The presence of an aromatic ring or other
... more than 5 minutes because oxidation of the alcohol will begin slowly. Record your observations. Perform this test on cyclohexene, toluene, and your unknown. Ignition Test The presence of an aromatic ring or other centers of unsaturation will lead to the production of a sooty yellow flame in this t ...
... more than 5 minutes because oxidation of the alcohol will begin slowly. Record your observations. Perform this test on cyclohexene, toluene, and your unknown. Ignition Test The presence of an aromatic ring or other centers of unsaturation will lead to the production of a sooty yellow flame in this t ...
Document
... addition and then substitution at the carbonyl groups, is of great practical and historic importance in stepwise polymerization. The general reaction, leading to acetal formation, is ...
... addition and then substitution at the carbonyl groups, is of great practical and historic importance in stepwise polymerization. The general reaction, leading to acetal formation, is ...
A Direct Access to 3-(2-Oxoalkyl)indoles via
... Madelung cyclization of N-acyl-o-toluidines are used very often. While a number of methods are available for the synthesis of 3-alkyl-substituted indoles,6,7 only a few are known for the synthesis of 3-(2-oxoalkyl)indoles. These includes (a) the alkylation of indole with R-diazocarbonyl compounds8a, ...
... Madelung cyclization of N-acyl-o-toluidines are used very often. While a number of methods are available for the synthesis of 3-alkyl-substituted indoles,6,7 only a few are known for the synthesis of 3-(2-oxoalkyl)indoles. These includes (a) the alkylation of indole with R-diazocarbonyl compounds8a, ...
13. Alcohols
... The presence of the hydroxyl group with its electronegative oxygen atom means that alcohols are polar. They can therefore take part in hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding between alcohol molecules means that an alcohol’s boiling point is higher than that of an alkane of similar molecular mass. For ex ...
... The presence of the hydroxyl group with its electronegative oxygen atom means that alcohols are polar. They can therefore take part in hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding between alcohol molecules means that an alcohol’s boiling point is higher than that of an alkane of similar molecular mass. For ex ...
Bromine
... orthorhombic structure. At 100 GPa it converts to a body centered orthorhombic monoatomic form. ...
... orthorhombic structure. At 100 GPa it converts to a body centered orthorhombic monoatomic form. ...
Chapter Fourteen
... one another. Simple ethers are higher boiling than comparable alkanes but lower boiling than alcohols. ► Dimethyl ether is soluble and diethyl ether is partially soluble in water. ► Ethers with large organic groups are insoluble in water. Ethers are alkane-like and do not react with most acids, base ...
... one another. Simple ethers are higher boiling than comparable alkanes but lower boiling than alcohols. ► Dimethyl ether is soluble and diethyl ether is partially soluble in water. ► Ethers with large organic groups are insoluble in water. Ethers are alkane-like and do not react with most acids, base ...
Synthetic Strategy – Lecture 2 (DC, 19.1.05)
... to think about the polarity of the simpler structures revealed by this disconnection. This is not usually the case; it is much more common for a disconnection to reveal two imaginary fragments, or synthons, which carry a positive or negative charge. Subsequently we need to identify the real (i.e. no ...
... to think about the polarity of the simpler structures revealed by this disconnection. This is not usually the case; it is much more common for a disconnection to reveal two imaginary fragments, or synthons, which carry a positive or negative charge. Subsequently we need to identify the real (i.e. no ...
Experiment Download
... made a logical guess between the two in matching. Heck, 50/50 chance at getting it right. Yes, I was able to separate each spectra as one of three possible functional groups; alcohol, ether, or alkene (hydrocarbon). Then between the two spectra of the same functional group, an educated guess was mad ...
... made a logical guess between the two in matching. Heck, 50/50 chance at getting it right. Yes, I was able to separate each spectra as one of three possible functional groups; alcohol, ether, or alkene (hydrocarbon). Then between the two spectra of the same functional group, an educated guess was mad ...
New System of Deprotection Step for the Hydroxide Radicals: Boron
... Abstract A new efficient method for dealkylation of ethers is reported. Ethers could transform into corresponding alcohols with boron trifluoride etherate and sodium iodide in acetonitrile after hydrolysis. This reaction can proceed at room temperature, and the yield is excellent. It’s useful for de ...
... Abstract A new efficient method for dealkylation of ethers is reported. Ethers could transform into corresponding alcohols with boron trifluoride etherate and sodium iodide in acetonitrile after hydrolysis. This reaction can proceed at room temperature, and the yield is excellent. It’s useful for de ...
Required Resources and Materials
... As a group, they will build models of organic reactions and their products, by picking up package and following instructions and using included model They will also write down the equation on a paper. When time ends, the researchers will go to another reaction and learn what took place, while ...
... As a group, they will build models of organic reactions and their products, by picking up package and following instructions and using included model They will also write down the equation on a paper. When time ends, the researchers will go to another reaction and learn what took place, while ...
Boston University Dresden Science Program Instructor: Meeting Times
... Lectures: twice a week at 90 minutes each Discussions: once a week at 60 minutes Note well: The lectures and the discussions are not repeated. Lecture Textbooks and Other Course Material.: Organic Chemistry, Boston University, Custom 7e by William H. Brown et. all., Cengage Learning 2013, Solutions ...
... Lectures: twice a week at 90 minutes each Discussions: once a week at 60 minutes Note well: The lectures and the discussions are not repeated. Lecture Textbooks and Other Course Material.: Organic Chemistry, Boston University, Custom 7e by William H. Brown et. all., Cengage Learning 2013, Solutions ...
Chapter 10 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Alkanes
... Copyright © 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Alcohols and Thiols
... The alcoholic proton is also somewhat acidic. The pKa for alcohols runs between 15 and 18 - certainly more acidic than your average alkyne! The general trend in acidity is 1°>2°>3°, with t-butanol being about the least acidic alcohol you’ll find...this is why t-butoxide is used as a base in many of ...
... The alcoholic proton is also somewhat acidic. The pKa for alcohols runs between 15 and 18 - certainly more acidic than your average alkyne! The general trend in acidity is 1°>2°>3°, with t-butanol being about the least acidic alcohol you’ll find...this is why t-butoxide is used as a base in many of ...
Oxidation Reactions
... Observation: the rate of dihydroxylation is increased by the presence of tertiary amines - an example of Ligand Accelerated catalysis. Therefore by using CHIRAL tertiary amines there is the potential for developing an enantioselective version of the OsO4 dihydroxylation. ...
... Observation: the rate of dihydroxylation is increased by the presence of tertiary amines - an example of Ligand Accelerated catalysis. Therefore by using CHIRAL tertiary amines there is the potential for developing an enantioselective version of the OsO4 dihydroxylation. ...
Derivatization of polar compounds for GC - Sigma
... •Ease of silylation generally follows this trend: • Alcohol > phenol > carboxylic acid > amine > amide • Alcohols and Amines: 1° > 2° > 3° ...
... •Ease of silylation generally follows this trend: • Alcohol > phenol > carboxylic acid > amine > amide • Alcohols and Amines: 1° > 2° > 3° ...
rev2
... 2. Know that aldehydes and ketones are functional isomers (constitutional isomers that involve having different functional groups) 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes an ...
... 2. Know that aldehydes and ketones are functional isomers (constitutional isomers that involve having different functional groups) 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes an ...
enespp - Knockhardy
... CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKENES ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION MECHANISM The electrophile, having some positive character, is attracted to the alkene. The electrons in the pi bond come out to form a bond to the positive end. Because hydrogen can only have two electrons in its orbital, its other bond breaks ...
... CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKENES ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION MECHANISM The electrophile, having some positive character, is attracted to the alkene. The electrons in the pi bond come out to form a bond to the positive end. Because hydrogen can only have two electrons in its orbital, its other bond breaks ...
CHM 222 - Jefferson State Community College
... carboxylic acids and their derivatives including nomenclature, synthesis and mechanisms. 1. Name and draw aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives. 2. Propose a synthesis for each type of compound listed above. 3. Explain the reactivity difference between aldehydes and ketones and ...
... carboxylic acids and their derivatives including nomenclature, synthesis and mechanisms. 1. Name and draw aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives. 2. Propose a synthesis for each type of compound listed above. 3. Explain the reactivity difference between aldehydes and ketones and ...
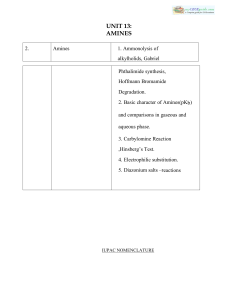
12_chemistry_impq_CH13_amines_02
... 1. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis Gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of primary amines. Phthalimide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide forms potassium salt of phthalimide which on heating with alkyl halide followed by alkaline hydrolysis produces the corresponding primary amin ...
... 1. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis Gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of primary amines. Phthalimide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide forms potassium salt of phthalimide which on heating with alkyl halide followed by alkaline hydrolysis produces the corresponding primary amin ...
Powerpoint - Naming alcohols and their physical properties
... • remove the e and add ol after the basic name • number the chain starting from the end nearer the O-H group • the number is placed after the an and before the ol ... e.g butan-2-ol • as in alkanes, prefix with alkyl substituents ...
... • remove the e and add ol after the basic name • number the chain starting from the end nearer the O-H group • the number is placed after the an and before the ol ... e.g butan-2-ol • as in alkanes, prefix with alkyl substituents ...
Slide 1 - Alfred State College intranet site
... Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
... Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
Elimination Reactions
... For SN2 reactions, you saw that the nucleophile had to attack from the backside of the electrophilic site. This restriction is still valid for E2 reactions. In E2, since we are concerned with bases and not nucleophiles, this restriction reads ‘the proton removed must be anti-periplanar to the leavin ...
... For SN2 reactions, you saw that the nucleophile had to attack from the backside of the electrophilic site. This restriction is still valid for E2 reactions. In E2, since we are concerned with bases and not nucleophiles, this restriction reads ‘the proton removed must be anti-periplanar to the leavin ...
Elimination Reactions
... For SN2 reactions, you saw that the nucleophile had to attack from the backside of the electrophilic site. This restriction is still valid for E2 reactions. In E2, since we are concerned with bases and not nucleophiles, this restriction reads „the proton removed must be anti-periplanar to the leavin ...
... For SN2 reactions, you saw that the nucleophile had to attack from the backside of the electrophilic site. This restriction is still valid for E2 reactions. In E2, since we are concerned with bases and not nucleophiles, this restriction reads „the proton removed must be anti-periplanar to the leavin ...
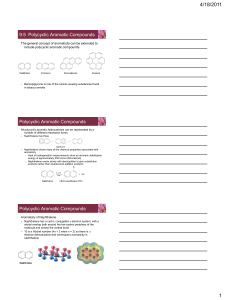
Aromatic Compounds
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds: Electrophilic Substitution One difference between electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions and electrophilic alkene addition reactions is that aromatic rings are less reactive toward electrophiles than alkenes are ...
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds: Electrophilic Substitution One difference between electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions and electrophilic alkene addition reactions is that aromatic rings are less reactive toward electrophiles than alkenes are ...
Chemistry 30 – Organic Chemistry
... • Alcohols undergo elimination to produce water and an alkene • Alkyl halides can undergo elimination to produce alkene and hydrogen halide ...
... • Alcohols undergo elimination to produce water and an alkene • Alkyl halides can undergo elimination to produce alkene and hydrogen halide ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.