Nucleophilic Additions to Carbonyl Group
... group itself. Thus, even a nucleophile that is not very reactive with a carbonyl reacts readily with the conjugate acid. Of the seven functional groups containing a carbonyl group, only aldehydes and ketones commonly undergo nucleophilic addition. The remaining five carbonyl functional groups underg ...
... group itself. Thus, even a nucleophile that is not very reactive with a carbonyl reacts readily with the conjugate acid. Of the seven functional groups containing a carbonyl group, only aldehydes and ketones commonly undergo nucleophilic addition. The remaining five carbonyl functional groups underg ...
It was first isolated by A.J. Balard in 1826 from the salts in the waters
... Isotopes: Bromine has 26 isotopes whose half-lives are known, with mass numbers 68 to 94. Of these, only two are stable: 79Br and 81Br. Current uses Silver bromide (AgBr), used in photograph accounts for the largest use of bromine. Other bromine compounds are used in fumigants, in flameproofing and ...
... Isotopes: Bromine has 26 isotopes whose half-lives are known, with mass numbers 68 to 94. Of these, only two are stable: 79Br and 81Br. Current uses Silver bromide (AgBr), used in photograph accounts for the largest use of bromine. Other bromine compounds are used in fumigants, in flameproofing and ...
2.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
... carcinogenic. Carbon tetrachloride also has a long history of use in fire extinguishers, as a fabric cleaner, and as a solvent, but it causes liver damage and now is used much less. An important class of alkyl halides is the chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which have been used in air conditioners, etc., ...
... carcinogenic. Carbon tetrachloride also has a long history of use in fire extinguishers, as a fabric cleaner, and as a solvent, but it causes liver damage and now is used much less. An important class of alkyl halides is the chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which have been used in air conditioners, etc., ...
HIGHER CfE CHEMISTRY Nature`s Chemistry
... 22. Propan-1-ol, can be oxidised by passing the alcohol vapour over hot copper(II) oxide. a) Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus that would be used to carry out this experiment in the laboratory. b) Oxidation of propan-1-ol yields a compound X, formula C3H6O, which can be further oxidised to co ...
... 22. Propan-1-ol, can be oxidised by passing the alcohol vapour over hot copper(II) oxide. a) Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus that would be used to carry out this experiment in the laboratory. b) Oxidation of propan-1-ol yields a compound X, formula C3H6O, which can be further oxidised to co ...
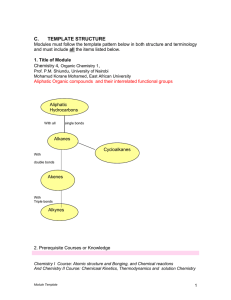
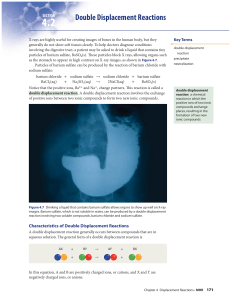
Double Displacement Reactions
... double displacement reaction produces a gas. Give the general form of each reaction. ...
... double displacement reaction produces a gas. Give the general form of each reaction. ...
Enantioselective Henry Reactions under Dual Lewis Acid/Amine
... selectivity (entry 1), whereas increasing the ligand loading above 45 mol % did not improve the result. The quantity of iPr2EtN was crucial too. Lower loading or absence of iPr2EtN (entries 3 and 4) led to diminished yields and ee values. Interestingly, the absence of iPr2EtN could be partially comp ...
... selectivity (entry 1), whereas increasing the ligand loading above 45 mol % did not improve the result. The quantity of iPr2EtN was crucial too. Lower loading or absence of iPr2EtN (entries 3 and 4) led to diminished yields and ee values. Interestingly, the absence of iPr2EtN could be partially comp ...
CH102 Practice exam 2
... ____ 13.The carboxyl group found in carboxylic acids must be on a terminal carbon, like the carbonyl of an aldehyde ____ 14.Carboxylic acids have the functional groups found in both aldehyde / ketones and alcohols. ____ 15.Pure liquid carboxylic acids are strongly hydrogen bonded. ____ 16.Butyric ac ...
... ____ 13.The carboxyl group found in carboxylic acids must be on a terminal carbon, like the carbonyl of an aldehyde ____ 14.Carboxylic acids have the functional groups found in both aldehyde / ketones and alcohols. ____ 15.Pure liquid carboxylic acids are strongly hydrogen bonded. ____ 16.Butyric ac ...
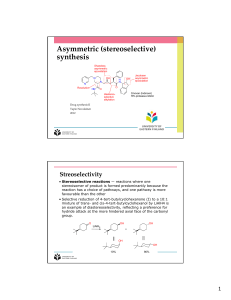
Asymmetric (stereoselective) synthesis
... then separated by chromatography. The resolving agent was removed from one of the diastereoisomers to give a single enantiomer of the alcohol, which could be cyclized to the natural (R)‐pheromone using base and then acid. ...
... then separated by chromatography. The resolving agent was removed from one of the diastereoisomers to give a single enantiomer of the alcohol, which could be cyclized to the natural (R)‐pheromone using base and then acid. ...
Document
... LESS THAN FOUR attachments. – Alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated. – They contain at least one double or triple bond, respectively. – They have fewer hydrogen atoms per carbon atom than alkanes. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... LESS THAN FOUR attachments. – Alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated. – They contain at least one double or triple bond, respectively. – They have fewer hydrogen atoms per carbon atom than alkanes. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
... years. Ethers are significant solvents and synthetic important supplements for the production of fragrances, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reaction is the best technique for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The Williamson reaction generally inv ...
... years. Ethers are significant solvents and synthetic important supplements for the production of fragrances, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reaction is the best technique for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The Williamson reaction generally inv ...
Acetal Formation
... The acetal is a functional group in which a carbon atom is bonded to two –OR groups Acetal formation is a condensation reaction between two hydroxyl groups and a ketone or aldehyde in which water is lost. ...
... The acetal is a functional group in which a carbon atom is bonded to two –OR groups Acetal formation is a condensation reaction between two hydroxyl groups and a ketone or aldehyde in which water is lost. ...
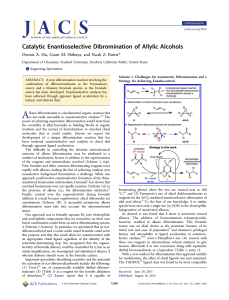
Catalytic Enantioselective Dibromination of Allylic Alcohols
... (entry 3). Allylic ethers, amides, and sulfonamides were all less reactive, and the products were racemic. Optimization12 of the backbone and aryl groups on the diol led to the identification of (R,R)-9 as the optimal diol, with 100 mol % loading leading to the dibromination of cinnamyl alcohol with ...
... (entry 3). Allylic ethers, amides, and sulfonamides were all less reactive, and the products were racemic. Optimization12 of the backbone and aryl groups on the diol led to the identification of (R,R)-9 as the optimal diol, with 100 mol % loading leading to the dibromination of cinnamyl alcohol with ...
Document
... • For E2 elimination, the C-Cl bond must be anti periplanar to the C—H bond on a carbon, and this occurs only when the H and Cl atoms are both in the axial position. The requirement for trans diaxial geometry means that elimination must occur from the ...
... • For E2 elimination, the C-Cl bond must be anti periplanar to the C—H bond on a carbon, and this occurs only when the H and Cl atoms are both in the axial position. The requirement for trans diaxial geometry means that elimination must occur from the ...
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
... Polymers: Large molecules (chains, branched chains) built up by bonding together many smaller units called monomers Hydrocarbon (chain-growth) polymers from alkenes were introduced in Ch. 7 Polymers form by chain reactions (free radical or electrophilic addition) started by an initiator These includ ...
... Polymers: Large molecules (chains, branched chains) built up by bonding together many smaller units called monomers Hydrocarbon (chain-growth) polymers from alkenes were introduced in Ch. 7 Polymers form by chain reactions (free radical or electrophilic addition) started by an initiator These includ ...
carboxylic acid - Career Launcher
... Esters, 3 amides, and nitriles are good polar aprotic solvents. Solvents commonly used in organic reactions: – Ethyl acetate – Dimethylformamide (DMF) – Acetonitrile ...
... Esters, 3 amides, and nitriles are good polar aprotic solvents. Solvents commonly used in organic reactions: – Ethyl acetate – Dimethylformamide (DMF) – Acetonitrile ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
... Electronically, aldehyde is also more reactive than ketone because the presence of two alkyl groups in ketones will reduce the electrophilicity (partial positive charge ) of the carbonyl carbon due to inductive effect by the alkyl groups. Therefore, attack of nucleophile on carbonyl carbon in ketone ...
... Electronically, aldehyde is also more reactive than ketone because the presence of two alkyl groups in ketones will reduce the electrophilicity (partial positive charge ) of the carbonyl carbon due to inductive effect by the alkyl groups. Therefore, attack of nucleophile on carbonyl carbon in ketone ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... • Ethers, thiols, sufides and disulfides have b.p. lower than alcohols. ...
... • Ethers, thiols, sufides and disulfides have b.p. lower than alcohols. ...
Working with Hazardous Chemicals
... to their stability and the minimal electronic impact that they impart on the oxygen atom to which they are attached.6 For example, benzyl ethers do not interfere with chelation-controlled addition of external nucleophiles to chiral aldehydes, in contrast to silyl ethers.7 Benzyl (and modified arylme ...
... to their stability and the minimal electronic impact that they impart on the oxygen atom to which they are attached.6 For example, benzyl ethers do not interfere with chelation-controlled addition of external nucleophiles to chiral aldehydes, in contrast to silyl ethers.7 Benzyl (and modified arylme ...
Document
... • In cycloalkenes, the double bond is located between C1 and C2, and the “1” is usually omitted in the name. • The ring is numbered clockwise or counterclockwise to give the first substituent the lower number. • Compounds that contain both a double bond and a hydroxy group are named as alkenols and ...
... • In cycloalkenes, the double bond is located between C1 and C2, and the “1” is usually omitted in the name. • The ring is numbered clockwise or counterclockwise to give the first substituent the lower number. • Compounds that contain both a double bond and a hydroxy group are named as alkenols and ...
11. 5-member heterocycles with 1 and heteroatoms
... Biological significance and applications Imidazole is incorporated into many important biological molecules. The most pervasive is the amino acid histidine, which has an imidazole side chain. Histidine is present in many proteins and enzymes and plays a vital part in the structure and binding funct ...
... Biological significance and applications Imidazole is incorporated into many important biological molecules. The most pervasive is the amino acid histidine, which has an imidazole side chain. Histidine is present in many proteins and enzymes and plays a vital part in the structure and binding funct ...
Chem341_outcomes
... Understand the role of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution as a major reaction type in organic chemistry Understand major factors affecting nucleophilic substitution, including the role of nucleophile, leaving and neighboring groups, and solvents ...
... Understand the role of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution as a major reaction type in organic chemistry Understand major factors affecting nucleophilic substitution, including the role of nucleophile, leaving and neighboring groups, and solvents ...
Question paper - Unit F322 - Chains, energy and resources
... Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the boxes above. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Answer all the questions. ...
... Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the boxes above. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Answer all the questions. ...
The presence of an aromatic ring or other
... The identification and characterization of the structures of unknown substances are an important part of organic chemistry. Although it is often possible to establish the structure of a compound on the basis of spectra alone (IR, NMR, etc.), the spectra typically must be supplemented with other info ...
... The identification and characterization of the structures of unknown substances are an important part of organic chemistry. Although it is often possible to establish the structure of a compound on the basis of spectra alone (IR, NMR, etc.), the spectra typically must be supplemented with other info ...
An Epoxidation Reaction: The Epoxidation of Cholesterol to 5 ,6
... Water, alcohols and ethers are similar in that they all contain a single oxygen atom. Figure 1 shows the structural relationships among them. ...
... Water, alcohols and ethers are similar in that they all contain a single oxygen atom. Figure 1 shows the structural relationships among them. ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.