Reactions
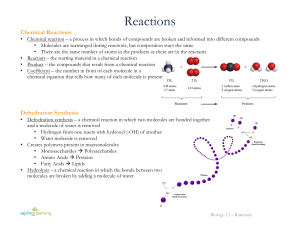
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
Chemistry Study Guide What is matter made of? Matter is anything
... properties that are the same or very similar. The elements in each group also have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. The horizontal rows are called periods. The elements in each period are arranged by atomic number and have the same number of electron shells around the nucleus. Eac ...
... properties that are the same or very similar. The elements in each group also have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. The horizontal rows are called periods. The elements in each period are arranged by atomic number and have the same number of electron shells around the nucleus. Eac ...
Course __Chemistry Sept Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb March April May June
... Use appropriate tools and techniques to make observations and gather data. D INQ.9 Articulate conclusions and explanations based on research data, and assess results based on the design of the investigation. D INQ.10 Communicate about science in different formats, using relevant science vocabulary, ...
... Use appropriate tools and techniques to make observations and gather data. D INQ.9 Articulate conclusions and explanations based on research data, and assess results based on the design of the investigation. D INQ.10 Communicate about science in different formats, using relevant science vocabulary, ...
Semester Exam Review Guide
... 26. If the mass of a steel bolt is 4.0 grams and its volume is 2 milliliters, what is the bolt’s density? a. 2 ml / g b. 2 g / ml c. .5 g / ml d. 8 ml / g 27. How many Hydrogen atoms are in the following chemical unit: 5HN2(OH)2 a. 10 b. 5 c. 15 d. 7 ...
... 26. If the mass of a steel bolt is 4.0 grams and its volume is 2 milliliters, what is the bolt’s density? a. 2 ml / g b. 2 g / ml c. .5 g / ml d. 8 ml / g 27. How many Hydrogen atoms are in the following chemical unit: 5HN2(OH)2 a. 10 b. 5 c. 15 d. 7 ...
Lecture 1 – Matter, Atomic Structure
... 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 3. Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element. In any compound, the ratio of the numbers of atoms of any two o ...
... 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 3. Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element. In any compound, the ratio of the numbers of atoms of any two o ...
Sub Unit Plan 1 Chem Periodic Table
... behaves during a chemical reaction. (3.1x) II.6 Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These forms differ in their molecular or crystal structure, and hence in their properties. (5.2f) II.7 For Groups 1, 2, and 13-18 on the Periodic Table, elements within the same group have the ...
... behaves during a chemical reaction. (3.1x) II.6 Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These forms differ in their molecular or crystal structure, and hence in their properties. (5.2f) II.7 For Groups 1, 2, and 13-18 on the Periodic Table, elements within the same group have the ...
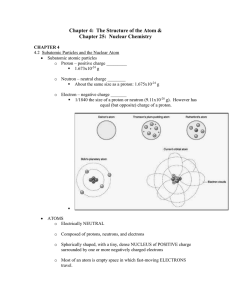
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... Nuclear equations are used to show the radioactive decay process o Mass number and Atomic number are CONSERVED ...
... Nuclear equations are used to show the radioactive decay process o Mass number and Atomic number are CONSERVED ...
Semester 1 Final Review Powerpoint
... • A physical change is one that does not involve breaking bonds and rearranging atoms. The products of the physical change are nearly the same as the originals. (EX: phase changes, cutting, mixing) • A chemical change involves the recombination of atoms. The properties of this rearrangement are dif ...
... • A physical change is one that does not involve breaking bonds and rearranging atoms. The products of the physical change are nearly the same as the originals. (EX: phase changes, cutting, mixing) • A chemical change involves the recombination of atoms. The properties of this rearrangement are dif ...
The Chemical Context of Life Chapter 2 Notes
... Organisms are composed of matter: anything that takes up space or has mass Element: a substance that cannot be broken down by chemical reactions Compound: substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio ...
... Organisms are composed of matter: anything that takes up space or has mass Element: a substance that cannot be broken down by chemical reactions Compound: substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio ...
Introduction to Chemical Reactions
... Chemical Reactions are represented by Chemical Equations. Chemical Equations are balanced to show the same number of atoms of each element on each side. The Law of Conservation of Mass says that atoms won’t be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. That is why you have to balance chemical equa ...
... Chemical Reactions are represented by Chemical Equations. Chemical Equations are balanced to show the same number of atoms of each element on each side. The Law of Conservation of Mass says that atoms won’t be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. That is why you have to balance chemical equa ...
Matter – Properties and Changes 1 Intensive properties
... Chemistry: Study of matter and the changes it undergoes Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space ...
... Chemistry: Study of matter and the changes it undergoes Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space ...
A-level Chemistry
... Teaching and learning methods used Teaching and learning methods used include lectures, group work, extensive practical work, independent learning and external workshops through professional membership of external organisations How your work will be assessed Routine formative and summative assessmen ...
... Teaching and learning methods used Teaching and learning methods used include lectures, group work, extensive practical work, independent learning and external workshops through professional membership of external organisations How your work will be assessed Routine formative and summative assessmen ...
Chapter 4 REVIEW
... 21. Ionic compounds and metals have different physical properties because of the different forces involved. For example, while sodium chloride and nickel have nearly identical molar masses, their melting points, conductivity, and solubility in water are quite different. (a) Explain the large differe ...
... 21. Ionic compounds and metals have different physical properties because of the different forces involved. For example, while sodium chloride and nickel have nearly identical molar masses, their melting points, conductivity, and solubility in water are quite different. (a) Explain the large differe ...
Chapter 2 Notes - Duplin County Schools
... Compounds can be made with three different kinds of bonds: 1) Covalent Share electrons to be stable Strongest and most common bond Molecule: group of atoms held together with covalent bonds with no overall charge Van der Waals forces (what holds molecules together) ...
... Compounds can be made with three different kinds of bonds: 1) Covalent Share electrons to be stable Strongest and most common bond Molecule: group of atoms held together with covalent bonds with no overall charge Van der Waals forces (what holds molecules together) ...
Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice Section A
... a. a substance dissolves in any liquid b. a substance is dissolved in water c. when a substance is mixed with water and doesn’t dissolve d. water is removed from a substance 2. The graph shows the relative amount of chemical substances which can be taken up by plants at different pH levels. The narr ...
... a. a substance dissolves in any liquid b. a substance is dissolved in water c. when a substance is mixed with water and doesn’t dissolve d. water is removed from a substance 2. The graph shows the relative amount of chemical substances which can be taken up by plants at different pH levels. The narr ...
1 st Nine Weeks Study Guide for Chemistry
... Collaboration-Working with other scientists or people for a common goal. It is important because it can lead to more discoveries and information in science. 3. Reporting Scientific Data A. Define qualitative data. Give three examples. Data that is observed or changes appearance. Examples include: bu ...
... Collaboration-Working with other scientists or people for a common goal. It is important because it can lead to more discoveries and information in science. 3. Reporting Scientific Data A. Define qualitative data. Give three examples. Data that is observed or changes appearance. Examples include: bu ...
File
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found ...
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found ...
Chapter 2
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found ...
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found ...
Chemistry Notes
... More Terms (You know you love ‘em.) WEAK ACID: An acid that only partially ionizes in an aqueous solution. That means not every molecule breaks apart. They usually have a pH close to 7 (3-6). WEAK BASE: A base that only partially ionizes in an aqueous solution. That means not every molecule breaks a ...
... More Terms (You know you love ‘em.) WEAK ACID: An acid that only partially ionizes in an aqueous solution. That means not every molecule breaks apart. They usually have a pH close to 7 (3-6). WEAK BASE: A base that only partially ionizes in an aqueous solution. That means not every molecule breaks a ...
Chemistry Terms
... endothermic (reaction) A chemical reaction that requires an input of energy to drive it. exothermic (reaction) A chemical reaction in which energy is released to the environment. ionic bond A bond between atoms in which an electron from one atom leaves and resides in the other shell of the other ato ...
... endothermic (reaction) A chemical reaction that requires an input of energy to drive it. exothermic (reaction) A chemical reaction in which energy is released to the environment. ionic bond A bond between atoms in which an electron from one atom leaves and resides in the other shell of the other ato ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.