HPLC and LC–MS Studies of the Transesterification Reaction of
... of the reaction on the effectiveness of the paraben preservatives in pharmaceutical formulation, the kinetics of the transesterification reaction has been studied for parabens with sorbitol, xylitol, erythritol, and glycerol (2). The identities of the reaction products have been investigated for met ...
... of the reaction on the effectiveness of the paraben preservatives in pharmaceutical formulation, the kinetics of the transesterification reaction has been studied for parabens with sorbitol, xylitol, erythritol, and glycerol (2). The identities of the reaction products have been investigated for met ...
15. Benzene and Aromaticity
... 3 bonding orbitals with 6 e-s, 3 antibonding with no electrons Orbitals with same energy are degenerate ...
... 3 bonding orbitals with 6 e-s, 3 antibonding with no electrons Orbitals with same energy are degenerate ...
Organic Chemistry Notes by Jim Maxka jim.maxka
... First some stuff to memorize: Oxidation means gain of bonds Æ O; Loss of bonds Æ H. Reduction means gain of bonds Æ H; Loss of bonds Æ O. CH4 is the most oxidized or reduced organic molecule? What is the oxidation state of C? What is the most oxidized? What is the oxidation state of C? How about the ...
... First some stuff to memorize: Oxidation means gain of bonds Æ O; Loss of bonds Æ H. Reduction means gain of bonds Æ H; Loss of bonds Æ O. CH4 is the most oxidized or reduced organic molecule? What is the oxidation state of C? What is the most oxidized? What is the oxidation state of C? How about the ...
Topic 7: Manipulating Molecules and Designing Drugs
... distance of 1.20 .....................................................4 distance of 1.34 .....................................................4 distance of 1.54 .....................................................4 drug candidate to market ......................................... 21 ...
... distance of 1.20 .....................................................4 distance of 1.34 .....................................................4 distance of 1.54 .....................................................4 drug candidate to market ......................................... 21 ...
Topic 7: Manipulating Molecules and Designing Drugs
... distance of 1.20 .....................................................4 distance of 1.34 .....................................................4 distance of 1.54 .....................................................4 drug candidate to market ......................................... 21 ...
... distance of 1.20 .....................................................4 distance of 1.34 .....................................................4 distance of 1.54 .....................................................4 drug candidate to market ......................................... 21 ...
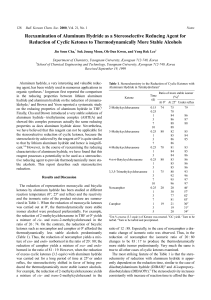
Reexamination of Aluminum Hydride as a Stereoselective Reducing
... The reduction of representative monocyclic and bicyclic ketones by aluminum hydride has been studied at different reaction temperature (0o, 25o and reflux) and the reactivity and the isomeric ratio of the product mixture are summarized in Table 1. When the reduction of monocyclic ketones was carried ...
... The reduction of representative monocyclic and bicyclic ketones by aluminum hydride has been studied at different reaction temperature (0o, 25o and reflux) and the reactivity and the isomeric ratio of the product mixture are summarized in Table 1. When the reduction of monocyclic ketones was carried ...
Chapter 3
... Multivalent atoms are 1º, 2º, or 3º by bonding to C’s. Univalent atom or group not really 1º, 2º, or 3º on its own - ID depends on type of carbon it is bonded to. ...
... Multivalent atoms are 1º, 2º, or 3º by bonding to C’s. Univalent atom or group not really 1º, 2º, or 3º on its own - ID depends on type of carbon it is bonded to. ...
C1 polymerization and related C-C bond forming - UvA-DARE
... electronic components. Given the above synthetic problems, it is questionable if this will be possible at all using C2 polymerization techniques. As such we are facing important challenges in future polymer synthesis, which require us to develop new polymerization methods, that will allow us to prep ...
... electronic components. Given the above synthetic problems, it is questionable if this will be possible at all using C2 polymerization techniques. As such we are facing important challenges in future polymer synthesis, which require us to develop new polymerization methods, that will allow us to prep ...
Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid
... a. Esters have two carbon containing components; one bonded to the oxygen atom ("alkyl") and one bonded to the carbonyl group ("alkanoate"). Esters are named by combining these two components. 4. Nomenclature of Amides a. Primary amides are named by replacing the "oic acid" or "ic acid" ending of th ...
... a. Esters have two carbon containing components; one bonded to the oxygen atom ("alkyl") and one bonded to the carbonyl group ("alkanoate"). Esters are named by combining these two components. 4. Nomenclature of Amides a. Primary amides are named by replacing the "oic acid" or "ic acid" ending of th ...
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution, General Corrected Mechanism
... can proceed in the same molecule of a halo nitrobenzene they can be considered as complementary processes. Moreover it is possible that the same reactants (nitroarenes and nucleophile) can react in two or even more different ways depending on the structure and conditions. For instance, carbanion of ...
... can proceed in the same molecule of a halo nitrobenzene they can be considered as complementary processes. Moreover it is possible that the same reactants (nitroarenes and nucleophile) can react in two or even more different ways depending on the structure and conditions. For instance, carbanion of ...
New insights into the mechanism of sorbitol transformation
... pressure separator cooled by water circulation. The liquid effluents were collected in vials at the exit of the separator to be further analyzed. After the separator, the gaseous effluent flowed through a back pressure regulator and then through a gas bulb. A drumtype gas meter measured the gas flo ...
... pressure separator cooled by water circulation. The liquid effluents were collected in vials at the exit of the separator to be further analyzed. After the separator, the gaseous effluent flowed through a back pressure regulator and then through a gas bulb. A drumtype gas meter measured the gas flo ...
Chapter 7 Hydrosilylation of Carbon
... Palladium-catalyzed hydrosilylation of 1,3-dienes is one of the important synthetic methods for allylic silanes, and considerable attention has been directed to the asymmetric synthesis of the latter by catalytic methods [9]. Optically active allylic silanes have been used as chiral allylating reage ...
... Palladium-catalyzed hydrosilylation of 1,3-dienes is one of the important synthetic methods for allylic silanes, and considerable attention has been directed to the asymmetric synthesis of the latter by catalytic methods [9]. Optically active allylic silanes have been used as chiral allylating reage ...
Rapid and Efficient Functionalized Ionic Liquid-Catalyzed
... 2.2. Comparison of the Aldol Condensation Reactions under Different Heating Conditions We then compared the aldol reactions under different heating conditions. Figure 2 shows the kinetic profiles in the aldol condensation of model reaction. For clarification, the kinetic profiles in 30 min are shown ...
... 2.2. Comparison of the Aldol Condensation Reactions under Different Heating Conditions We then compared the aldol reactions under different heating conditions. Figure 2 shows the kinetic profiles in the aldol condensation of model reaction. For clarification, the kinetic profiles in 30 min are shown ...
Chemistry 500: Chemistry in Modern Living Topic 7: Manipulating
... 7A Organic Chemistry Ø Organic Chemistry is the study of the chemistry of carbon Ø What makes carbon special? Ø Many bond types Ø Forms long chains Ø Forms strong bonds to almost all elements Ø Over 16,000,000 organic compounds known Ø Being discovered at the rate of over 1,000,000 per year ...
... 7A Organic Chemistry Ø Organic Chemistry is the study of the chemistry of carbon Ø What makes carbon special? Ø Many bond types Ø Forms long chains Ø Forms strong bonds to almost all elements Ø Over 16,000,000 organic compounds known Ø Being discovered at the rate of over 1,000,000 per year ...
Grignard-syn-12-ques
... ethylmagnesium bromide (CH3CH2MgBr) with butanal (CH3CH2CH2CH=O) followed by dilute ...
... ethylmagnesium bromide (CH3CH2MgBr) with butanal (CH3CH2CH2CH=O) followed by dilute ...
Chapter 12. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... 3. The boiling point of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular mass due to high magnitude of dipole-dipole interactions. 4. Aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling point than those of alcohols of similar molecular www.ncerthelp.com (Visit for all ncert ...
... 3. The boiling point of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular mass due to high magnitude of dipole-dipole interactions. 4. Aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling point than those of alcohols of similar molecular www.ncerthelp.com (Visit for all ncert ...
Homogeneously catalysed hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids
... This equation, which represents a hyperbola, allows a simple representation of a complicated chemical reaction and is of practical importance for a systematic study of catalytic processes. It was found that the course of the hydrogenation of unsaturated acids under influence of Cu- and Cd-soaps can ...
... This equation, which represents a hyperbola, allows a simple representation of a complicated chemical reaction and is of practical importance for a systematic study of catalytic processes. It was found that the course of the hydrogenation of unsaturated acids under influence of Cu- and Cd-soaps can ...
Drug Metabolism
... hemiketal. which undergoes spontaneous carbon—oxygen bond cleavage to yield the dealkylated oxygen species (phenol or alcohol) and a carbon moiety (aldehyde or ketone). Small alkyl groups (e.g., methyl or ethyl) attached to oxygen are Odealkylaced rapidly. ...
... hemiketal. which undergoes spontaneous carbon—oxygen bond cleavage to yield the dealkylated oxygen species (phenol or alcohol) and a carbon moiety (aldehyde or ketone). Small alkyl groups (e.g., methyl or ethyl) attached to oxygen are Odealkylaced rapidly. ...
3.2 Organic Synthesis (Reaction Pathways)
... Solubility (in water) is also largely dependant on the polarity of the molecule. To dissolve in water a molecule would need to be able to establish attractions similar in strength to the hydrogen bonding that already exists between water molecules. Alcohols and acids are amongst the most soluble bec ...
... Solubility (in water) is also largely dependant on the polarity of the molecule. To dissolve in water a molecule would need to be able to establish attractions similar in strength to the hydrogen bonding that already exists between water molecules. Alcohols and acids are amongst the most soluble bec ...
Aromatic Compounds
... • Electrophilic substitutions are favored by electrondonating substituents which stabilize the carbocation intermediate • Nucleophilic substitutions are favored by electronwithdrawing substituents which stabilize a carbanion intermediate • Electron-withdrawing groups that deactivate rings for electr ...
... • Electrophilic substitutions are favored by electrondonating substituents which stabilize the carbocation intermediate • Nucleophilic substitutions are favored by electronwithdrawing substituents which stabilize a carbanion intermediate • Electron-withdrawing groups that deactivate rings for electr ...
Acid derivatives
... to the replacement group must be formed. The timing of these events may vary with the reacting system. In nucleophilic substitution reactions of alkyl compounds examples of bond-breaking preceding bond-making (the SN1 mechanism), and of bond-breaking and bond-making occuring simultaneously (the SN2 ...
... to the replacement group must be formed. The timing of these events may vary with the reacting system. In nucleophilic substitution reactions of alkyl compounds examples of bond-breaking preceding bond-making (the SN1 mechanism), and of bond-breaking and bond-making occuring simultaneously (the SN2 ...
Unit 16: Chemistry for Biology Technicians
... The notion of equilibrium will be extended to introduce the concept of an equilibrium constant and, in particular, the acid dissociation constant. Learners will be introduced to the concept of acids in equilibrium with conjugate bases. Where possible, learners should have the opportunity to measure ...
... The notion of equilibrium will be extended to introduce the concept of an equilibrium constant and, in particular, the acid dissociation constant. Learners will be introduced to the concept of acids in equilibrium with conjugate bases. Where possible, learners should have the opportunity to measure ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.