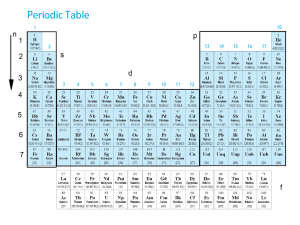
1 of 52
... Key: Both compounds have C2H6O as the formula. Because they have the same formula, their mass percent composition will be identical. However, these are different compounds with different properties since the atoms are bonded together differently. These compounds are called isomers of each other. ...
... Key: Both compounds have C2H6O as the formula. Because they have the same formula, their mass percent composition will be identical. However, these are different compounds with different properties since the atoms are bonded together differently. These compounds are called isomers of each other. ...
1411FINALSAMPLEs and Key
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
lecture 3
... Energy is easily converted from one form to another During conversion, some energy is “lost” as heat ...
... Energy is easily converted from one form to another During conversion, some energy is “lost” as heat ...
Atoms and bonds in molecules and chemical
... answer that their glass absorbs light selectively, so that the transmitted light has a different spectrum from that of sunlight; but a chemist would answer that it is because ordinary glass contains ferrous ions. This example shows that several causal processes may be invoked to explain a fact. In t ...
... answer that their glass absorbs light selectively, so that the transmitted light has a different spectrum from that of sunlight; but a chemist would answer that it is because ordinary glass contains ferrous ions. This example shows that several causal processes may be invoked to explain a fact. In t ...
Three-body dynamics in hydrogen ionization by fast highly charged
... order to perform a fair comparison between the two theories, the CDW results for n = 2 have been averaged over the 2s and 2p 0, ±1 states. Quantum mechanical calculations for the n = 3 initial state are not presented because their computing times are prohibitive within the present approximations. Th ...
... order to perform a fair comparison between the two theories, the CDW results for n = 2 have been averaged over the 2s and 2p 0, ±1 states. Quantum mechanical calculations for the n = 3 initial state are not presented because their computing times are prohibitive within the present approximations. Th ...
Monday, Oct. 3, 2016
... • An early attempt to incorporate quantum effects • Assumes nucleus as a gas of free protons and neutrons confined to the nuclear volume – The nucleons occupy quantized (discrete) energy levels – Nucleons are moving inside a spherically symmetric well with the range determined by the radius of the n ...
... • An early attempt to incorporate quantum effects • Assumes nucleus as a gas of free protons and neutrons confined to the nuclear volume – The nucleons occupy quantized (discrete) energy levels – Nucleons are moving inside a spherically symmetric well with the range determined by the radius of the n ...
Quantum computing with cavity QED
... are stored in the Zeeman ground state levels of the trapped atoms. Different laser beams can address them individually in order to manipulate the qubits for writing and reading purposes as shown schematically in Fig.1. This is similar to the ideas of one of the first proposals of QC [13] where ions ...
... are stored in the Zeeman ground state levels of the trapped atoms. Different laser beams can address them individually in order to manipulate the qubits for writing and reading purposes as shown schematically in Fig.1. This is similar to the ideas of one of the first proposals of QC [13] where ions ...
the vacuum, light speed, and the redshift
... the innate uncertainty described by Heisenberg’s uncertainly principle [4,16]. Therefore, the zero-point fields are the ultimate source of this fundamental limitation with which we can measure some atomic phenomena and, as such, give rise to the indeterminacy or uncertainty of quantum theory mention ...
... the innate uncertainty described by Heisenberg’s uncertainly principle [4,16]. Therefore, the zero-point fields are the ultimate source of this fundamental limitation with which we can measure some atomic phenomena and, as such, give rise to the indeterminacy or uncertainty of quantum theory mention ...
Print this article - International Journal of Scientific Reports
... atomic energy is invented. The process of getting this kind of method is introduced. At last, the energy of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and other atoms are calculated by this method. By using this method, the energy of the atom can be calculated by atomic number, and the accuracy can reach more than 95 ...
... atomic energy is invented. The process of getting this kind of method is introduced. At last, the energy of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and other atoms are calculated by this method. By using this method, the energy of the atom can be calculated by atomic number, and the accuracy can reach more than 95 ...
JSUNIL TUTORIAL , SAMASTIPUR, BIHAR
... of small particles called atoms. The postulates of this theory may be stated as follows: (i) All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms. (ii) Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. (iii) Atoms of a given element are identical in mass ...
... of small particles called atoms. The postulates of this theory may be stated as follows: (i) All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms. (ii) Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. (iii) Atoms of a given element are identical in mass ...
Pauli Exclusion Principle
... 7-31. The optical spectra of atoms with two electrons in the same outer shell are similar, but they are quite different from the spectra of atoms with just one outer electron because of the interaction of the two electrons. Separate the following elements into two groups such that those in each gro ...
... 7-31. The optical spectra of atoms with two electrons in the same outer shell are similar, but they are quite different from the spectra of atoms with just one outer electron because of the interaction of the two electrons. Separate the following elements into two groups such that those in each gro ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... Oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions, are technically defined as any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of the participating atom, ion, or molecule of a chemical compound changes. Some common redox reactions include fire, rusting of metals, browning of fruit, and photosynth ...
... Oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions, are technically defined as any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of the participating atom, ion, or molecule of a chemical compound changes. Some common redox reactions include fire, rusting of metals, browning of fruit, and photosynth ...
molecular formula
... Formula or molecular mass = S of atomic masses in the chemical formula Molecular mass = mass in amu for a molecule, from nonmetal elements forming covalent bonds Molecule is a covalent compound’s smallest unit, made of nonmetals in covalent bonds Formula mass = mass in amu for a formula unit or for ...
... Formula or molecular mass = S of atomic masses in the chemical formula Molecular mass = mass in amu for a molecule, from nonmetal elements forming covalent bonds Molecule is a covalent compound’s smallest unit, made of nonmetals in covalent bonds Formula mass = mass in amu for a formula unit or for ...
Observing Atomic Collapse Resonances in Artificial Nuclei on
... resonances are absent) was observed for charged impurities in graphene (14), but the observation of atomic collapse around supercritical impurities has remained elusive due to the difficulty of producing highly charged impurities. Here we report the observation of supercritical Coulomb behavior in a ...
... resonances are absent) was observed for charged impurities in graphene (14), but the observation of atomic collapse around supercritical impurities has remained elusive due to the difficulty of producing highly charged impurities. Here we report the observation of supercritical Coulomb behavior in a ...