esters and nitriles, which are not as easily reduced as the correspond ...
Kazzie`s Guide to Orgo 2
... General Note: Some of these questions have been previously used in examples, etcetera, but they cover the things that I think are important to know from this semester. Try to work through them with as few resources as possible, and we will go through this at the final review. Chem 210 Stuff Identify ...
... General Note: Some of these questions have been previously used in examples, etcetera, but they cover the things that I think are important to know from this semester. Try to work through them with as few resources as possible, and we will go through this at the final review. Chem 210 Stuff Identify ...
chemistry_23 - Bonar Law Memorial
... Ethanol is the intoxicating substance in alcoholic beverages. It is a depressant that can be fatal if taken in large doses at once. ...
... Ethanol is the intoxicating substance in alcoholic beverages. It is a depressant that can be fatal if taken in large doses at once. ...
alcohols, alkyl halides, and nucleophilic substitutions
... reagent. Consider the aliphatic alcohols first and then consider the aromatic compounds separately. What structural change correlates with reactivity? Assuming this to be an SN1 reaction (see scheme in part B), and that the reaction is faster for more stable cation intermediates, indicate the order ...
... reagent. Consider the aliphatic alcohols first and then consider the aromatic compounds separately. What structural change correlates with reactivity? Assuming this to be an SN1 reaction (see scheme in part B), and that the reaction is faster for more stable cation intermediates, indicate the order ...
ALDOL CONDENSATION
... In the first step of the mechanism, an α‐proton is removed by a strong base, resulting in the formation of an enolate anion, which is made relatively stable by the delocalization of electrons. ¾ Next, the carbonyl carbon of the (other) ester is nucleophilically attacked by the enolate anion. ...
... In the first step of the mechanism, an α‐proton is removed by a strong base, resulting in the formation of an enolate anion, which is made relatively stable by the delocalization of electrons. ¾ Next, the carbonyl carbon of the (other) ester is nucleophilically attacked by the enolate anion. ...
Regents Unit 15b: Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, & Esters
... • Contain –COOH group. • H is bonded to O. Hydrogen bonding occurs. Leads to increases in boiling point over corresponding alkane. • Also can form hydrogen bonds with water so the smaller acids are pretty soluble. ...
... • Contain –COOH group. • H is bonded to O. Hydrogen bonding occurs. Leads to increases in boiling point over corresponding alkane. • Also can form hydrogen bonds with water so the smaller acids are pretty soluble. ...
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
Chapter 1-
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
CHAPTER 17: Carbonyl group (1)
... 17.8 Acetals as protecting groups Due to interference of functional groups during a reaction we often need to transform them to "unreactive species". This is accomplished using "protecting groups" which should be inert to the subsequent reactions. At the end of the synthetic strategy, these protecti ...
... 17.8 Acetals as protecting groups Due to interference of functional groups during a reaction we often need to transform them to "unreactive species". This is accomplished using "protecting groups" which should be inert to the subsequent reactions. At the end of the synthetic strategy, these protecti ...
Nugget
... improved solubility of the organometallic compounds. Currently we are working on optimization of the crystallization conditions for the ruthenium products. Ruthenium ditriflate analog of the carborane complexes oxidizes alcohols to yield aldehydes (or ketones). We continued the kinetic and thermodyn ...
... improved solubility of the organometallic compounds. Currently we are working on optimization of the crystallization conditions for the ruthenium products. Ruthenium ditriflate analog of the carborane complexes oxidizes alcohols to yield aldehydes (or ketones). We continued the kinetic and thermodyn ...
Ch 17- Aldehydes and Ketones
... bonds can be reduced by the addition of H2 with a metal catalyst to produce an alcohol. OH ...
... bonds can be reduced by the addition of H2 with a metal catalyst to produce an alcohol. OH ...
Formation of N-Methylated Cyclic Ligand Systems from Unusual
... (Scheme 2). In the process, a C-H bond of one methyl group of trimethylamine is activated and transformed into an iminium group, which adds to the R-carbon of the ferrocenylacetylene. In 1, there is no net loss of carbonyl groups. Although not isolated, a similar type of iminium formation has been i ...
... (Scheme 2). In the process, a C-H bond of one methyl group of trimethylamine is activated and transformed into an iminium group, which adds to the R-carbon of the ferrocenylacetylene. In 1, there is no net loss of carbonyl groups. Although not isolated, a similar type of iminium formation has been i ...
Organic Chemistry - Unit 2
... There are many different families or classes of organic compounds. The thing that differentiates them is a functional group. The functional group is a specific arrangement of atoms that is capable of characteristic chemical reactions. The double and triple bonds are considered functional groups as t ...
... There are many different families or classes of organic compounds. The thing that differentiates them is a functional group. The functional group is a specific arrangement of atoms that is capable of characteristic chemical reactions. The double and triple bonds are considered functional groups as t ...
St.Mont Fort School Bhopal Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Q 1 Give
... 12. CCl4 and water are immiscible whereas ethanol and water are miscible in all proportions. Correlate this behaviour with molecular structure of these compounds. 13. State Henry’s Law ? What is the significance ? 14. Derive an equation to express that relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solu ...
... 12. CCl4 and water are immiscible whereas ethanol and water are miscible in all proportions. Correlate this behaviour with molecular structure of these compounds. 13. State Henry’s Law ? What is the significance ? 14. Derive an equation to express that relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solu ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
... nucleophilic addition reactions than propanal? Explain your answer. 3. Carbonyl carbon of carboxylic acid is less electronegative than aldehydes and ketones give reason. 4. Carboxylic acids are having higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Exp ...
... nucleophilic addition reactions than propanal? Explain your answer. 3. Carbonyl carbon of carboxylic acid is less electronegative than aldehydes and ketones give reason. 4. Carboxylic acids are having higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Exp ...
Document
... Fischer esterification is an example of an acyl transfer reaction. The acyl group from the acid is transferred to the alcohol. Acid chlorides and anhydrides also serve as acylating agents. Because acid chlorides and anhydrides contain good leaving groups, these compounds are very reactive toward nuc ...
... Fischer esterification is an example of an acyl transfer reaction. The acyl group from the acid is transferred to the alcohol. Acid chlorides and anhydrides also serve as acylating agents. Because acid chlorides and anhydrides contain good leaving groups, these compounds are very reactive toward nuc ...
Alcohol oxidation
... III Semester M Sc-Organic synthesis via Oxidation and Reduction[Type the document title] iodine, which can easily be observed by its violet color. For closer control of the reaction itself, an indicator such as Sudan Red III can be added to the reaction mixture. Ozone reacts with this indicator mor ...
... III Semester M Sc-Organic synthesis via Oxidation and Reduction[Type the document title] iodine, which can easily be observed by its violet color. For closer control of the reaction itself, an indicator such as Sudan Red III can be added to the reaction mixture. Ozone reacts with this indicator mor ...
"Introduction" Kinetics in Process Chemistry: Case Studies Baran Group Meeting Mike DeMartino
... coupling reactions. There are advantages to using CDI: price -$8/mol (large-scale purchase), and the byproducts are the innocuous CO2 and imidazole. It is not without its problems though. The acyl imidazole is less reactive than, for instance, the corresponding acid chloride. As a result, particular ...
... coupling reactions. There are advantages to using CDI: price -$8/mol (large-scale purchase), and the byproducts are the innocuous CO2 and imidazole. It is not without its problems though. The acyl imidazole is less reactive than, for instance, the corresponding acid chloride. As a result, particular ...
Reaction of Alkenes
... alkenes, the electrophile adds to the least substituted carbon giving rise to the more stable intermediate. Example: Addition of HX Markovnikov Addition (only product) ...
... alkenes, the electrophile adds to the least substituted carbon giving rise to the more stable intermediate. Example: Addition of HX Markovnikov Addition (only product) ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.