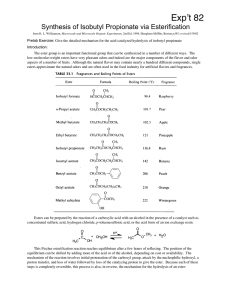
Synthesis of Isobutyl Propionate via Esterification
... vertical position. Close the valve, and fill the column with dichloromethane to the bottom of the funnel. Prepare a slurry of 1 g of silica gel in 4 mL of dichloromethane in a small beaker. Stir the slurry gently to get rid of air bubbles, and gently swirl, pour, and scrape the slurry into the funne ...
... vertical position. Close the valve, and fill the column with dichloromethane to the bottom of the funnel. Prepare a slurry of 1 g of silica gel in 4 mL of dichloromethane in a small beaker. Stir the slurry gently to get rid of air bubbles, and gently swirl, pour, and scrape the slurry into the funne ...
22.4: Acidity of Phenols.
... Chapter 22: Phenols. Alcohols contain an OH group bonded to an sp3-hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an OH group bonded to an sp2-hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 22.1: Nomenclature (please read) 22.2: Structure and Bonding (please read) 22.3: Physical Properties (please read). Like other alcoho ...
... Chapter 22: Phenols. Alcohols contain an OH group bonded to an sp3-hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an OH group bonded to an sp2-hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 22.1: Nomenclature (please read) 22.2: Structure and Bonding (please read) 22.3: Physical Properties (please read). Like other alcoho ...
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
... distinguish between enantiomers, diastereomers, and meso compounds. name configurational isomers by either the R-S or E-Z convention where appropriate. define a racemic mixture and explain how to resolve it. relate stereoisomerism to biological compounds. explain the role of stereoisomers in definin ...
... distinguish between enantiomers, diastereomers, and meso compounds. name configurational isomers by either the R-S or E-Z convention where appropriate. define a racemic mixture and explain how to resolve it. relate stereoisomerism to biological compounds. explain the role of stereoisomers in definin ...
CH 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... • Carboxyl carbon sp2 hybridized: carboxylic acid groups are planar with C–C=O and O=C–O bond angles of approximately 120° • Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds, existing as cyclic dimers held together by two hydrogen bonds • Strong hydrogen bonding causes much higher boiling points than the corres ...
... • Carboxyl carbon sp2 hybridized: carboxylic acid groups are planar with C–C=O and O=C–O bond angles of approximately 120° • Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds, existing as cyclic dimers held together by two hydrogen bonds • Strong hydrogen bonding causes much higher boiling points than the corres ...
mascp.adv_resveratrol_stm[1]_new
... Windberg Jan Olof Drosophila Melanogaster Alcohol Dehydrogenase: Pridyct- Inhibition 1994 Ulrike Heverlein Molecular Genetic Analysis of Ethanol Intoxication in Drosohoila Melanogaster 2004 Department of Anatomy and Program in Neuroscience Morozava Transcriptional Response to Alcohol exposure in Dro ...
... Windberg Jan Olof Drosophila Melanogaster Alcohol Dehydrogenase: Pridyct- Inhibition 1994 Ulrike Heverlein Molecular Genetic Analysis of Ethanol Intoxication in Drosohoila Melanogaster 2004 Department of Anatomy and Program in Neuroscience Morozava Transcriptional Response to Alcohol exposure in Dro ...
Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... ◦ SN2 reaction between a carboxylate anion (Nu) and a 1o alkyl halide ◦ Fischer esterification using an acid, an alcohol, and a strong acid catalyst ◦ Reaction between an acid halide and an alcohol - Esters are less reactive than halides and anhydrides. However, they still undergo some Nu acyl subst ...
... ◦ SN2 reaction between a carboxylate anion (Nu) and a 1o alkyl halide ◦ Fischer esterification using an acid, an alcohol, and a strong acid catalyst ◦ Reaction between an acid halide and an alcohol - Esters are less reactive than halides and anhydrides. However, they still undergo some Nu acyl subst ...
Module 2 Alcohols, halogenoalkanes and analysis
... Halogenoalkanes are important starting materials for many synthetic routes. This is because they are readily converted into alcohols and other functional groups – you will become familiar with many of these compounds during your Advanced level work. For centuries, alcohols have been widely known and ...
... Halogenoalkanes are important starting materials for many synthetic routes. This is because they are readily converted into alcohols and other functional groups – you will become familiar with many of these compounds during your Advanced level work. For centuries, alcohols have been widely known and ...
Unit 8 – Organic Chemistry
... – Some bonds are single and filled with hydrogen, while others are double bonds – Names end in “ene” – Give the position of the bond by using the smallest ...
... – Some bonds are single and filled with hydrogen, while others are double bonds – Names end in “ene” – Give the position of the bond by using the smallest ...
Chapter 13 - WebAssign
... molecule can add across a multiple bond to form two C-H bonds. For example, ethene can be hydrogenated to ethane: H2C=CH2 + H2 → H3C-CH3. Thus, alkenes are unsaturated. Molecules with many double bonds (polyenes) are said to be polyunsaturated. ...
... molecule can add across a multiple bond to form two C-H bonds. For example, ethene can be hydrogenated to ethane: H2C=CH2 + H2 → H3C-CH3. Thus, alkenes are unsaturated. Molecules with many double bonds (polyenes) are said to be polyunsaturated. ...
Samantha Landolfa Amy Ryan Section 10 Experiment 9 – Alkenes
... Experiment 9 – Alkenes from Alcohols: Analysis of a Mixture by Gas Chromatography H2SO4 ...
... Experiment 9 – Alkenes from Alcohols: Analysis of a Mixture by Gas Chromatography H2SO4 ...
Chapter 15 Multistep Syntheses
... • Grouping Chemical Reactions • Retrosynthetic Analysis • Reactions Requiring Both Functional-Group Transformation and Skeletal Construction • Extending the Retrosynthetic Approach: Alternative Routes ...
... • Grouping Chemical Reactions • Retrosynthetic Analysis • Reactions Requiring Both Functional-Group Transformation and Skeletal Construction • Extending the Retrosynthetic Approach: Alternative Routes ...
Reactions of esters:
... inside cells that can catalyze this reaction. So energy rich diphosphates can exist in cells despite the abundance of water. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is the most common and widely occurring member of a small family of energy rich triphosphate esters. Because triphosphate esters have two phosp ...
... inside cells that can catalyze this reaction. So energy rich diphosphates can exist in cells despite the abundance of water. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is the most common and widely occurring member of a small family of energy rich triphosphate esters. Because triphosphate esters have two phosp ...
CH2=CH2
... Each of the carbon-hydrogen bonds is formed by overlap of on sp2 hybrid on carbon with the 1s orbital of a hydrogen atom. The C-H bond length in ethylene (1.08 A0) is slightly shorter than the C-H bond in ethane (1.09 A0) ,because the sp2 orbital in ethylene has more s character (one-third s) than a ...
... Each of the carbon-hydrogen bonds is formed by overlap of on sp2 hybrid on carbon with the 1s orbital of a hydrogen atom. The C-H bond length in ethylene (1.08 A0) is slightly shorter than the C-H bond in ethane (1.09 A0) ,because the sp2 orbital in ethylene has more s character (one-third s) than a ...
excess
... 4. Sodium hydride, NaH, is an ionic compound. Na H a) Write the Lewis electron-dot structure for NaH. b) If NaH is placed into water (a foolish thing to do), the hydride ion is converted to hydrogen gas (H2). The resulting solution turns red litmus paper blue and has a pH OH Na>>7.H + H2O H2 + Na Wr ...
... 4. Sodium hydride, NaH, is an ionic compound. Na H a) Write the Lewis electron-dot structure for NaH. b) If NaH is placed into water (a foolish thing to do), the hydride ion is converted to hydrogen gas (H2). The resulting solution turns red litmus paper blue and has a pH OH Na>>7.H + H2O H2 + Na Wr ...
chemistry 30 / unit c chemical changes of organic compounds
... their origins and applications(eg. methane,methanol,ethane,ethanol,ethanioic acid,propane,benzene,octane glucose, polyethylene . K.3 Name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using IUPAC nomenclature guidelines for saturated and unsaturated aliphatic(including cy ...
... their origins and applications(eg. methane,methanol,ethane,ethanol,ethanioic acid,propane,benzene,octane glucose, polyethylene . K.3 Name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using IUPAC nomenclature guidelines for saturated and unsaturated aliphatic(including cy ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.







![mascp.adv_resveratrol_stm[1]_new](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008195330_1-e016cb7c8bad6a8972721cc545ffcfe1-300x300.png)














