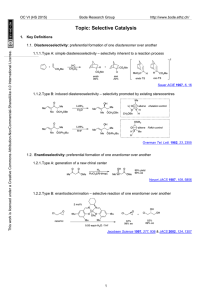
Carbonyl α-substitution and Condensation Reactions
... Carbonyl condensation reactions take place between two carbonyl partners and involve a combination of nucleophilic addition and a-substitution steps. One partner (the nucleophilic donor) is converted into an enolate ion and undergoes an a-substitution reaction, while the other partner (the electroph ...
... Carbonyl condensation reactions take place between two carbonyl partners and involve a combination of nucleophilic addition and a-substitution steps. One partner (the nucleophilic donor) is converted into an enolate ion and undergoes an a-substitution reaction, while the other partner (the electroph ...
Amino Alcohol Oxidation with Gold Catalysts: The Effect of Amino
... acids by direct oxidation of amino alcohols, using O2 as oxidant, in the presence of heterogeneous catalysts, represents a suitable alternative. The main problem lies on the high affinity of nitrogen for metal such as Pt or Pd, which lead to active sites blocking [7]. Gold catalyst appeared more res ...
... acids by direct oxidation of amino alcohols, using O2 as oxidant, in the presence of heterogeneous catalysts, represents a suitable alternative. The main problem lies on the high affinity of nitrogen for metal such as Pt or Pd, which lead to active sites blocking [7]. Gold catalyst appeared more res ...
DEVELOPMENT OF GREEN AND OF POLYMER
... Cerium (IV) salts are strong oxidants that show selectivity for the oxidation of secondary alcohols relative to primary alcohols.4 Cerium (IV) sulfate oxidation, done in acidic media, is a selective oxidant for the preparation of quinones. Ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) in water or in 50% acetic acid ...
... Cerium (IV) salts are strong oxidants that show selectivity for the oxidation of secondary alcohols relative to primary alcohols.4 Cerium (IV) sulfate oxidation, done in acidic media, is a selective oxidant for the preparation of quinones. Ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) in water or in 50% acetic acid ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... ___________________ of OH groups and place the numbers between the parent name and the suffix ***Note, if the suffix starts with a vowel, drop the “e” on the parent name; if the suffix starts with a consonant, keep the “e” on the parent name ...
... ___________________ of OH groups and place the numbers between the parent name and the suffix ***Note, if the suffix starts with a vowel, drop the “e” on the parent name; if the suffix starts with a consonant, keep the “e” on the parent name ...
Get PDF - Wiley Online Library
... Interestingly, ring-closing metathesis of 10 proceeded without problems in a yield of 79 %. Apparently, the impossibility of isomerization of 10 in combination with a constrained geometry eliminates all side reactions. Thus, formation of six-membered cyclic dehydroamino acids by RCM can indeed occur ...
... Interestingly, ring-closing metathesis of 10 proceeded without problems in a yield of 79 %. Apparently, the impossibility of isomerization of 10 in combination with a constrained geometry eliminates all side reactions. Thus, formation of six-membered cyclic dehydroamino acids by RCM can indeed occur ...
CHEM 121 Chapter 14. Name: Date: ______ 1. The simplest alcohol
... 23. The solubility of alcohols in water A) decreases as the carbon chain length increases. B) decreases as the number of –OH groups present increases. C) increases with increasing molecular mass. D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 24. In a secondary alcohol, the hydroxyl-bearin ...
... 23. The solubility of alcohols in water A) decreases as the carbon chain length increases. B) decreases as the number of –OH groups present increases. C) increases with increasing molecular mass. D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 24. In a secondary alcohol, the hydroxyl-bearin ...
Chapter 16_CHEM 131
... • The N-H bond is not quite as polar as the O-H bond. • Primary and secondary amines can form hydrogen bonds between molecules. • The hydrogen bonds are not as strong as those of alcohols, so amine boiling points are somewhat lower than those of alcohols. • Simple, low molecular weight amines are ga ...
... • The N-H bond is not quite as polar as the O-H bond. • Primary and secondary amines can form hydrogen bonds between molecules. • The hydrogen bonds are not as strong as those of alcohols, so amine boiling points are somewhat lower than those of alcohols. • Simple, low molecular weight amines are ga ...
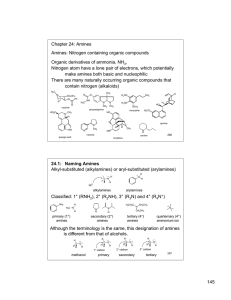
Chapter 24. Amines
... Alkyl group (-R) migrates to the neighboring electron-deficient nitrogen. Hydration of the resultant isocyanate gives carboxamic acid. ...
... Alkyl group (-R) migrates to the neighboring electron-deficient nitrogen. Hydration of the resultant isocyanate gives carboxamic acid. ...
Monomer
... ⇒ -TiCl3 (brown color) was found to be effective for the polymerization (prepared by mixing TiCl4 with H2, aluminium, or alkylaluminiums Still isotacticity 20 – 40 % with Al(C2H5)2Cl -, -, -crystals of TiCl3 were found to increase the isoctacticity ...
... ⇒ -TiCl3 (brown color) was found to be effective for the polymerization (prepared by mixing TiCl4 with H2, aluminium, or alkylaluminiums Still isotacticity 20 – 40 % with Al(C2H5)2Cl -, -, -crystals of TiCl3 were found to increase the isoctacticity ...
Changing counterion can switch the preference for selective 1,2
... Through tuning of conditions, this catalyst system can achieve either ketone- or aldehyde-selectivity. ...
... Through tuning of conditions, this catalyst system can achieve either ketone- or aldehyde-selectivity. ...
000217986-Tajbakhsh_et_al_
... diethyl ether (10 mL) the reagent (1.0 mmol) was added and the mixture stirred at room temperature or under reflux for the specified time (Tables 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6).6 The progress of the reaction was followed by TLC (eluent: CCl4 /diethyl ether). On completion of the reaction, the mixture was filtered a ...
... diethyl ether (10 mL) the reagent (1.0 mmol) was added and the mixture stirred at room temperature or under reflux for the specified time (Tables 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6).6 The progress of the reaction was followed by TLC (eluent: CCl4 /diethyl ether). On completion of the reaction, the mixture was filtered a ...
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
... Amines are more basic than alcohols, and they react with the carboxylic acid by acidbase reaction. The resulting ammonium ions do not have lone pairs, and therefore do not act as nucleophiles. This prevents the amine from reacting with the carbonyl (C=O) carbon and forming the amide. ...
... Amines are more basic than alcohols, and they react with the carboxylic acid by acidbase reaction. The resulting ammonium ions do not have lone pairs, and therefore do not act as nucleophiles. This prevents the amine from reacting with the carbonyl (C=O) carbon and forming the amide. ...
Organic Chemistry II
... Alkyl Halides We did talk about halo-alkanes (called alkyl halides) which are alkanes with a halogen attached. These molecules do, in fact, have polar bonds: C-Br, C-I, C-Cl are all polar bonds. Carbon is slightly positive, the halogen is slightly negative. ...
... Alkyl Halides We did talk about halo-alkanes (called alkyl halides) which are alkanes with a halogen attached. These molecules do, in fact, have polar bonds: C-Br, C-I, C-Cl are all polar bonds. Carbon is slightly positive, the halogen is slightly negative. ...
IR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectroscopy
... Variations in C=O Absorption ¾ The position of the absorption band depends on electron delocalization, the electronic effect of neighboring substituents, and hydrogen bonding. ¾ As conjugation lower the C=C stretching frequency, it also lower the C=O absorption frequency to ~ 1680 cm-1. ...
... Variations in C=O Absorption ¾ The position of the absorption band depends on electron delocalization, the electronic effect of neighboring substituents, and hydrogen bonding. ¾ As conjugation lower the C=C stretching frequency, it also lower the C=O absorption frequency to ~ 1680 cm-1. ...
Class Notes Test 1
... A. IUPAC, when alcohol is priority functional group and is part of the core name: alkan-x-ol • Choose longest carbon chain that has the OH attached • Remember to number! (including if it’s on carbon number 1) • The oxygen itself does not count as a number OH ...
... A. IUPAC, when alcohol is priority functional group and is part of the core name: alkan-x-ol • Choose longest carbon chain that has the OH attached • Remember to number! (including if it’s on carbon number 1) • The oxygen itself does not count as a number OH ...
Stereoselective synthesis: chiral auxiliaries
... • A number of alternative boron reagents have been developed for the synthesis of homoallylic alcohols • These either give improved enantiomeric excess, diastereoselectivity or ease of ...
... • A number of alternative boron reagents have been developed for the synthesis of homoallylic alcohols • These either give improved enantiomeric excess, diastereoselectivity or ease of ...
145 Chapter 24: Amines Amines: Nitrogen containing organic
... Synthesis of primary amines from the reaction of alkyl halides or tosylates with “ammonia equivalents” Azide ion is a very strong nucleophile and react with 1° or 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction. The resulting azide can be reduced to a 1° amine. H N N N ...
... Synthesis of primary amines from the reaction of alkyl halides or tosylates with “ammonia equivalents” Azide ion is a very strong nucleophile and react with 1° or 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction. The resulting azide can be reduced to a 1° amine. H N N N ...
1 Bite Angle Effects of Diphosphines in Carbonylation Reactions
... years to the development of systems with improved regioselectivity toward the formation of the industrially more important linear aldehyde. Both phosphine- and phosphite-based systems giving high regioselectivities to linear aldehyde for the hydroformylation of terminal and internal alkenes have bee ...
... years to the development of systems with improved regioselectivity toward the formation of the industrially more important linear aldehyde. Both phosphine- and phosphite-based systems giving high regioselectivities to linear aldehyde for the hydroformylation of terminal and internal alkenes have bee ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.