Chapter 4 Review - Blue Valley Schools
... Molecules that differ in the arrangement of their atoms about a double bond are called A B C D E ...
... Molecules that differ in the arrangement of their atoms about a double bond are called A B C D E ...
Ligand-Based CarbonАNitrogen Bond Forming Reactions of Metal
... cyclopentadienylcobalt dinitrosyl complex CpCo(NO)2 reacts reversibly with alkenes to give, in many cases, stable and isolable cobalt dinitrosoalkane complexes. More recently, we found that treatment with strong bases, such as lithium hexamethyldisilazide, Verkade's base, and phosphazene bases, depr ...
... cyclopentadienylcobalt dinitrosyl complex CpCo(NO)2 reacts reversibly with alkenes to give, in many cases, stable and isolable cobalt dinitrosoalkane complexes. More recently, we found that treatment with strong bases, such as lithium hexamethyldisilazide, Verkade's base, and phosphazene bases, depr ...
This is the first exam with targeted syntheses that you
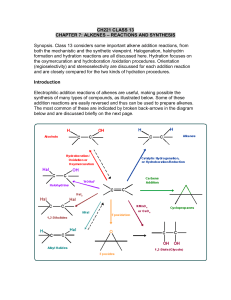
... Most of the reactions of aldehydes and ketones in these chapters are nucleophilic addition reactions. The oxygen in C=O polarizes the bond. Therefore, while electrophilic addition (electrophile first, followed by nucleophile) was favored for the comparatively non-polar, electron-rich alkene, carbony ...
... Most of the reactions of aldehydes and ketones in these chapters are nucleophilic addition reactions. The oxygen in C=O polarizes the bond. Therefore, while electrophilic addition (electrophile first, followed by nucleophile) was favored for the comparatively non-polar, electron-rich alkene, carbony ...
NOTES: Carbohydrates / Lipids
... Double bond makes them more inflexible-cannot rotate freely like in single bond! (variation in arrangement around a double bond) ...
... Double bond makes them more inflexible-cannot rotate freely like in single bond! (variation in arrangement around a double bond) ...
Some comments and hints for the March 9 Biochemistry
... carbons and an amine to its R-group. This newly formed side chain positions an ammonium (conjugate acid of the amine) at about the same position as the ammonium in lysine-close enough for trypsin to recognize it as a good fit for its recognition site. 5. This is analogous to a ketone or aldehyde. St ...
... carbons and an amine to its R-group. This newly formed side chain positions an ammonium (conjugate acid of the amine) at about the same position as the ammonium in lysine-close enough for trypsin to recognize it as a good fit for its recognition site. 5. This is analogous to a ketone or aldehyde. St ...
CHE 312 Answers in BOLD RED EXAM 1 KEY (Ch. 16
... A. an alcohol with dilute warm acid B. the alkoxide of a primary alcohol with any alkyl halide C. any alkoxide with a primary alkyl halide D. two alcohols with dilute warm acid ...
... A. an alcohol with dilute warm acid B. the alkoxide of a primary alcohol with any alkyl halide C. any alkoxide with a primary alkyl halide D. two alcohols with dilute warm acid ...
bonding
... the high priority groups can be on the same side or on opposite Sides of the double bond. If the high priority groups are on opposite sides then the double bond is designated as E (entgegen- across) If the high priority groups are on the same side then the double bond is designated as Z (zusammen- t ...
... the high priority groups can be on the same side or on opposite Sides of the double bond. If the high priority groups are on opposite sides then the double bond is designated as E (entgegen- across) If the high priority groups are on the same side then the double bond is designated as Z (zusammen- t ...
無投影片標題 - SKHSBS
... 1. Determine the stem name by selecting the longest possible straight chain containing the C = C double bond and use the ending ‘-ene’ 2. Number the parent chain so as to include both carbon atoms of the double bond, and begin numbering with the end of the chain nearer the C = C double bond 3. Desig ...
... 1. Determine the stem name by selecting the longest possible straight chain containing the C = C double bond and use the ending ‘-ene’ 2. Number the parent chain so as to include both carbon atoms of the double bond, and begin numbering with the end of the chain nearer the C = C double bond 3. Desig ...
Production of Materials by Jimmy Huang
... pressure while keeping the concentrations of the reacting gases low enough to ensure that the desired result occur. Sometimes, the feedstock for thermal cracking is a mixture of ethane and propane obtained from natural gas. Usefulness of Ethene The presence of a double bond in alkenes makes them muc ...
... pressure while keeping the concentrations of the reacting gases low enough to ensure that the desired result occur. Sometimes, the feedstock for thermal cracking is a mixture of ethane and propane obtained from natural gas. Usefulness of Ethene The presence of a double bond in alkenes makes them muc ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions
... - must consider regioselectivity when using substituted benzenes directing effects: o/p or m (see handout) ...
... - must consider regioselectivity when using substituted benzenes directing effects: o/p or m (see handout) ...
CHE-05 year 2004
... Suggest the structure of the alkene/diene that give the following products: i) ...
... Suggest the structure of the alkene/diene that give the following products: i) ...
Chapter 4 Review - Blue Valley Schools
... Molecules that differ in the arrangement of their atoms about a double bond are called A B C D E ...
... Molecules that differ in the arrangement of their atoms about a double bond are called A B C D E ...
Ch04 Organic Chem 9e
... Pick up a copy of the “Functional Groups” chart on the back counter. Use pages 64-65 to fill it out. ...
... Pick up a copy of the “Functional Groups” chart on the back counter. Use pages 64-65 to fill it out. ...
Ch. 2 In-Class Notes (all, p 1-8)
... • Hybrid orbitals are big and point in one direction. Their directionality leads to better overlap which leads to strong bonds. • Hybrid orbitals leads to nice VSEPR angles If hybridization is so great, why aren’t pure monatomic atoms hybridized? 3 • For an isolated atom, having 1 s and 3 p atomic o ...
... • Hybrid orbitals are big and point in one direction. Their directionality leads to better overlap which leads to strong bonds. • Hybrid orbitals leads to nice VSEPR angles If hybridization is so great, why aren’t pure monatomic atoms hybridized? 3 • For an isolated atom, having 1 s and 3 p atomic o ...
Revision Y12 Chemistry PLC
... (f) the benefits of chlorine use in water treatment (killing bacteria) contrasted with associated risks (e.g. hazards of toxic chlorine gas and possible risks from formation of chlorinated hydrocarbons) Characteristic reactions of halide ions (g) the precipitation reactions, including ionic equation ...
... (f) the benefits of chlorine use in water treatment (killing bacteria) contrasted with associated risks (e.g. hazards of toxic chlorine gas and possible risks from formation of chlorinated hydrocarbons) Characteristic reactions of halide ions (g) the precipitation reactions, including ionic equation ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.