Turpentine Oil Hydration using Trichloroacetic Acid as Catalyst
... Hydration and isomerization of the α-pinene to several alcohol or terpenic hydrocarbons have been studied since the 1940s. Román-Aguirre et al. [9] utilised oxalic and chloroacetic acid for the transformation of α-pinene and obtained conversion of 80% with selectivity of 70% for α-terpineol after 4 ...
... Hydration and isomerization of the α-pinene to several alcohol or terpenic hydrocarbons have been studied since the 1940s. Román-Aguirre et al. [9] utilised oxalic and chloroacetic acid for the transformation of α-pinene and obtained conversion of 80% with selectivity of 70% for α-terpineol after 4 ...
C:\Users\mrh70950\Documents\My Files\WordPerfect
... i. anti-addition stereochemistry yields 1-alkenes from terminal alkynes and (E)-alkenes from internal alkynes 2. double hydrogenation: addition of 2 mol of H2 to yield alkanes a. noble metal catalyst + excess H2 3. electrophilic additions (all by very similar mechanisms) a. hydrohalogenation: addit ...
... i. anti-addition stereochemistry yields 1-alkenes from terminal alkynes and (E)-alkenes from internal alkynes 2. double hydrogenation: addition of 2 mol of H2 to yield alkanes a. noble metal catalyst + excess H2 3. electrophilic additions (all by very similar mechanisms) a. hydrohalogenation: addit ...
organic chemistry ii
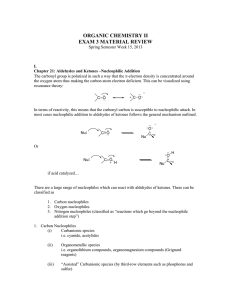
... Aldehydes and ketones which possess -hydrogens can undergo enolization. Most enols are unstable and reactive and instantly equilibrate to the “keto” form. Certain enols, such as -dicarbonyl compounds, among others, are exceptionally stable. Under basic conditions aldehydes and ketones form enolate ...
... Aldehydes and ketones which possess -hydrogens can undergo enolization. Most enols are unstable and reactive and instantly equilibrate to the “keto” form. Certain enols, such as -dicarbonyl compounds, among others, are exceptionally stable. Under basic conditions aldehydes and ketones form enolate ...
Gas Stoichiometry Worksheet
... Ammonium sulfate, an important fertilizer, can be prepared by the reaction of ammonia with sulfuric acid according to the following balanced equation: 2 NH3 (g) + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4 (aq) Calculate the volume of NH3 (in liters) needed at 20ºC and 25.0 atm to react with 150 kg of H2SO4. ...
... Ammonium sulfate, an important fertilizer, can be prepared by the reaction of ammonia with sulfuric acid according to the following balanced equation: 2 NH3 (g) + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4 (aq) Calculate the volume of NH3 (in liters) needed at 20ºC and 25.0 atm to react with 150 kg of H2SO4. ...
reactions of organic compounds
... • Common monomers are glucose and fructose. • Carbs found in bread, pasta, potatoes and fruits. • Primary source of energy – used in cellular ...
... • Common monomers are glucose and fructose. • Carbs found in bread, pasta, potatoes and fruits. • Primary source of energy – used in cellular ...
Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Which of the following statements is true? (A) a chiral molecule is not superimposable on its mirror image (B) glycine (Gly) is an amino acid which only has 1 chiral carbon (C) all amino acids are chiral (D) a chiral carbon has 3 identical groups bound to it (E) the following molecule is chiral: Cl ...
... Which of the following statements is true? (A) a chiral molecule is not superimposable on its mirror image (B) glycine (Gly) is an amino acid which only has 1 chiral carbon (C) all amino acids are chiral (D) a chiral carbon has 3 identical groups bound to it (E) the following molecule is chiral: Cl ...
Dissertation:
... Compounds such as hydroxyesters: methyl and ethyl lactate, and alcohols containing chlorine and fluorine (2-chloroethanol and 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol), allyl alcohol having a carbon-carbon double bonds (C=C) and long-chain aliphatic alcohols (C10-C16) were used. It has been shown that in the presence ...
... Compounds such as hydroxyesters: methyl and ethyl lactate, and alcohols containing chlorine and fluorine (2-chloroethanol and 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol), allyl alcohol having a carbon-carbon double bonds (C=C) and long-chain aliphatic alcohols (C10-C16) were used. It has been shown that in the presence ...
Study Questions - Labs - Department of Plant Biology, Cornell
... the vital force a dehydration reaction atom smashing ...
... the vital force a dehydration reaction atom smashing ...
Notes 07 Organometallic Compounds with notes
... The acidic work-up intermediate metal alkoxide salt alcohol via a simple acid-base reaction. ...
... The acidic work-up intermediate metal alkoxide salt alcohol via a simple acid-base reaction. ...
Week 11 Problem Set (Solutions)
... the product and starting material and where the starting material ends up in the product. The starting material has 2 carbons and a phenyl group, while the product has 6 carbons and two phenyl groups. The deuterium label helps to show that the starting material was most likely used twice in the synt ...
... the product and starting material and where the starting material ends up in the product. The starting material has 2 carbons and a phenyl group, while the product has 6 carbons and two phenyl groups. The deuterium label helps to show that the starting material was most likely used twice in the synt ...
L-13
... the reaction and led to the production of allylated product 3a in 80% yield (entry 2).[6] Strong Lewis acids such as AlCl3 or BF3・OEt2 were not effective for the allylation (entries 3 and 4), probably because these catalysts are not stable under protic conditions. Sc(OTf)3 only gave a low yield of 3 ...
... the reaction and led to the production of allylated product 3a in 80% yield (entry 2).[6] Strong Lewis acids such as AlCl3 or BF3・OEt2 were not effective for the allylation (entries 3 and 4), probably because these catalysts are not stable under protic conditions. Sc(OTf)3 only gave a low yield of 3 ...
ASYMMETRIC HYDROGENATIONS
... L-lysine and L-menthol have been made traditionally by biochemical routes even though efficient procedures are available to make their racemic forms. In the early 1960’s we became aware of this problem, when we made a paper evaluation of a monosodium glutamate process. The racemic mixture was easy t ...
... L-lysine and L-menthol have been made traditionally by biochemical routes even though efficient procedures are available to make their racemic forms. In the early 1960’s we became aware of this problem, when we made a paper evaluation of a monosodium glutamate process. The racemic mixture was easy t ...
Theory
... Formation of esters (esterification) The carboxylic acids, in general, react with alcohols in the presence of a mineral acid to form esters. Thus, reaction of acetic (ethanoic) acid with ethanol produces ethyl acetate (ethyl ethanoate). The sulfuric acid catalyses the esterification, and simultaneou ...
... Formation of esters (esterification) The carboxylic acids, in general, react with alcohols in the presence of a mineral acid to form esters. Thus, reaction of acetic (ethanoic) acid with ethanol produces ethyl acetate (ethyl ethanoate). The sulfuric acid catalyses the esterification, and simultaneou ...
C3 Knowledge Test – Higher Tier 1. Why was Mendeleev`s periodic
... What do we add to solutions to test for sulphate ions? Give two reasons why barium sulphate is given as a barium meal. What is an ‘end point’? 25.00cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution was pipetted into a conical flask. It was titrated against 0.10mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid. The mean volume of acid n ...
... What do we add to solutions to test for sulphate ions? Give two reasons why barium sulphate is given as a barium meal. What is an ‘end point’? 25.00cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution was pipetted into a conical flask. It was titrated against 0.10mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid. The mean volume of acid n ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.