lecture 7 reductive eliminations
... however, a vacant 2e site is always required on the metal. • We can either start with a 16e complex or a 2e site must be opened up in an 18e complex by the loss of a ligand producing a 16e intermediate species. • The change in oxidation state means that the starting metal complex of a given oxidatio ...
... however, a vacant 2e site is always required on the metal. • We can either start with a 16e complex or a 2e site must be opened up in an 18e complex by the loss of a ligand producing a 16e intermediate species. • The change in oxidation state means that the starting metal complex of a given oxidatio ...
phenol
... larger, the compound begins to look more like an alkane, and more of the hydrogen bonds in water must be broken to make room for the hydrocarbon chain. Since the hydrogen bonds that are lost are not completely compensated by bonding to the alcohol ОН, solubility decreases as the hydrocarbon chain ge ...
... larger, the compound begins to look more like an alkane, and more of the hydrogen bonds in water must be broken to make room for the hydrocarbon chain. Since the hydrogen bonds that are lost are not completely compensated by bonding to the alcohol ОН, solubility decreases as the hydrocarbon chain ge ...
AMINES
... Ans) This is because FeCl2 formed gets hydrolysed to release HCl in the reaction. Thus, only a small amount of HCl is required to initiate the reaction. Q2) Ammonlysis of R-X is not a preferred method for preparing amines Ans) This method yields a mixture of primary, secondary, tertiary a mines and ...
... Ans) This is because FeCl2 formed gets hydrolysed to release HCl in the reaction. Thus, only a small amount of HCl is required to initiate the reaction. Q2) Ammonlysis of R-X is not a preferred method for preparing amines Ans) This method yields a mixture of primary, secondary, tertiary a mines and ...
Cl3CCN/PPh3 and CBr4/PPh3: two efficient reagent systems for the
... The utility of N-heteroaromatic halides is well documented. They represent important intermediates in organic transformations and are of pharmaceutical interest. These halides often participate as valuable precursors for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds via cross-coupling reactions, such as Stil ...
... The utility of N-heteroaromatic halides is well documented. They represent important intermediates in organic transformations and are of pharmaceutical interest. These halides often participate as valuable precursors for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds via cross-coupling reactions, such as Stil ...
Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Norbornene by Cp
... equiv of MAO per Cp*2Os2Br4 unit are sufficient. In toluene with Cp*2Os2Br4/MAO as the catalyst, 1000 equiv of NBE is polymerized at room temperature to give 77 kg per mole of catalyst, which corresponds to 81% conversion. When 2000 equiv of NBE are added to a toluene solution of Cp*2Os2Br4 and MAO, ...
... equiv of MAO per Cp*2Os2Br4 unit are sufficient. In toluene with Cp*2Os2Br4/MAO as the catalyst, 1000 equiv of NBE is polymerized at room temperature to give 77 kg per mole of catalyst, which corresponds to 81% conversion. When 2000 equiv of NBE are added to a toluene solution of Cp*2Os2Br4 and MAO, ...
molecules Palladium and Organocatalysis: An Excellent Recipe for Asymmetric Synthesis
... combined for the improvement of catalytic processes [4–6]. The combination of organocatalysis and transition-metal catalysis allows not only the development of novel transformations, but also the enhancement of the stereochemistry, efficiency and/or scope of well known reactions [7]. One of the main ...
... combined for the improvement of catalytic processes [4–6]. The combination of organocatalysis and transition-metal catalysis allows not only the development of novel transformations, but also the enhancement of the stereochemistry, efficiency and/or scope of well known reactions [7]. One of the main ...
- University at Albany
... Alkynes: Are hydrocarbons that contain carbon-carbon triple bonds. Are also known as acetylenes. Have the general structural formula CnH2n-2. Are similar in physical properties to alkanes and alkenes. They are nonpolar and water insoluble. The triple bond is shorter than C=C and C-C bonds wit ...
... Alkynes: Are hydrocarbons that contain carbon-carbon triple bonds. Are also known as acetylenes. Have the general structural formula CnH2n-2. Are similar in physical properties to alkanes and alkenes. They are nonpolar and water insoluble. The triple bond is shorter than C=C and C-C bonds wit ...
Organic Compounds containing Oxygen
... Finally this method is not useful for the preparation of ether with 30 alcohol because they form alkene too easily. This method is not useful for the praparation of unsymmetrical ethers from primary alcohols because the reaction leads to a mixture of products. ...
... Finally this method is not useful for the preparation of ether with 30 alcohol because they form alkene too easily. This method is not useful for the praparation of unsymmetrical ethers from primary alcohols because the reaction leads to a mixture of products. ...
alcohols (2013)
... Recall and explain the physical properties of alcohols Recall the different structural types of alcohols Recall and explain the chemical reactions of alcohols Write balanced equations representing any reactions in the section Understand how oxidation is affected by structure Recall how conditions an ...
... Recall and explain the physical properties of alcohols Recall the different structural types of alcohols Recall and explain the chemical reactions of alcohols Write balanced equations representing any reactions in the section Understand how oxidation is affected by structure Recall how conditions an ...
- kunleoloruntegbe.com
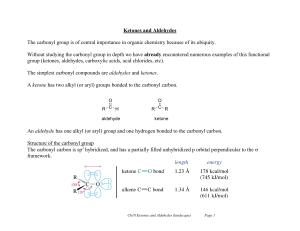
... And this carbonyl compound is produced by which the carbon atom reacts with a double bond of oxygen atom. O C Carbonyl group Alkanal have at least one hydrogen atom bonded to the carbon atom as well as the oxygen. O R C H where R= H alkyl group Alkanal therefore has two organic radicals attached to ...
... And this carbonyl compound is produced by which the carbon atom reacts with a double bond of oxygen atom. O C Carbonyl group Alkanal have at least one hydrogen atom bonded to the carbon atom as well as the oxygen. O R C H where R= H alkyl group Alkanal therefore has two organic radicals attached to ...
New Phenylglycine-Derived Primary Amine Organocatalysts for the
... anticipated by us that introducing sterically more demanding side chains through cyclohexylglycine or tert-leucine (amino alcohols 16–17) would enhance the enantioselectivity even further, a hypothesis obviously invalidated by experiment. Clearly, the presence of an aromatic moiety is crucial. Among ...
... anticipated by us that introducing sterically more demanding side chains through cyclohexylglycine or tert-leucine (amino alcohols 16–17) would enhance the enantioselectivity even further, a hypothesis obviously invalidated by experiment. Clearly, the presence of an aromatic moiety is crucial. Among ...
REASONING QUESTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... 33. Carboxylic acids are having higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive associatio ...
... 33. Carboxylic acids are having higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive associatio ...
REASONING QUESTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TEXT
... 33. Carboxylic acids are having higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive associatio ...
... 33. Carboxylic acids are having higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive associatio ...
Advanced Practical Organic Chemistry
... are called single bonds and are generally stable and resistant to attack by other chemicals. Alkanes contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible. They are said to be saturated. The alkanes are not the only hydrocarbons. Alkenes Another series of compounds is called the alkenes. These have ...
... are called single bonds and are generally stable and resistant to attack by other chemicals. Alkanes contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible. They are said to be saturated. The alkanes are not the only hydrocarbons. Alkenes Another series of compounds is called the alkenes. These have ...
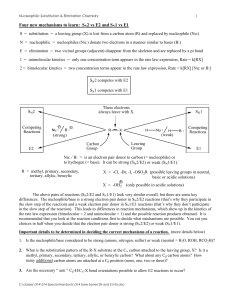
Four new mechanisms to learn: SN2 vs E2 and SN1 vs E1
... 1. Is the nucleophile/base considered to be strong (anions, nitrogen, sulfur) or weak (neutral = H2O, ROH, RCO2H)? 2. What is the substitution pattern of the R-X substrate at the Cα carbon attached to the leaving group, X? Is it a methyl, primary, secondary, tertiary, allylic, or benzylic carbon? Wh ...
... 1. Is the nucleophile/base considered to be strong (anions, nitrogen, sulfur) or weak (neutral = H2O, ROH, RCO2H)? 2. What is the substitution pattern of the R-X substrate at the Cα carbon attached to the leaving group, X? Is it a methyl, primary, secondary, tertiary, allylic, or benzylic carbon? Wh ...
MAGNESIUM STEARATE
... Other contamination can also occur during the manufacturing process of the magnesium stearate. According to a December 2011 report by the World Health Organization (WHO), several batches of magnesium stearate by a particular manufacturer were found to contain various levels of harmful contaminants s ...
... Other contamination can also occur during the manufacturing process of the magnesium stearate. According to a December 2011 report by the World Health Organization (WHO), several batches of magnesium stearate by a particular manufacturer were found to contain various levels of harmful contaminants s ...
Organic Chemistry - UCR Chemistry
... We can prevent this by using modified Cr(VI) reagents that we describe later in this section. We can also distill the intermediate aldehyde from the reaction mixture as it forms before it is oxidized further. This is often possible because boiling points of aldehydes are usually much lower than thos ...
... We can prevent this by using modified Cr(VI) reagents that we describe later in this section. We can also distill the intermediate aldehyde from the reaction mixture as it forms before it is oxidized further. This is often possible because boiling points of aldehydes are usually much lower than thos ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.