Aldehydes and Ketones Both contain the functional group C O
... 3-chloropropionaldehyde Ketones Nomenclature. IUPAC: drop the 'e' from the name of the corresponding alkane and add 'one'. Indicate the position of the carbonyl group if necessary. Common names are similar to those of ethers using the names of the groups attached to the carbonyl. ...
... 3-chloropropionaldehyde Ketones Nomenclature. IUPAC: drop the 'e' from the name of the corresponding alkane and add 'one'. Indicate the position of the carbonyl group if necessary. Common names are similar to those of ethers using the names of the groups attached to the carbonyl. ...
Line-Angle Notation for Depicting Chemical
... A shorthand notation for drawing chemical structures involves the use of lines to depict bonds and angles to depict atoms. By convention, hydrogen atoms are not indicated. Therefore, the line-angle notation for butane, CH3CH2CH2CH3 would be: ...
... A shorthand notation for drawing chemical structures involves the use of lines to depict bonds and angles to depict atoms. By convention, hydrogen atoms are not indicated. Therefore, the line-angle notation for butane, CH3CH2CH2CH3 would be: ...
Organic Chemistry
... Have a mixture of 2 or more organics Heat column to change liquids to gases (boil). Collect gases in a tube & cool down to change gas to liquid (condense) ...
... Have a mixture of 2 or more organics Heat column to change liquids to gases (boil). Collect gases in a tube & cool down to change gas to liquid (condense) ...
+ H 2 SO 4(aq) - Rothschild Science
... Conservation of Mass Law of Conservation of Mass In any physical or chemical reaction, mass is neither created nor destroyed; it is conserved! Reactants Products Same number of atoms on both sides of the equation! ...
... Conservation of Mass Law of Conservation of Mass In any physical or chemical reaction, mass is neither created nor destroyed; it is conserved! Reactants Products Same number of atoms on both sides of the equation! ...
Carbon - Napa Valley College
... Know the vocabulary of the lecture Understand the importance of carbon in organic molecules What are the different types of isomers? Be able to identify examples of each type of isomer. What are the structure and the properties of the common functional groups? ...
... Know the vocabulary of the lecture Understand the importance of carbon in organic molecules What are the different types of isomers? Be able to identify examples of each type of isomer. What are the structure and the properties of the common functional groups? ...
Gr - loyolascience2
... Figure 7 (p. 19) shows the condensed structural formula of the molecule methylbenzene, which can also be named phenylmethane – both names being acceptable by IUPAC. Its common name is toluene. On a separate page, draw both the structural and condensed structural formulas for this molecule, and list ...
... Figure 7 (p. 19) shows the condensed structural formula of the molecule methylbenzene, which can also be named phenylmethane – both names being acceptable by IUPAC. Its common name is toluene. On a separate page, draw both the structural and condensed structural formulas for this molecule, and list ...
Chemistry for Changing Times 11th Edition Hill and Kolb
... that contain a carbon-tocarbon triple bond. Their general formulas are CnH2n-2. Their names begin with a prefix denoting the number of carbon atoms followed by the suffix –yne. Ethyne (acetylene) is the simplest alkyne. ...
... that contain a carbon-tocarbon triple bond. Their general formulas are CnH2n-2. Their names begin with a prefix denoting the number of carbon atoms followed by the suffix –yne. Ethyne (acetylene) is the simplest alkyne. ...
Study_guide_2010-01
... Retrosynthetic analysis This chapter provides detail on retrosynthetic formalisms called “synthons” that are NOT AT ALL required for this course, but that some may find helpful for synthetic ...
... Retrosynthetic analysis This chapter provides detail on retrosynthetic formalisms called “synthons” that are NOT AT ALL required for this course, but that some may find helpful for synthetic ...
1. Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds.
... commonly involved in chemical reactions are known as functional groups. If we consider hydrocarbons to be the simplest organic molecules, we can view functional groups as attachments that replace one or more of the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon skeleton of the hydrocarbon. Each functional grou ...
... commonly involved in chemical reactions are known as functional groups. If we consider hydrocarbons to be the simplest organic molecules, we can view functional groups as attachments that replace one or more of the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon skeleton of the hydrocarbon. Each functional grou ...
اســـم المـــدرس: د
... ] The reaction of Butanol with HCl is faster than the reaction of t-butyl alcohol ...
... ] The reaction of Butanol with HCl is faster than the reaction of t-butyl alcohol ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Homework Unit 2: Natures Chemistry Soaps
... What term can be applied to aspirin but not oil of wintergreen? ...
... What term can be applied to aspirin but not oil of wintergreen? ...
Test Review
... You should know how to name and draw the structures for the following classes of compounds: alcohols, ethers (both IUPAC and common ways), phenols (see ch. 12), and thiols. ...
... You should know how to name and draw the structures for the following classes of compounds: alcohols, ethers (both IUPAC and common ways), phenols (see ch. 12), and thiols. ...
Chapter 10, section 10.5
... • with four bonds. • mostly with H and other C atoms. • sometimes to O, N, S, • sometimes to halogens F, Cl, and Br. ...
... • with four bonds. • mostly with H and other C atoms. • sometimes to O, N, S, • sometimes to halogens F, Cl, and Br. ...
Soaps, Fragrances and Skin Care 1. In which line of the table are fat
... What term can be applied to aspirin but not oil of wintergreen? 4. A student carried out four tests on ethanol and ethanoic acids to compare the properties of the two homologous series, alcohols and carboxylic acids. a. Choose one test in which ethanol and ethanoic acid will give different results a ...
... What term can be applied to aspirin but not oil of wintergreen? 4. A student carried out four tests on ethanol and ethanoic acids to compare the properties of the two homologous series, alcohols and carboxylic acids. a. Choose one test in which ethanol and ethanoic acid will give different results a ...
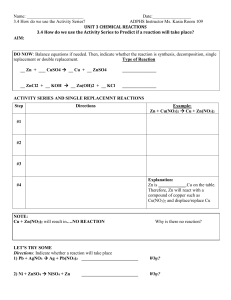
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
Organic Chemistry 2014 finalzzz
... branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (use the suffix –yl for branches) Write the complete IUPAC name, following the format: (number of location, if necessary) – (branch name) (parent chain) ...
... branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (use the suffix –yl for branches) Write the complete IUPAC name, following the format: (number of location, if necessary) – (branch name) (parent chain) ...
Ethers
... • To name an ether, identify the longest chain of carbon atoms. The longest chain that contains an oxygen are alkyl groups, which are alkoxy groups. • Example: CH3–CH2ethyl CH3–CH2–O ethyloxy Common Name • Ethers can be named by naming the carbon groups as a separate word and ending it with the word ...
... • To name an ether, identify the longest chain of carbon atoms. The longest chain that contains an oxygen are alkyl groups, which are alkoxy groups. • Example: CH3–CH2ethyl CH3–CH2–O ethyloxy Common Name • Ethers can be named by naming the carbon groups as a separate word and ending it with the word ...
Organic Structure Notes
... f. Larger molecules have stronger Ldf b/c there are more e- to e- interaction g. Cylindrical shape molecules have higher Ldf than their branched relatives (isomers) which have the same molecular formula h. Branched isomers have less e-/e- interaction and thus have weaker IMFA than the cylindrical is ...
... f. Larger molecules have stronger Ldf b/c there are more e- to e- interaction g. Cylindrical shape molecules have higher Ldf than their branched relatives (isomers) which have the same molecular formula h. Branched isomers have less e-/e- interaction and thus have weaker IMFA than the cylindrical is ...
File - Dr KHALID SHADID
... • Although acetals are hydrolyzed to aldehydes and kctones in aqueous acid, they are stable in basic solutions. • Because of this property, acetal give a convenient method for protecting aldehyde and ketone groups from undesired reactions in • As an example, let us consider the problem of converting ...
... • Although acetals are hydrolyzed to aldehydes and kctones in aqueous acid, they are stable in basic solutions. • Because of this property, acetal give a convenient method for protecting aldehyde and ketone groups from undesired reactions in • As an example, let us consider the problem of converting ...
organic compounds in three dimensions
... Cis- and Trans- Isomers: An important difference between alkanes and alkenes is the degree of flexibility of the carbon-carbon bonds in the molecules. Rotation around single carbon-carbon bonds in alkanes occurs readily at room temperature, but the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes is strong enou ...
... Cis- and Trans- Isomers: An important difference between alkanes and alkenes is the degree of flexibility of the carbon-carbon bonds in the molecules. Rotation around single carbon-carbon bonds in alkanes occurs readily at room temperature, but the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes is strong enou ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.