Synthesis of 1
... The upper layer that soon separates in the reaction flask is the alkyl bromide, because the aqueous solution of inorganic salts has the greater density. Remove the cotton, insulate the flask with cotton or glass wool, and distill the product into a collection vial until no more water-insoluble dropl ...
... The upper layer that soon separates in the reaction flask is the alkyl bromide, because the aqueous solution of inorganic salts has the greater density. Remove the cotton, insulate the flask with cotton or glass wool, and distill the product into a collection vial until no more water-insoluble dropl ...
Applications of Phosphorus, Sulfur, Silicon and Boron Chemistry:
... Predict the stereochemistry of the product(s) arising from reactions covered (see LO6, 7 and 8) using reaction mechanisms to explain the stereochemical outcome of the transformations. 10. Show how silyl ethers can be used as hydroxyl protecting groups in organic chemistry. These notes, self-study wo ...
... Predict the stereochemistry of the product(s) arising from reactions covered (see LO6, 7 and 8) using reaction mechanisms to explain the stereochemical outcome of the transformations. 10. Show how silyl ethers can be used as hydroxyl protecting groups in organic chemistry. These notes, self-study wo ...
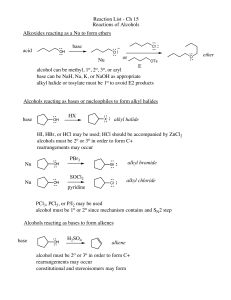
Reaction List - Ch 15 Reactions of Alcohols Alkoxides reacting as a
... HI, HBr, or HCl may be used; HCl should be accompanied by ZnCl2 alcohols must be 2o or 3o in order to form C+ rearrangements may occur Nu ...
... HI, HBr, or HCl may be used; HCl should be accompanied by ZnCl2 alcohols must be 2o or 3o in order to form C+ rearrangements may occur Nu ...
alcohols, alkyl halides, and nucleophilic substitutions
... separately. What structural change correlates with reactivity? Assuming this to be an SN1 reaction (see scheme in part B), and that the reaction is faster for more stable cation intermediates, indicate the order of stability of all the carbon cations formed from each alcohol. Examine the cations and ...
... separately. What structural change correlates with reactivity? Assuming this to be an SN1 reaction (see scheme in part B), and that the reaction is faster for more stable cation intermediates, indicate the order of stability of all the carbon cations formed from each alcohol. Examine the cations and ...
Chemistry 3719L – Week 9 Reduction of Benzil with Sodium
... • Filter the solid, dry for 15 minutes then weigh the product and obtain the melting point. • If possible you should obtain an IR spectrum of your product to compare with that of the benzil starting material. This information will be used in your report to prove that the functional group conversion ...
... • Filter the solid, dry for 15 minutes then weigh the product and obtain the melting point. • If possible you should obtain an IR spectrum of your product to compare with that of the benzil starting material. This information will be used in your report to prove that the functional group conversion ...
Nucleophilic substitution at saturated carbon
... different in size, another factor comes into play—the polarizability of the atom. Because the electrons are farther away in the larger atom, they are not held as tightly and can, therefore, move more freely toward a positive charge. As a result, the electrons are able to overlap from farther away wi ...
... different in size, another factor comes into play—the polarizability of the atom. Because the electrons are farther away in the larger atom, they are not held as tightly and can, therefore, move more freely toward a positive charge. As a result, the electrons are able to overlap from farther away wi ...
- KCN K+ R KOH + H2O
... i) The reactions involve nucleophilic addition to yield a carbinolamine (hemiaminal) followed by E1 elimination of H2O. Note that this reaction requires the presence of at least two hydrogens in the starting amine (H+ comes from N; O is protonated before it leaves) ii) Equilibrium favors imine form ...
... i) The reactions involve nucleophilic addition to yield a carbinolamine (hemiaminal) followed by E1 elimination of H2O. Note that this reaction requires the presence of at least two hydrogens in the starting amine (H+ comes from N; O is protonated before it leaves) ii) Equilibrium favors imine form ...
Lecture6-Organometallic Chemistry
... •How strong or weak is a M-C bond? •How stable are the organometallic compounds? ...
... •How strong or weak is a M-C bond? •How stable are the organometallic compounds? ...
handout alkenes from alcohols
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE HYDROCARBONS 1. Name the least
... 7. Name the reaction, which involves the conversion of benzaldehyde to a mixture of benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid using sodium hydroxide. 8. Name the reducing agent used in Clemmensen`s reduction. 9. What type of aldehydes undergo Cannizzaro`s reaction? 10. Name the aldehyde which does not give Fe ...
... 7. Name the reaction, which involves the conversion of benzaldehyde to a mixture of benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid using sodium hydroxide. 8. Name the reducing agent used in Clemmensen`s reduction. 9. What type of aldehydes undergo Cannizzaro`s reaction? 10. Name the aldehyde which does not give Fe ...
Document
... :B can be the excess of the amine Since it can provide the mixture of products, this process is less applied (see later) ...
... :B can be the excess of the amine Since it can provide the mixture of products, this process is less applied (see later) ...
Chapter 13 - WebAssign
... Lone pairs and pi electrons are Lewis base sites. Oxygen and nitrogen obey the octet rule, but lone pairs are frequently omitted ...
... Lone pairs and pi electrons are Lewis base sites. Oxygen and nitrogen obey the octet rule, but lone pairs are frequently omitted ...
Slides, Set 12
... Monosaccharides that are capable of assuming a form in solution that contains a free carbonyl group can be oxidized by relatively mild oxidizing agents such as Fe+3 or Cu+2 (Fehling s reaction). The saccharide is oxidized and the reagent is reduced.! COO- ...
... Monosaccharides that are capable of assuming a form in solution that contains a free carbonyl group can be oxidized by relatively mild oxidizing agents such as Fe+3 or Cu+2 (Fehling s reaction). The saccharide is oxidized and the reagent is reduced.! COO- ...
handout alkenes from alcohols
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
Organic Synthesis
... C-C bond forming reactions. Second, the product must contain an alcohol group. That may have survived from the starting material, or been produced along the way. One good tip is to try to find disconnections that simplify the molecule a lot, especailly disconnections at branch points. In this case, ...
... C-C bond forming reactions. Second, the product must contain an alcohol group. That may have survived from the starting material, or been produced along the way. One good tip is to try to find disconnections that simplify the molecule a lot, especailly disconnections at branch points. In this case, ...
10. Alkyl Halides - Clayton State University
... Properties and some uses Fire-resistant solvents Refrigerants Pharmaceuticals and precursors ...
... Properties and some uses Fire-resistant solvents Refrigerants Pharmaceuticals and precursors ...
Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups
... The reverse of acetal formation if acetal hydrolysis. This is achieved by excess water in the presence of an acid catalyst. ...
... The reverse of acetal formation if acetal hydrolysis. This is achieved by excess water in the presence of an acid catalyst. ...
Q1. Give I.U.P.A..C Name of the following Organic Compound. 1 CH
... (1) ICl is more reactive than I2. (2) Why does NO2 dimerise? (3) H2S is less acidic than H2 Te why? OR (1) Which form of sulphur shows paramagnetic behaviour? (2) Halogens have maximum negative electron gain Enthalpy in the respective periods of the ...
... (1) ICl is more reactive than I2. (2) Why does NO2 dimerise? (3) H2S is less acidic than H2 Te why? OR (1) Which form of sulphur shows paramagnetic behaviour? (2) Halogens have maximum negative electron gain Enthalpy in the respective periods of the ...
Addition reactions
... Electrophilic addition: an alkene or alkyne serves as the Nu: and donates : to the electropositive atom of a molecule, typically an acid • Substrate is unsaturated • Reactant is often an acid • The two halves (electropositive & electronegative) are both added “across” the double bond Nu:- ...
... Electrophilic addition: an alkene or alkyne serves as the Nu: and donates : to the electropositive atom of a molecule, typically an acid • Substrate is unsaturated • Reactant is often an acid • The two halves (electropositive & electronegative) are both added “across” the double bond Nu:- ...
Diels-Alder Reaction
... of a reaction type known as a cycloaddition reaction, in which the conjugated p-systems of two reactants join to generate a new ring. The reactants in the Diels-Alder reaction are a 1,3-diene and an alkene called the dienophile. The carbon-carbon double bond in the dienophile is usually conjugated w ...
... of a reaction type known as a cycloaddition reaction, in which the conjugated p-systems of two reactants join to generate a new ring. The reactants in the Diels-Alder reaction are a 1,3-diene and an alkene called the dienophile. The carbon-carbon double bond in the dienophile is usually conjugated w ...
Chemistry 235, Winter 2008 Name: General rules:
... • Atoms in elemental form, like C or O2, are assigned an oxidation number of 0. • In compounds, the more electronegative element (p. 137) is assigned the negative oxidation number. • Hydrogen in an organic compound is assigned an oxidation number of +1. • Oxygen in an organic compound generally is a ...
... • Atoms in elemental form, like C or O2, are assigned an oxidation number of 0. • In compounds, the more electronegative element (p. 137) is assigned the negative oxidation number. • Hydrogen in an organic compound is assigned an oxidation number of +1. • Oxygen in an organic compound generally is a ...
Chem 263 Nov 3 2016 notes
... carbon-oxygen double bond then become localized on the oxygen atom to form an alkoxide ion. This alkoxide ion then reacts with an electrophile (E+, which is usually a proton - H+) to quench the negative charge. Alternatively (especially in reaction with weak nucleophiles), the oxygen is protonated f ...
... carbon-oxygen double bond then become localized on the oxygen atom to form an alkoxide ion. This alkoxide ion then reacts with an electrophile (E+, which is usually a proton - H+) to quench the negative charge. Alternatively (especially in reaction with weak nucleophiles), the oxygen is protonated f ...
Hydrocarbon Derivatives
... • this is called polymerization – The atom or group of atoms that are added to the hydrocarbon are called functional groups. • Functional groups usually have multiple bonds or lone pairs of electrons that make them very reactive. ...
... • this is called polymerization – The atom or group of atoms that are added to the hydrocarbon are called functional groups. • Functional groups usually have multiple bonds or lone pairs of electrons that make them very reactive. ...
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement

The Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement (TDR) is the chemical reaction of a 1-aminomethyl-cycloalkanol with nitrous acid to form an enlarged cycloketone.The Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion, Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement, or TDR, provides an easy way to increase amino-substituted cycloalkanes and cycloalkanols in size by one carbon. Ring sizes from cyclopropane through cyclooctane are able to undergo Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion with some degree of success. Yields decrease as initial ring size increases, and the ideal use of TDR is for synthesis of five, six, and seven membered rings. A principal synthetic application of Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion is to bicyclic or polycyclic systems. Several reviews on this reaction have been published.