oxidation–reduction reaction
... • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an oxidation–reduction reaction. • Also called redox reactions ...
... • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an oxidation–reduction reaction. • Also called redox reactions ...
No Slide Title
... • are polypeptides with high molecular masses • chains can be lined up with each other • the C=O and N-H bonds are polar due to a difference in electronegativity ...
... • are polypeptides with high molecular masses • chains can be lined up with each other • the C=O and N-H bonds are polar due to a difference in electronegativity ...
Sample pages 6 PDF
... acids. On the other hand, Cella’s procedure involves the use of a peracid as secondary oxidant, which is a strong oxidant that interferes with many functional groups. In 1987, Anelli et al. published 3 a landmark paper in which they showed that primary alcohols can be oxidized either to aldehydes or ...
... acids. On the other hand, Cella’s procedure involves the use of a peracid as secondary oxidant, which is a strong oxidant that interferes with many functional groups. In 1987, Anelli et al. published 3 a landmark paper in which they showed that primary alcohols can be oxidized either to aldehydes or ...
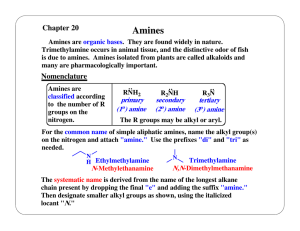
(C 2 H 5 ) 2 NH diethylamine, 2° amine
... • are polypeptides with high molecular masses • chains can be lined up with each other • the C=O and N-H bonds are polar due to a difference in electronegativity ...
... • are polypeptides with high molecular masses • chains can be lined up with each other • the C=O and N-H bonds are polar due to a difference in electronegativity ...
ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS
... The reactions involving the hydrogens of alcoholic O H groups are expected to be similar to those of water, H O H , the simplest hydroxylic compound. Alcohols, ROH, can be regarded in this respect as substitution products of water. However, with alcohols we shall be interested not only in reactions ...
... The reactions involving the hydrogens of alcoholic O H groups are expected to be similar to those of water, H O H , the simplest hydroxylic compound. Alcohols, ROH, can be regarded in this respect as substitution products of water. However, with alcohols we shall be interested not only in reactions ...
Solution Stoichiometry - Angelo State University
... • For a chemical reaction to occur, the reacting species have to come in close contact with each other. Most chemical reactions are performed in a solution (or in the gas phase) rather than in the solid state. • A solution consists of a smaller amount of one substance, the solute (usually a liquid o ...
... • For a chemical reaction to occur, the reacting species have to come in close contact with each other. Most chemical reactions are performed in a solution (or in the gas phase) rather than in the solid state. • A solution consists of a smaller amount of one substance, the solute (usually a liquid o ...
05 Halogen deriv. of hydrocarbons. Alcohols,ethers, esters
... ASSAY. Pharmacopoeia quantitative definition does not demand, but it is possible to use reaction with spirit solution of alkali for the back acid-base titration. To defined volume of investigated substance add excess of standard solution of alkali KOH: CHCl3 + 4KOH → НСООК + 3KCl + 2H2O ...
... ASSAY. Pharmacopoeia quantitative definition does not demand, but it is possible to use reaction with spirit solution of alkali for the back acid-base titration. To defined volume of investigated substance add excess of standard solution of alkali KOH: CHCl3 + 4KOH → НСООК + 3KCl + 2H2O ...
Chapter 2: Nomenclature and Structure
... a. longest carbon chain with parent (chain includes alcohol, for ex) 2. if a tie, parent chain (two or more possible), parent is one that has more substituents (more substituents = easier to name) 3. name and number substituents a. substituent is prefix b. number from side that gives smaller number ...
... a. longest carbon chain with parent (chain includes alcohol, for ex) 2. if a tie, parent chain (two or more possible), parent is one that has more substituents (more substituents = easier to name) 3. name and number substituents a. substituent is prefix b. number from side that gives smaller number ...
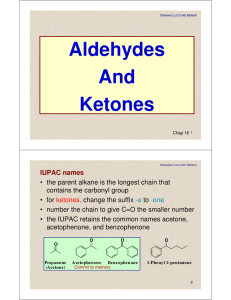
Aldehydes And Ketones
... zinc in concentrated HCl converts the carbonyl group to a methylene group – Classic reaction but harsh conditions limit its use ...
... zinc in concentrated HCl converts the carbonyl group to a methylene group – Classic reaction but harsh conditions limit its use ...
Magic of Chemical Reactions 2. - mt
... *1. Grills of doors and windows are always painted before they are used. Ans. 1. Railings, iron bridges, grills of doors and windows, railway coaches, steel furniture, and bodies of truck, cars, buses are made of iron. 2. To protect them from rusting, a coating of paint is applied. By doing this, ai ...
... *1. Grills of doors and windows are always painted before they are used. Ans. 1. Railings, iron bridges, grills of doors and windows, railway coaches, steel furniture, and bodies of truck, cars, buses are made of iron. 2. To protect them from rusting, a coating of paint is applied. By doing this, ai ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... 2.2.3 Zeroth-Order Reactions Zeroth order with respect to a particular reactant means that the chemical reaction rate does not depend on the concentration of that reactant. This can occur when the reactant is not involved in the slowest step of the reaction (the rate-limiting or rate-determining ste ...
... 2.2.3 Zeroth-Order Reactions Zeroth order with respect to a particular reactant means that the chemical reaction rate does not depend on the concentration of that reactant. This can occur when the reactant is not involved in the slowest step of the reaction (the rate-limiting or rate-determining ste ...
Ch 8 Lecture Notes
... Balance oxygen by adding water Balance hydrogen by adding (a) H+ in acidic solutions, (b) in basic solutions, continue as if in acidic solution, but at the end each H + ion will be neutralized by adding OH- ions 6. Balance charge by adding electrons; for the oxidation half-reaction, the electrons wi ...
... Balance oxygen by adding water Balance hydrogen by adding (a) H+ in acidic solutions, (b) in basic solutions, continue as if in acidic solution, but at the end each H + ion will be neutralized by adding OH- ions 6. Balance charge by adding electrons; for the oxidation half-reaction, the electrons wi ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2: Organic
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...
Chapter 3: Phase I File - E-Learning/An
... CYP2D6- 1950s patients were given sparteine as an inducer of labor –but in about 7% of the people tested, sparteine prolonged uterine contraction and produced abnormally rapid labor. Polymorphic: mutation in CYP2D6 which causes people to metabolize drugs poorly. CYP2E1: metabolize ethanol along with ...
... CYP2D6- 1950s patients were given sparteine as an inducer of labor –but in about 7% of the people tested, sparteine prolonged uterine contraction and produced abnormally rapid labor. Polymorphic: mutation in CYP2D6 which causes people to metabolize drugs poorly. CYP2E1: metabolize ethanol along with ...
Course Syllabus - San Diego Mesa College
... Textbook: Organic Chemistry 7th edition by John McMurray., Brooks/Cole Thomson Learning Pub., 1999. Student Guide and Solution Manual by Susan McMurray. The books can be purchased at the Mesa bookstore. Course Description, Goals, and Objectives; This is the first semester of one year course in Organ ...
... Textbook: Organic Chemistry 7th edition by John McMurray., Brooks/Cole Thomson Learning Pub., 1999. Student Guide and Solution Manual by Susan McMurray. The books can be purchased at the Mesa bookstore. Course Description, Goals, and Objectives; This is the first semester of one year course in Organ ...
answers to part a of the canadian chemistry
... answer in MB, compared with only 37% in AB). It requires students to choose the atom with the smallest atomic radius, which means that they need to know (1) that periods that are lower in the periodic table have larger atoms in them (because larger atoms have more electrons and some of these will be ...
... answer in MB, compared with only 37% in AB). It requires students to choose the atom with the smallest atomic radius, which means that they need to know (1) that periods that are lower in the periodic table have larger atoms in them (because larger atoms have more electrons and some of these will be ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... The Rules 1. The rule is that the cation is written first in a formula, followed by the anion. Example: in NaH, the H is H-; in HCl, the H is H+. + + 2. The oxidation number of a free element is always 0. Example: The atoms in He and N2, for example, have oxidation numbers of 0. 3. The oxidation nu ...
... The Rules 1. The rule is that the cation is written first in a formula, followed by the anion. Example: in NaH, the H is H-; in HCl, the H is H+. + + 2. The oxidation number of a free element is always 0. Example: The atoms in He and N2, for example, have oxidation numbers of 0. 3. The oxidation nu ...
2-D 3-D
... Optical Isomerism - The Optically Active Tetrahedral Carbon Optical isomerism is a type of isomerism that is frequently encounter throughout organic chemistry. It occurs because of the tetrahedral nature of the bonding around a carbon atom. Molecules may be chiral, or handed; think of your left and ...
... Optical Isomerism - The Optically Active Tetrahedral Carbon Optical isomerism is a type of isomerism that is frequently encounter throughout organic chemistry. It occurs because of the tetrahedral nature of the bonding around a carbon atom. Molecules may be chiral, or handed; think of your left and ...
Acids - Beck-Shop
... An acid is neutralised by a metal oxide or metal hydroxide to form a salt and water only. The equations below show the neutralisation of sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid by copper(II) oxide to form a salt and water only. Figure 3 shows solutions of the salts formed. CuO(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CuSO4(aq) ...
... An acid is neutralised by a metal oxide or metal hydroxide to form a salt and water only. The equations below show the neutralisation of sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid by copper(II) oxide to form a salt and water only. Figure 3 shows solutions of the salts formed. CuO(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CuSO4(aq) ...
Nuggets of Knowledge - Dixie State University
... • Intermolecular forces: The forces that attract molecules to each other are called intermolecular forces. They have a strong influence on physical properties. The three intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces (London forces), dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding. o Don’t confuse intermolecul ...
... • Intermolecular forces: The forces that attract molecules to each other are called intermolecular forces. They have a strong influence on physical properties. The three intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces (London forces), dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding. o Don’t confuse intermolecul ...
CHEM110P1_06_2015_Y_P1
... Antimony (atomic symbol Sb) consists of two naturally occurring isotopes; 121Sb with mass 120.904 u and an abundance of 57.21% and 123Sb with mass of 122.904 u and an abundance of 42.79%. Using this data, calculate the weighted average atomic mass of antimony. a) ...
... Antimony (atomic symbol Sb) consists of two naturally occurring isotopes; 121Sb with mass 120.904 u and an abundance of 57.21% and 123Sb with mass of 122.904 u and an abundance of 42.79%. Using this data, calculate the weighted average atomic mass of antimony. a) ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.