AP Chemistry Ch. 3 Sections 3.7-3.8 Notes Chemical Equations
... AP Chemistry Ch. 3 Sections 3.7-3.8 Notes Chemical Equations, Balancing Chemical Equations Chemical Equations • Chemical change – reorganization of the atoms in one or more substances. • Represented by a chemical equation with the reactants on the left side of an arrow and the products on the right ...
... AP Chemistry Ch. 3 Sections 3.7-3.8 Notes Chemical Equations, Balancing Chemical Equations Chemical Equations • Chemical change – reorganization of the atoms in one or more substances. • Represented by a chemical equation with the reactants on the left side of an arrow and the products on the right ...
Chpt1
... Microscopic properties cannot be measured as such; indirect methods have to be devised for these. Each measurement results in a value. Depending on what tool is used, this value may change. In order to have a unified system across the scientific world, an international set of units was agreed upon i ...
... Microscopic properties cannot be measured as such; indirect methods have to be devised for these. Each measurement results in a value. Depending on what tool is used, this value may change. In order to have a unified system across the scientific world, an international set of units was agreed upon i ...
Chemical reaction
... Compounds • A pure substance made up of atoms of 2 or more elements • A molecule is the simplest part of a substance that retains all of the properties of the substance ...
... Compounds • A pure substance made up of atoms of 2 or more elements • A molecule is the simplest part of a substance that retains all of the properties of the substance ...
Atomic Structure. Chemical Bonds.
... Covalent bond one or more pairs of electrons are shared by atoms (H2). Polar covalent bond one part of the molecule attracts ...
... Covalent bond one or more pairs of electrons are shared by atoms (H2). Polar covalent bond one part of the molecule attracts ...
Unit 1 – Physical Science and Chemical Reactions
... (heat, sound, light, etc.) is released then it is an exothermic ...
... (heat, sound, light, etc.) is released then it is an exothermic ...
Chemical Equation
... particles. • In general: the electrons are shared between the ions. Metals tend to give up their electrons to an incomplete nonmetal. • All Ionic compounds are represented by their empirical formulas. They are always in the smallest whole number ratios. ...
... particles. • In general: the electrons are shared between the ions. Metals tend to give up their electrons to an incomplete nonmetal. • All Ionic compounds are represented by their empirical formulas. They are always in the smallest whole number ratios. ...
Chemistry Review - pams-hoey
... 2. Endothermic: Heat, or energy, goes into (gets cold), reaction is the form of heat or light 3. Kinetics: the study of reaction rates 4. Collision Theory: The rate of a reaction is affected by concentration, surface area, temperature and catalysts ...
... 2. Endothermic: Heat, or energy, goes into (gets cold), reaction is the form of heat or light 3. Kinetics: the study of reaction rates 4. Collision Theory: The rate of a reaction is affected by concentration, surface area, temperature and catalysts ...
chem – mixtures elements compounds for ib 1 10-10
... I can state that atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds, which have different properties from their component elements. I can write and recognize a chemical symbol for an element using the periodic table. I can give examples of chemical compounds. I can explain that el ...
... I can state that atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds, which have different properties from their component elements. I can write and recognize a chemical symbol for an element using the periodic table. I can give examples of chemical compounds. I can explain that el ...
Matter—anything that has mass and occupies space Weight—pull of
... A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. Textbook: ...
... A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. Textbook: ...
Scientific Principles: Chemical Properties
... • To discuss elements, compounds, mixtures and formulas • To compare elements and compounds • To analyze chemical and physical changes in food • To examine the occurrence of specific chemical reactions ...
... • To discuss elements, compounds, mixtures and formulas • To compare elements and compounds • To analyze chemical and physical changes in food • To examine the occurrence of specific chemical reactions ...
Test Booklet
... 10 According to this balanced chemical equation, what volume of C2 H2 is required to form 40.0 L of CO2 ? 2C2 H2 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 2H2 O (g) + 4CO2 (g) ...
... 10 According to this balanced chemical equation, what volume of C2 H2 is required to form 40.0 L of CO2 ? 2C2 H2 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 2H2 O (g) + 4CO2 (g) ...
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary)
... Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary) ...
... Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary) ...
6.5 Main Group
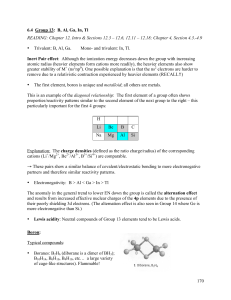
... The elements: • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of ...
... The elements: • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of ...
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
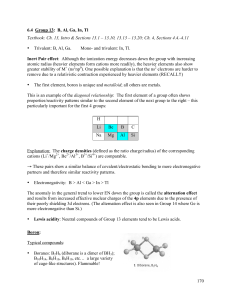
... The elements: • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of ...
... The elements: • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
chapt02_lecture from text
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
Atomic Theory - Hicksville Public Schools
... All elements are composed of atoms, which are indivisible and indestructible particles (spheres) ...
... All elements are composed of atoms, which are indivisible and indestructible particles (spheres) ...
53 word equations
... the reactants come in front of the arrow the products come after the arrow ...
... the reactants come in front of the arrow the products come after the arrow ...
Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties
... Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a liquid…add more energy and you get a gas…all physical changes as it is still water Example – Dissolving things is a phys ...
... Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a liquid…add more energy and you get a gas…all physical changes as it is still water Example – Dissolving things is a phys ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.