幻灯片 1
... The compound is termed as ortho if the two substituents are on the adjacent carbon atoms. In IUPAC system to indicate these positions are 1, 2. (b) Meta. The compound is termed as meta if the two substituents are on alternate carbon atom. In IUPAC system to indicate these position are 1, 3. (c) Par ...
... The compound is termed as ortho if the two substituents are on the adjacent carbon atoms. In IUPAC system to indicate these positions are 1, 2. (b) Meta. The compound is termed as meta if the two substituents are on alternate carbon atom. In IUPAC system to indicate these position are 1, 3. (c) Par ...
Introduction to Biodiesel Chemistry
... Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with organic compounds. Organic compounds are compounds that (with a few exceptions such as carbon dioxide gas) contain the element carbon. The properties of organic compounds are dependent primarily on the physical structure of the molecules a ...
... Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with organic compounds. Organic compounds are compounds that (with a few exceptions such as carbon dioxide gas) contain the element carbon. The properties of organic compounds are dependent primarily on the physical structure of the molecules a ...
Chapter 8. CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
... Aldehydes and ketones have the carbonyl group >C=O as a functional group and they are classified as carbonyl compounds. The carbonyl group is also a constituent of other functional groups generally expressed as -C(O)Z, where Z is a substituent that has an atom with the unshared electron pair, i. e. ...
... Aldehydes and ketones have the carbonyl group >C=O as a functional group and they are classified as carbonyl compounds. The carbonyl group is also a constituent of other functional groups generally expressed as -C(O)Z, where Z is a substituent that has an atom with the unshared electron pair, i. e. ...
O R` R
... results in the formation of new C-C bonds. The following carbon nucleophiles will be discussed: 1. Grignard reagents (________) and organolithium compounds ...
... results in the formation of new C-C bonds. The following carbon nucleophiles will be discussed: 1. Grignard reagents (________) and organolithium compounds ...
Organic Functional Groups Organic Functional Groups
... as an intermediate in energy transfers. • Note the presence of two phosphoanhydrides in ATP. ...
... as an intermediate in energy transfers. • Note the presence of two phosphoanhydrides in ATP. ...
The Acid-Catalyzed Reaction of Acetic
... Ester syntheses are one of the more enjoyable experiments in organic chemistry, as one can't help but notice the special odors associated with esters - some fruity, some more like nail polish. In contrast, the acids which are used in their syntheses usually have a rotten odor. The reverse reaction, ...
... Ester syntheses are one of the more enjoyable experiments in organic chemistry, as one can't help but notice the special odors associated with esters - some fruity, some more like nail polish. In contrast, the acids which are used in their syntheses usually have a rotten odor. The reverse reaction, ...
Identification of Functional Groups
... Note that the above equations are unbalanced skeleton equations showing only the major organic and inorganic products of the reactions. The most important feature of the reactions with KMnO4, is the disappearance of the purple color characteristic of the MnO4- ions in solution and the appearance of ...
... Note that the above equations are unbalanced skeleton equations showing only the major organic and inorganic products of the reactions. The most important feature of the reactions with KMnO4, is the disappearance of the purple color characteristic of the MnO4- ions in solution and the appearance of ...
PPT File
... 10.5 Reaction of Amines Amines are less reactive than alcohols. • This can be evaluated by inspection of the pKa values of the leaving group. ...
... 10.5 Reaction of Amines Amines are less reactive than alcohols. • This can be evaluated by inspection of the pKa values of the leaving group. ...
PAKISTAN SHIPOWNERS` GOVERNMENT COLLEGE,
... * HCl * Cl2 (v) The atomic number of an element, belonging to 3rd period and group V-A is ...
... * HCl * Cl2 (v) The atomic number of an element, belonging to 3rd period and group V-A is ...
1 SECONDARY SCHOOL IMPROVEMENT PROGRAMME (SSIP
... Condensed structural formula – This notation shows the way in which atoms are bonded together in the molecule but it does not show all the bonds e.g. CH 3CH2CH2 CH2CH3 Hydrocarbon – organic compounds that consist of only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Homologous series – a series of organic compounds th ...
... Condensed structural formula – This notation shows the way in which atoms are bonded together in the molecule but it does not show all the bonds e.g. CH 3CH2CH2 CH2CH3 Hydrocarbon – organic compounds that consist of only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Homologous series – a series of organic compounds th ...
NOMENCLATURE VI This exercise covers the basics of organic
... numbering the chain, and it must be part of the longest chain (this is true even when another chain contains more carbon atoms). Only functional groups containing oxygen and/or nitrogen will be considered at this time. For indicating the formulas of various derivatives, it is common practice to use ...
... numbering the chain, and it must be part of the longest chain (this is true even when another chain contains more carbon atoms). Only functional groups containing oxygen and/or nitrogen will be considered at this time. For indicating the formulas of various derivatives, it is common practice to use ...
OCR A Level Chemistry B (Salters) Multiple Choice Questions Quiz
... aldehydes also have permanent dipole– permanent dipole bonds and alcohols can form hydrogen bonds between molecules. Your answer ...
... aldehydes also have permanent dipole– permanent dipole bonds and alcohols can form hydrogen bonds between molecules. Your answer ...
Oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes
... Further oxidation of a primary alcohol • Using a process known as REFLUX, the reaction contents are continually heated at their boiling point temperature, so HOTTER and LONGER heating then alcohol conversion to an aldehyde • Still uses acidified potassium dichromate Primary + Oxidising Carboxylic ...
... Further oxidation of a primary alcohol • Using a process known as REFLUX, the reaction contents are continually heated at their boiling point temperature, so HOTTER and LONGER heating then alcohol conversion to an aldehyde • Still uses acidified potassium dichromate Primary + Oxidising Carboxylic ...
Chapter 18
... (usually see these compounds in 1,3 ring structure but can have different connectivity) ...
... (usually see these compounds in 1,3 ring structure but can have different connectivity) ...
Wed March 3 lecture
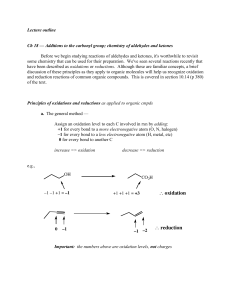
... Ch 18 — Additions to the carbonyl group; chemistry of aldehydes and ketones Before we begin studying reactions of aldehydes and ketones, it's worthwhile to revisit some chemistry that can be used for their preparation. We've seen several reactions recently that have been described as oxidations or r ...
... Ch 18 — Additions to the carbonyl group; chemistry of aldehydes and ketones Before we begin studying reactions of aldehydes and ketones, it's worthwhile to revisit some chemistry that can be used for their preparation. We've seen several reactions recently that have been described as oxidations or r ...
File
... 3. The root chain must be numbered from the end nearest a triple bond carbon atom. If the triple bond is in the center of the chain, the nearest substituent rule is used to determine the end where numbering starts. 4. The smaller of the two numbers designating the carbon atoms of the triple bond is ...
... 3. The root chain must be numbered from the end nearest a triple bond carbon atom. If the triple bond is in the center of the chain, the nearest substituent rule is used to determine the end where numbering starts. 4. The smaller of the two numbers designating the carbon atoms of the triple bond is ...
$doc.title
... • A heterocycle is a cyclic compound that contains atoms of two or more elements in its ring, usually C along with N, O, or S ...
... • A heterocycle is a cyclic compound that contains atoms of two or more elements in its ring, usually C along with N, O, or S ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... What is the range of Infrared radiations ?What are the units used in IR spectroscopy. What is chemical shift ?Why do we choose Tetra methyl silane (TMS) as a standard substance for recording chemical shift values. How many NMR signals would you expect from the following compounds i.Toluene ii.Allyl ...
... What is the range of Infrared radiations ?What are the units used in IR spectroscopy. What is chemical shift ?Why do we choose Tetra methyl silane (TMS) as a standard substance for recording chemical shift values. How many NMR signals would you expect from the following compounds i.Toluene ii.Allyl ...
Alcohols
... Give one advantage and one disadvantage of manufacturing ethanol by fermentation rather than by hydration. Do not include energy consumption or cost. Advantage .................................................................................................... ...
... Give one advantage and one disadvantage of manufacturing ethanol by fermentation rather than by hydration. Do not include energy consumption or cost. Advantage .................................................................................................... ...
Alkenes—The Products of Elimination
... General Features of Elimination • Removal of the elements HX is called dehydrohalogenation. • Dehydrohalogenation is an example of elimination. • The curved arrow formalism shown below illustrates how four bonds are broken or formed in the process. ...
... General Features of Elimination • Removal of the elements HX is called dehydrohalogenation. • Dehydrohalogenation is an example of elimination. • The curved arrow formalism shown below illustrates how four bonds are broken or formed in the process. ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... When a nucleophile attacks an aldehyde or ketone carbon, there is no leaving group. The incoming nucleophile simply “pushes” the electrons in the pi bond up to the oxygen. (eg: ) Alternatively, if start with the minor resonance contributor: attack by a nucleophile on a carbocation. (eg: ) Afte ...
... When a nucleophile attacks an aldehyde or ketone carbon, there is no leaving group. The incoming nucleophile simply “pushes” the electrons in the pi bond up to the oxygen. (eg: ) Alternatively, if start with the minor resonance contributor: attack by a nucleophile on a carbocation. (eg: ) Afte ...
Chapter 9: Aldehydes and Ketones
... Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the presence of the carbonyl group, which is perhaps the most important functional group in organic chemistry. Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon atom. The remaining group may be another hydrogen atom or any aliphatic ...
... Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the presence of the carbonyl group, which is perhaps the most important functional group in organic chemistry. Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon atom. The remaining group may be another hydrogen atom or any aliphatic ...
Alcohols
... Any of these three syntheses would probably work, but only the third begins with fragments containing no more than five carbon atoms. The other two syntheses would require further steps to generate the ketones from compounds containing no more than five carbon atoms. ...
... Any of these three syntheses would probably work, but only the third begins with fragments containing no more than five carbon atoms. The other two syntheses would require further steps to generate the ketones from compounds containing no more than five carbon atoms. ...
reactions of alcohols
... Any of these three syntheses would probably work, but only the third begins with fragments containing no more than five carbon atoms. The other two syntheses would require further steps to generate the ketones from compounds containing no more than five carbon atoms. ...
... Any of these three syntheses would probably work, but only the third begins with fragments containing no more than five carbon atoms. The other two syntheses would require further steps to generate the ketones from compounds containing no more than five carbon atoms. ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.