* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic chemistry
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Polythiophene wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
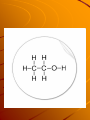
Organic chemistry Organic chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of carbon based molecules. Carbon has _______valence electrons, So it can make up to _________ bonds. This allows carbon to make limitless compounds. Carbon Using only 3 carbon molecules and as many hydrogen's as you want make as many molecules as you can. Saturated vs. non saturated Make 2 chains of carbons How many hydrogens can fit in each chain? Saturated vs. unsaturated In one of the chains make a double bond. Now add hydrogen's to each. Is the one with the double bond filled with the maximum capacity of hydrogens? Saturated When a carbon chain has a double (or triple bond) it does not need to have the maximum number of hydrogen's… so it is not full….. Or not saturated. When a carbon chain has only single bonds it needs the max number of hydrogen's…. It is saturated. Isomers Build a chain of 4 carbons, 1 oxygen and 8 hydrogen's. Isomers There were a few different ways you could have built this molecule. Each one has the same formula but different shapes. When two molecules have the same formula but different shapes they are called isomers Naming hydrocarbons Look at table P on your reference table. This table tells you the 1st part of the name of a hydrocarbon, depending on how many carbons it has Naming compounds Next the second part of the name is given depending on is there are single, double or triple bonds. Look at table Q. Example Draw a hexane, hexene & a hexyne Draw a butane, butene, & butyne Draw an ethane, ethene & ethyne Draw a methane, methene,& methyne. Naming To name a compound given… 1- Find the longest chain and name the molecule after that chain. Naming 2- Find any carbons coming off and name them, based off of table P but add the suffix yl (methane = methyl) Naming 3- Assign numbers to each carbon on the main chain and write the number of the carbon that the chain comes off. Note: number the chain so that the branch gets the smallest number. Naming If more then one sidechain comes off the main chain, label each one, and write which carbon it branched from. Functional groups The hydrogen's of a hydrocarbon can often times be displaced by a more complicated set of atoms. Many times these atoms stay together as a group. These groups are called functional groups HALIDES When any of the halogens (group 17) combine on a hydrocarbon the new compound is called an organic halide. We name the molecule by adding the name of the halogen to the molecule. Alcohols When a OH groups adds onto a hydrocarbon the molecule in now called an alcohol. When an OH adds the molecule has the name ‘OL’ added to the end. Combustion Combustion reaction A combustion reaction is any time a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to give off CO2 and water Saponification Saponification is the reactions to make soap. That’s all you need to know, the regents wont ask you to identify, only know what it is. A polymer is a long repeated chain of something, and a monomer is the single unit. A subway car is a monomer, the polymer is the entire train Polymerization When the single units are linked together, to make a polymer It is called a polymerization reaction. Polymerization Halogenation When a halogen is added to a hydrocarbon it is called a halogenation Halogenation Recap Combustion Saponification Polymerization Halogenation