Isomers
... Optical isomerism is present in all compounds that contain at least one asymmetric (chiral) carbon atom An asymmetric carbon atom has four different atoms or groups attached In this case there are two different ways to arrange the four groups around the chiral carbon atom (shown in ...
... Optical isomerism is present in all compounds that contain at least one asymmetric (chiral) carbon atom An asymmetric carbon atom has four different atoms or groups attached In this case there are two different ways to arrange the four groups around the chiral carbon atom (shown in ...
Organic Chemistry I Laboratory
... were investigating a chemical reaction both backward and forward. Markovnikov was adding hydrogen iodide to alkenes to prepare alkyl iodides, and Zaitzev was removing hydrogen iodide from alkyl iodides to prepare alkenes. Markovnikov discovered that hydrogen iodide adds to propene to form mainly 2-i ...
... were investigating a chemical reaction both backward and forward. Markovnikov was adding hydrogen iodide to alkenes to prepare alkyl iodides, and Zaitzev was removing hydrogen iodide from alkyl iodides to prepare alkenes. Markovnikov discovered that hydrogen iodide adds to propene to form mainly 2-i ...
Organic Chemistry
... No more than one –OH group can be attached to any one carbon The carbon to which the –OH group is attached must have all single bonds Alcohols are not bases (do not ionize in water) Name: hydrocarbon name, replace the final –e with –ol ...
... No more than one –OH group can be attached to any one carbon The carbon to which the –OH group is attached must have all single bonds Alcohols are not bases (do not ionize in water) Name: hydrocarbon name, replace the final –e with –ol ...
Exam 4
... 3) The sum of the masses of two hydrogen atoms (mass number 1) and two neutrons is 4.0330. Why does this differ from the mass of a helium atom (4.0026)? a) Some hydrogen atoms are heavier than others b) The difference is the binding energy of the helium nucleus c) The difference is the experimental ...
... 3) The sum of the masses of two hydrogen atoms (mass number 1) and two neutrons is 4.0330. Why does this differ from the mass of a helium atom (4.0026)? a) Some hydrogen atoms are heavier than others b) The difference is the binding energy of the helium nucleus c) The difference is the experimental ...
ORGANIC REACTIONS 11 MARCH 2014 Lesson
... 1.4. In order to obtain product Y, C3H7Br is heated with a concentrates solution of KOH under reflux. Use condensed structural formulae to write a balanced equation for the reaction. 1.5. A group of learners decide to heat C3H7Br with dilute sodium hydroxide, instead of the concentrated potassium hy ...
... 1.4. In order to obtain product Y, C3H7Br is heated with a concentrates solution of KOH under reflux. Use condensed structural formulae to write a balanced equation for the reaction. 1.5. A group of learners decide to heat C3H7Br with dilute sodium hydroxide, instead of the concentrated potassium hy ...
organic chemistry - Turner Fenton Secondary School
... to produce a compound with a new name but more importantly with physical and chemical properties that are unique to the functional group. ALCOHOL NOMENCLATURE Alcohols are compounds that contain the functional group –OH (Hydroxyl group). This hydroxyl group can be attached to one, or two or even thr ...
... to produce a compound with a new name but more importantly with physical and chemical properties that are unique to the functional group. ALCOHOL NOMENCLATURE Alcohols are compounds that contain the functional group –OH (Hydroxyl group). This hydroxyl group can be attached to one, or two or even thr ...
Click for Section 2.9 notes
... Some Derivatives of Alkanes • When H atoms in alkanes are replaced by heteroatoms (atoms other than C or H), then we have introduced a functional group into the alkane • When H is replaced by –OH, the compound is an alcohol • Alcohols are also named by the number of C atoms ...
... Some Derivatives of Alkanes • When H atoms in alkanes are replaced by heteroatoms (atoms other than C or H), then we have introduced a functional group into the alkane • When H is replaced by –OH, the compound is an alcohol • Alcohols are also named by the number of C atoms ...
Group B_reaction of alkenes
... Limonene takes its name from the lemon, as the rind of the lemon, like other citrus fruits, contains considerable amounts of this compound, which contributes to their odor. Limonene is common in cosmetic products. As the main odor constituent of citrus (plant family Rutaceae), D-limonene is used ...
... Limonene takes its name from the lemon, as the rind of the lemon, like other citrus fruits, contains considerable amounts of this compound, which contributes to their odor. Limonene is common in cosmetic products. As the main odor constituent of citrus (plant family Rutaceae), D-limonene is used ...
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015
... Chiral starting material gives racemic mixture of enantiomeric products ...
... Chiral starting material gives racemic mixture of enantiomeric products ...
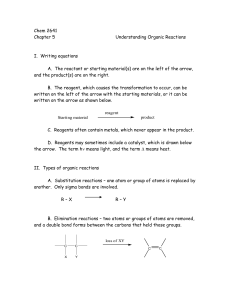
Chem 2641 Chapter 5 Understanding Organic Reactions I. Writing
... The initiation stage – Cl2 reacts with the uv light to form Cl. Propagation stage – The Cl. reacts with CH4 to form CH3. and HCl The CH3. reacts with Cl2 to form CH3Cl and Cl. Termination stage – any two radicals can combine to form a stable product. ...
... The initiation stage – Cl2 reacts with the uv light to form Cl. Propagation stage – The Cl. reacts with CH4 to form CH3. and HCl The CH3. reacts with Cl2 to form CH3Cl and Cl. Termination stage – any two radicals can combine to form a stable product. ...
Organic Chemistry
... c. in reaction mechanisms, curly arrows show how electrons move – generally electrons from nucleophile move to electrophile 3. Low reactivity: Alkanes have low reactivity because they have nonpolar CC and CH bonds. But they can react. 4. High reactivity: a. Alkenes have pi bonds in which electrons a ...
... c. in reaction mechanisms, curly arrows show how electrons move – generally electrons from nucleophile move to electrophile 3. Low reactivity: Alkanes have low reactivity because they have nonpolar CC and CH bonds. But they can react. 4. High reactivity: a. Alkenes have pi bonds in which electrons a ...
Reactions of Alkenes
... alcohol. Demercuration is the removal of the mercury containing species, which is achieved by reaction with Sodium borohydride, a powerful reducing agent, which replaces the mercury species with a hydrogen atom – giving the desired alcohol. Oxymercuration-demercuration also gives Markovnikov orienta ...
... alcohol. Demercuration is the removal of the mercury containing species, which is achieved by reaction with Sodium borohydride, a powerful reducing agent, which replaces the mercury species with a hydrogen atom – giving the desired alcohol. Oxymercuration-demercuration also gives Markovnikov orienta ...
Organic Chemistry II
... 10,13-dimethyl-17-(6-methylheptan-2-yl)2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol ...
... 10,13-dimethyl-17-(6-methylheptan-2-yl)2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol ...
+ Y
... cis addition – both groups attach to the same side of the double bond trans addition –groups attach to the opposite side of the double bond ...
... cis addition – both groups attach to the same side of the double bond trans addition –groups attach to the opposite side of the double bond ...
Chapter 14 Selenium reagents
... • Alcohols are converted into alkyl aryl selenides by reaction with aryl selenocyanates, ArSeCN. These react with bromine in the presence of a base, giving alkyl bromides: the overall reaction is ROH RBr with retention of configuration. • Aryl alkyl selenides are preparable either (as above) from el ...
... • Alcohols are converted into alkyl aryl selenides by reaction with aryl selenocyanates, ArSeCN. These react with bromine in the presence of a base, giving alkyl bromides: the overall reaction is ROH RBr with retention of configuration. • Aryl alkyl selenides are preparable either (as above) from el ...
Exam 2-Answer Key
... two pi bonds and a sigma bond, each formed by a lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by overlap of two s orbitals and two pi bonds, each formed by lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by end-on overlap of two sp" orbitals and a pi bond formed by lateral overlap of ...
... two pi bonds and a sigma bond, each formed by a lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by overlap of two s orbitals and two pi bonds, each formed by lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by end-on overlap of two sp" orbitals and a pi bond formed by lateral overlap of ...
$doc.title
... • Alkanes: Compounds with C-‐C single bonds and C-‐H bonds only (no func)onal groups), non-‐polar molecule • Easy to rotate around C-‐C single bonds • Connec)ng carbons can lead to large or small mole ...
... • Alkanes: Compounds with C-‐C single bonds and C-‐H bonds only (no func)onal groups), non-‐polar molecule • Easy to rotate around C-‐C single bonds • Connec)ng carbons can lead to large or small mole ...
Document
... In this rearrangement, an electron is donated through space; the other electron to form the bond comes from a bond to this atom. The initial cleavage does not cause fragmentation, only rearrangement and transfer of the radical site. This new radical site then initiates an alpha cleavage, resulting i ...
... In this rearrangement, an electron is donated through space; the other electron to form the bond comes from a bond to this atom. The initial cleavage does not cause fragmentation, only rearrangement and transfer of the radical site. This new radical site then initiates an alpha cleavage, resulting i ...
organic chemistry - Madison County Schools
... A group of atoms that give characteristics and properties to organic compounds. These functional groups may be aldehydes, alcohols, ethers, ketones, amino acids, amides, and others. We will study the alcohols because of their wide use in combustion reactions. ...
... A group of atoms that give characteristics and properties to organic compounds. These functional groups may be aldehydes, alcohols, ethers, ketones, amino acids, amides, and others. We will study the alcohols because of their wide use in combustion reactions. ...
BCH 201 lect2
... - The four single bonds that can be formed by a carbon atom are arranged tetrahedrally, with an angle of about 109.5 between any two bonds (Fig.) and an average length of 0.154 nm. - There is free rotation around each single bond, unless very large or highly charged groups are attached to both carb ...
... - The four single bonds that can be formed by a carbon atom are arranged tetrahedrally, with an angle of about 109.5 between any two bonds (Fig.) and an average length of 0.154 nm. - There is free rotation around each single bond, unless very large or highly charged groups are attached to both carb ...
Organic chemistry
... If more then one sidechain comes off the main chain, label each one, and write which carbon it branched from. ...
... If more then one sidechain comes off the main chain, label each one, and write which carbon it branched from. ...
Chemistry 201 C Alkenes
... A molecule is unsaturated when it contains fewer hydrogens (and/or halogens and oxygens) than an alkane of corresponding carbon content. The degree of unsaturation or index of hydrogen deficiency equals the number of H2 molecules it would take to saturate the molecule. ...
... A molecule is unsaturated when it contains fewer hydrogens (and/or halogens and oxygens) than an alkane of corresponding carbon content. The degree of unsaturation or index of hydrogen deficiency equals the number of H2 molecules it would take to saturate the molecule. ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.