IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Items essentials for human survival such as, food, medicine etc. are produced by chemical reactions directly or indirectly in nature or in industry. Other items such as cosmetics, which are also deemed essentials in affluent societies, are also obtained by above means. It is the biggest challenge in ...
... Items essentials for human survival such as, food, medicine etc. are produced by chemical reactions directly or indirectly in nature or in industry. Other items such as cosmetics, which are also deemed essentials in affluent societies, are also obtained by above means. It is the biggest challenge in ...
Answers / Solutions
... and irradiating it with ultraviolet light, it forms only one monochloroalkane. The alkane is: a) isopentane b) neopentane c)) p propane p d)) p pentane Neopentane (CH3)4C is a symmetrical alkane lk and d gives i only l one monoalkane derivative. ANSWER: b ...
... and irradiating it with ultraviolet light, it forms only one monochloroalkane. The alkane is: a) isopentane b) neopentane c)) p propane p d)) p pentane Neopentane (CH3)4C is a symmetrical alkane lk and d gives i only l one monoalkane derivative. ANSWER: b ...
chm238f02.exam2
... (d) This type of rearrangement can occur when trying to hydrate an alkene in acid. If we add water and acid (acid catalyzed hydration) to the 3-Methyl-1-butene, the main product is 2-methyl-2-butanol. ...
... (d) This type of rearrangement can occur when trying to hydrate an alkene in acid. If we add water and acid (acid catalyzed hydration) to the 3-Methyl-1-butene, the main product is 2-methyl-2-butanol. ...
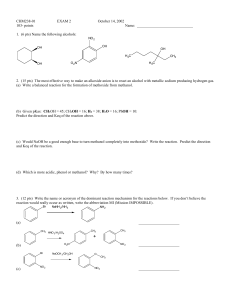
CHM238-01 EXAM 2 October 14, 2002 103
... 5. (12 pts) Preparation of alcohols by Grignard reagents reacted with C=O compounds is very important. (a) If the Grignard reagent were phenyl Grignard, PhMgBr, what C=O compound would be the best one to use in order to make the following alcohols. If it doesn’t work, write NR. (b) If the Grignard ...
... 5. (12 pts) Preparation of alcohols by Grignard reagents reacted with C=O compounds is very important. (a) If the Grignard reagent were phenyl Grignard, PhMgBr, what C=O compound would be the best one to use in order to make the following alcohols. If it doesn’t work, write NR. (b) If the Grignard ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... eliminations, often with his long-time collaborator E. D. Hughes, led to I ncorporation into the standard language of chemistry of such words as nucleophile, electrophile, inductive and mesomeric (resonance) effects, and such symbols as SN1, SN2, E1, E2, BAC2 and others. His monumental book "Structu ...
... eliminations, often with his long-time collaborator E. D. Hughes, led to I ncorporation into the standard language of chemistry of such words as nucleophile, electrophile, inductive and mesomeric (resonance) effects, and such symbols as SN1, SN2, E1, E2, BAC2 and others. His monumental book "Structu ...
Example 4
... Break the O-H bond of one alcohol. Break one of the C=O Break the H-H bond. bonds. Form a bond between the carbonyl carbon and the O of Break one of the C=O the alcohol. Form a bond between the H and the O of the bonds. Form a bond carbonyl to form a HEMIACETAL. between the alpha-carbon and one H. F ...
... Break the O-H bond of one alcohol. Break one of the C=O Break the H-H bond. bonds. Form a bond between the carbonyl carbon and the O of Break one of the C=O the alcohol. Form a bond between the H and the O of the bonds. Form a bond carbonyl to form a HEMIACETAL. between the alpha-carbon and one H. F ...
communication - Kyushu University Library
... given all the obtained NOEs, the alkoxide anion is likely located near hydroxy group of the ammonium cation. Furthermore, it was reported that BH4– anion of the N-9-anthracenylmethyl cinchonidinium tetrahydroborate salt prefers to be located near the 9-hydroxy group in the literature.[14] These fact ...
... given all the obtained NOEs, the alkoxide anion is likely located near hydroxy group of the ammonium cation. Furthermore, it was reported that BH4– anion of the N-9-anthracenylmethyl cinchonidinium tetrahydroborate salt prefers to be located near the 9-hydroxy group in the literature.[14] These fact ...
22.4: Acidity of Phenols.
... Chapter 22: Phenols. Alcohols contain an OH group bonded to an sp3-hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an OH group bonded to an sp2-hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 22.1: Nomenclature (please read) 22.2: Structure and Bonding (please read) 22.3: Physical Properties (please read). Like other alcoho ...
... Chapter 22: Phenols. Alcohols contain an OH group bonded to an sp3-hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an OH group bonded to an sp2-hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 22.1: Nomenclature (please read) 22.2: Structure and Bonding (please read) 22.3: Physical Properties (please read). Like other alcoho ...
Copper-catalysed selective hydroamination reactions of alkynes Please share
... vinylcopper species 11. In the absence of a proton source (alcohol), direct interception by electrophilic amine 2 (likely via oxidative addition/reductive elimination) would produce the (E)-enamine product 4 and copper benzoate complex 13 that, upon transmetalation with hydrosilane, would regenerate ...
... vinylcopper species 11. In the absence of a proton source (alcohol), direct interception by electrophilic amine 2 (likely via oxidative addition/reductive elimination) would produce the (E)-enamine product 4 and copper benzoate complex 13 that, upon transmetalation with hydrosilane, would regenerate ...
Review of Organic Chem II
... 3. The types of intermediates involved (cation, anion, or radical) should be consistent with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a r ...
... 3. The types of intermediates involved (cation, anion, or radical) should be consistent with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a r ...
Document
... • Halogen: normally forms one covalent bond and has three unshared pairs of electrons. © 2006 Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved ...
... • Halogen: normally forms one covalent bond and has three unshared pairs of electrons. © 2006 Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved ...
Chapter 8 I. Nucleophilic Substitution
... Physicist Roland Wester and his team in Matthias Weidemüller's group at the University of Freiburg, in Germany, in collaboration with William L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected m ...
... Physicist Roland Wester and his team in Matthias Weidemüller's group at the University of Freiburg, in Germany, in collaboration with William L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected m ...
Chem 240 - Napa Valley College
... good he added twice as much benzaldehyde as Grignard reagent and got a lot of white crystalline product. When he analyzed his product he found that he had not made diphenyl methanol, but diphenyl methanal (also called benzophenone) instead. When he asked his research director about it he was told th ...
... good he added twice as much benzaldehyde as Grignard reagent and got a lot of white crystalline product. When he analyzed his product he found that he had not made diphenyl methanol, but diphenyl methanal (also called benzophenone) instead. When he asked his research director about it he was told th ...
12_chemistry_impq_CH10_haloalkanes_and_haloarenes_02
... . Ans. The C-O bond in phenol acquires partial double bond character due to resonance and hence be cleared by X- ions to form halobenzenes. But in alcohols a pure C — O bond is maintained and can be cleared by X– ions. Q 3. Explain why o-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxy phenol? Ans . Due to ...
... . Ans. The C-O bond in phenol acquires partial double bond character due to resonance and hence be cleared by X- ions to form halobenzenes. But in alcohols a pure C — O bond is maintained and can be cleared by X– ions. Q 3. Explain why o-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxy phenol? Ans . Due to ...
Chapter 23 - Organic Chemistry
... Polar functional groups in these polymers produce strong intermolecular forces that add significant tensile strength to the material. ...
... Polar functional groups in these polymers produce strong intermolecular forces that add significant tensile strength to the material. ...
Module 5 Reactions with Miscellaneous Reagents
... Alkenes react with NBS in dry CCl4 under reflux conditions to give allyl bromide. The reaction is initiated by light or peroxide. Although a number of reagents are available for bromination of allylic C-H bond of alkenes, NBS is most commonly used. The reaction is called Wohl-Zigler bromination. For ...
... Alkenes react with NBS in dry CCl4 under reflux conditions to give allyl bromide. The reaction is initiated by light or peroxide. Although a number of reagents are available for bromination of allylic C-H bond of alkenes, NBS is most commonly used. The reaction is called Wohl-Zigler bromination. For ...
Si(OR - am Lehrstuhl für Bauchemie
... While carbon forms an extensive series of compounds with hydrogen, the list of silicon analogs is limited. Compounds between silicon and hydrogen are called hydrides and can be viewed as analogs of alkanes. The first silicon hydrides were made in 1857 by Friedrich Wöhler and Heinrich Buff who reacte ...
... While carbon forms an extensive series of compounds with hydrogen, the list of silicon analogs is limited. Compounds between silicon and hydrogen are called hydrides and can be viewed as analogs of alkanes. The first silicon hydrides were made in 1857 by Friedrich Wöhler and Heinrich Buff who reacte ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
... Task: convert to a staggered structure wherein H and Br are anti and predict product. We will convert to a Newman and see what we get… Ph ...
... Task: convert to a staggered structure wherein H and Br are anti and predict product. We will convert to a Newman and see what we get… Ph ...
Richard R. Schrock - Nobel Lecture
... state “homoleptic” or “peralkyl” compounds such as M[CH2Si(CH3)3]4, M(CH2C6H5)4, and M[CH2C(CH3)3]4 (M = Ti, Zr, or Hf; Fig 2), were rationalized on the basis of the fact that unlike a compound having an ethyl ligand, the alkyl ligands in these species lack  hydrogens and so of course cannot underg ...
... state “homoleptic” or “peralkyl” compounds such as M[CH2Si(CH3)3]4, M(CH2C6H5)4, and M[CH2C(CH3)3]4 (M = Ti, Zr, or Hf; Fig 2), were rationalized on the basis of the fact that unlike a compound having an ethyl ligand, the alkyl ligands in these species lack  hydrogens and so of course cannot underg ...
1 1. (20 pts.) Draw the major product of each of the following
... reactions. Assume aqueous workup in all cases (that is, draw neutral products). Do not draw mechanisms! (a) ...
... reactions. Assume aqueous workup in all cases (that is, draw neutral products). Do not draw mechanisms! (a) ...
HPLC and LC–MS Studies of the Transesterification Reaction of
... of the reaction on the effectiveness of the paraben preservatives in pharmaceutical formulation, the kinetics of the transesterification reaction has been studied for parabens with sorbitol, xylitol, erythritol, and glycerol (2). The identities of the reaction products have been investigated for met ...
... of the reaction on the effectiveness of the paraben preservatives in pharmaceutical formulation, the kinetics of the transesterification reaction has been studied for parabens with sorbitol, xylitol, erythritol, and glycerol (2). The identities of the reaction products have been investigated for met ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.