Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 10 – Alkyl Halides II Chem 2310 I
... Alkyl shifts (most commonly methyl shifts) and hydride shifts can occur. They will only happen if the new carbocation is more stable than the original. ...
... Alkyl shifts (most commonly methyl shifts) and hydride shifts can occur. They will only happen if the new carbocation is more stable than the original. ...
Answer - Assignment Expert
... example?? Answer: A complex is a substance in which a metal atom or ion is associated with a group of neutral molecules or anions called ligands. Coordination compounds are neutral substances (i.e. uncharged) in which at least one ion is present as a complex. The coordination compounds are named in ...
... example?? Answer: A complex is a substance in which a metal atom or ion is associated with a group of neutral molecules or anions called ligands. Coordination compounds are neutral substances (i.e. uncharged) in which at least one ion is present as a complex. The coordination compounds are named in ...
Notetakers
... Ethanol is already partially oxidized, so it releases less energy than burning and alkane of comparable mass. However, it can be obtained by the fermentation of biomass; thus, in some countries it is mixed with gasoline to produce “gasohol” which decreases dependence on crude oil. Oxidation of a ...
... Ethanol is already partially oxidized, so it releases less energy than burning and alkane of comparable mass. However, it can be obtained by the fermentation of biomass; thus, in some countries it is mixed with gasoline to produce “gasohol” which decreases dependence on crude oil. Oxidation of a ...
كيمياء عضويةc - جامعة دمنهور
... Deduce chemical and structural formulas of organic compounds. Describe differences between and similarities of reactions of alkyl and aryl halides, alcohols and phenols, aldehydes and ketones. Differentiate the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones, and hydroxyl group in alcohols and phenols. Corr ...
... Deduce chemical and structural formulas of organic compounds. Describe differences between and similarities of reactions of alkyl and aryl halides, alcohols and phenols, aldehydes and ketones. Differentiate the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones, and hydroxyl group in alcohols and phenols. Corr ...
Integration of chemical catalysis with extractive fermentation to
... deoxygenated to paraffins. These paraffins, from pentane to undecane, are components of petrol, diesel and jet fuel. Using a synthetic ABE mixture of pure acetone, n-butanol and ethanol, we investigated the double alkylation of acetone to obtain heptan-4-one (B in Fig. 1) (alkylation with ethanol), ...
... deoxygenated to paraffins. These paraffins, from pentane to undecane, are components of petrol, diesel and jet fuel. Using a synthetic ABE mixture of pure acetone, n-butanol and ethanol, we investigated the double alkylation of acetone to obtain heptan-4-one (B in Fig. 1) (alkylation with ethanol), ...
Bulent Terem - CH324 - Syllabus | Chaminade
... Students are advised to review further divisional policies regarding the use of digital communication devices during class, as well as behavior which would cause distraction, such as (but not limited to) coming late to class and/or walking out of the room during class. ...
... Students are advised to review further divisional policies regarding the use of digital communication devices during class, as well as behavior which would cause distraction, such as (but not limited to) coming late to class and/or walking out of the room during class. ...
Theoretical Enthalpy
... formation by the number of moles for the balanced reaction, we can determine the enthalpy change for the independent steps, then use Hess’s Law to determine the enthalpy for the net reaction for the combustion of methane. ...
... formation by the number of moles for the balanced reaction, we can determine the enthalpy change for the independent steps, then use Hess’s Law to determine the enthalpy for the net reaction for the combustion of methane. ...
Electrolytes 1. List whether each of the following is a strong, weak, or
... ammine complexes can be utilized in selective precipitation procedures that bring about separation of the metals. The purification of nickel can be effected by reaction with carbon monoxide to form the volatile tetracarbonylnickel complex, which can be distilled and thermally decomposed to deposit t ...
... ammine complexes can be utilized in selective precipitation procedures that bring about separation of the metals. The purification of nickel can be effected by reaction with carbon monoxide to form the volatile tetracarbonylnickel complex, which can be distilled and thermally decomposed to deposit t ...
Chapter #2 - FIU Faculty Websites
... Ethene (ethylene) is a major industrial feedstock (30 B lbs/yr) z Used for production of ethanol, ethylene oxide and polyethylene ...
... Ethene (ethylene) is a major industrial feedstock (30 B lbs/yr) z Used for production of ethanol, ethylene oxide and polyethylene ...
Document
... bond of the multiple bond breaks so that two new bonds can form. To recognize an addition reaction, remember that two compounds usually react to form one major product. (Sometimes two isomers are formed.) The product has more atoms bonded to carbon atoms than the organic reactant did. A general exam ...
... bond of the multiple bond breaks so that two new bonds can form. To recognize an addition reaction, remember that two compounds usually react to form one major product. (Sometimes two isomers are formed.) The product has more atoms bonded to carbon atoms than the organic reactant did. A general exam ...
Polymers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Step 1: Locate the longest chain that contains the –OH group attached one carbon atom Step 2: Replace the –e at the end of the alkane with –OH Step 3: Add the position number before the root name to identify th position of the –OH group. If there is more than one –OH group, leave the –e in the name ...
... Step 1: Locate the longest chain that contains the –OH group attached one carbon atom Step 2: Replace the –e at the end of the alkane with –OH Step 3: Add the position number before the root name to identify th position of the –OH group. If there is more than one –OH group, leave the –e in the name ...
Expanding cements with controlled hardening time
... speed what accounts for ettringite formation as wide prisms with low - up to 3-5 relation of axes capable of producing high crystallization pressures. In such conditions, formation of additional quantity of ettringite makes for expanding ability of the cement, at the same time this process is easily ...
... speed what accounts for ettringite formation as wide prisms with low - up to 3-5 relation of axes capable of producing high crystallization pressures. In such conditions, formation of additional quantity of ettringite makes for expanding ability of the cement, at the same time this process is easily ...
Experiment 7
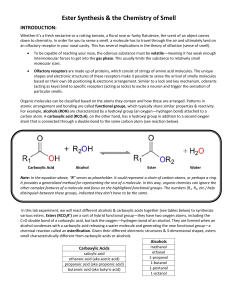
... 6. Repeat steps 3 through 5 until you have the two test tubes with two unique reactant mixtures: A) one making methyl salicylate, B) one making the ester of your choice. 7. Add a single drop of concentrated sulfuric acid to each of the test tubes. Your instructor will bring the sulfuric acid to your ...
... 6. Repeat steps 3 through 5 until you have the two test tubes with two unique reactant mixtures: A) one making methyl salicylate, B) one making the ester of your choice. 7. Add a single drop of concentrated sulfuric acid to each of the test tubes. Your instructor will bring the sulfuric acid to your ...
2010 Fall Final key
... carboxylic acid, aldehyde, ketone, ether, ester, amine, or amide? alcohol b. Does this image represent an alkane, alkene, alkyne, arene (aromatic), alcohol, carboxylic acid, aldehyde, ketone, ether, ester, amine, or amide? aldehyde c. Does this image represent an alkane, alkene, alkyne, arene (aroma ...
... carboxylic acid, aldehyde, ketone, ether, ester, amine, or amide? alcohol b. Does this image represent an alkane, alkene, alkyne, arene (aromatic), alcohol, carboxylic acid, aldehyde, ketone, ether, ester, amine, or amide? aldehyde c. Does this image represent an alkane, alkene, alkyne, arene (aroma ...
Why is sugar sweet?
... From last time we saw that the product of the Calvin cycle was glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. This can react with water to make the simplest sugar, glyceraldehyde, but most couples to form glucose. ...
... From last time we saw that the product of the Calvin cycle was glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. This can react with water to make the simplest sugar, glyceraldehyde, but most couples to form glucose. ...
Alcohols
... group OH attached to alkanes. • The general formula for alcohols is R-OH. Where “R” represents any chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • If there is more than one hydroxyl group, it is called a polyalcohol. They are named almost the same as regular alcohols except you add a “di”, “tri”, etc. before ...
... group OH attached to alkanes. • The general formula for alcohols is R-OH. Where “R” represents any chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • If there is more than one hydroxyl group, it is called a polyalcohol. They are named almost the same as regular alcohols except you add a “di”, “tri”, etc. before ...
Alcohols - WordPress.com
... not), forming soluble salts that are soluble in dilute aqueous A phenolic component can be separated from an organic solution by extraction into basic aqueous solution and is isolated after acid is added to the solution ...
... not), forming soluble salts that are soluble in dilute aqueous A phenolic component can be separated from an organic solution by extraction into basic aqueous solution and is isolated after acid is added to the solution ...
Additional Structures to Accompany Exp
... Structures of some Aldehydes and Ketones: Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group. In an aldehyde, the carbonyl group has a hydrogen attached; the aldehyde functional group occurs at the end of the carbon chain. In a ketone, the carbonyl group is located between two of the carbon atoms with ...
... Structures of some Aldehydes and Ketones: Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group. In an aldehyde, the carbonyl group has a hydrogen attached; the aldehyde functional group occurs at the end of the carbon chain. In a ketone, the carbonyl group is located between two of the carbon atoms with ...
CBS Reduction
... reduction of ketones , using chip-microreactors. • They used BH3 , (85% 2-MeTHF, 15% THF) and oxazaborolidine for reduction. • Under such reaction conditions, the reaction was complete in 10 minutes and alcohol was produced with 95% yield and a 91 : 9 enantiomeric ratio (highly enantioselectivety). ...
... reduction of ketones , using chip-microreactors. • They used BH3 , (85% 2-MeTHF, 15% THF) and oxazaborolidine for reduction. • Under such reaction conditions, the reaction was complete in 10 minutes and alcohol was produced with 95% yield and a 91 : 9 enantiomeric ratio (highly enantioselectivety). ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.