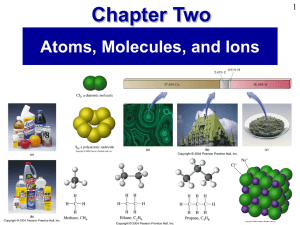
CHEM 101 Fall 09 Final Exam (a)
... a. If two atoms are widely separated, there is very little attraction between them. b. When two atoms are one bond length apart, the electrons on one atom are attracted ...
... a. If two atoms are widely separated, there is very little attraction between them. b. When two atoms are one bond length apart, the electrons on one atom are attracted ...
Electronic Structure of Atoms
... come from analysis of the light either emitted or absorbed by substances. To understand electronic structure, therefore, we must first learn more about light. The light that we can see with our eyes, visible light, is an example of electromagnetic radiation. Because electromagnetic radiation carries ...
... come from analysis of the light either emitted or absorbed by substances. To understand electronic structure, therefore, we must first learn more about light. The light that we can see with our eyes, visible light, is an example of electromagnetic radiation. Because electromagnetic radiation carries ...
JOURNAL OF CONDENSED MATTER NUCLEAR SCIENCE Experiments and Methods in Cold Fusion
... who often had sacrificed their own careers relentlessly continuing their efforts down this direction of research. The more and more absurd this sounded to me when after studying some of the more popular candidates, I realised that the more involved were the models and complicated the equations, the ...
... who often had sacrificed their own careers relentlessly continuing their efforts down this direction of research. The more and more absurd this sounded to me when after studying some of the more popular candidates, I realised that the more involved were the models and complicated the equations, the ...
2015_Final Exam Study Guide
... compounds or elements? a. direct combination c. single replacement b. double replacement d. decomposition How many atoms are in a sample of an element whose mass in grams is numerically equal to the atomic mass? a. 1 c. 1 1023 b. 6.02 d. 6.02 1023 Avogadro's number a. equals 1. c. depends on the ...
... compounds or elements? a. direct combination c. single replacement b. double replacement d. decomposition How many atoms are in a sample of an element whose mass in grams is numerically equal to the atomic mass? a. 1 c. 1 1023 b. 6.02 d. 6.02 1023 Avogadro's number a. equals 1. c. depends on the ...
chapter 7 multielectron atoms outline
... There are several methods by which the Equation can be solved approximately, to whatever degree of accuracy desired. One of these methods is Perturbation Theory, which was introduced in Chapter 5. A second method is the Variational Method, which is developed here, and will be applied to the Helium a ...
... There are several methods by which the Equation can be solved approximately, to whatever degree of accuracy desired. One of these methods is Perturbation Theory, which was introduced in Chapter 5. A second method is the Variational Method, which is developed here, and will be applied to the Helium a ...
Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Eligible Content: CHEM.B.1.1.1 – Apply the mole concept to representative particles (e.g., counting, determining mass of atoms, ions, molecules, and/or formula units). Standard: 3.2.C.A5 – Models – Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), a ...
... Eligible Content: CHEM.B.1.1.1 – Apply the mole concept to representative particles (e.g., counting, determining mass of atoms, ions, molecules, and/or formula units). Standard: 3.2.C.A5 – Models – Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), a ...
elements of chemistry unit
... reduction reactions are also known as redox reactions (red = reduction, ox = oxidation). OXIDATION AND REDUCTION Oxidation and reduction reactions take place at the same time. This is because electrons from one species need to find another species to accept them. OXIDATION NUMBERS Oxidation numbers ...
... reduction reactions are also known as redox reactions (red = reduction, ox = oxidation). OXIDATION AND REDUCTION Oxidation and reduction reactions take place at the same time. This is because electrons from one species need to find another species to accept them. OXIDATION NUMBERS Oxidation numbers ...
Chapter 2 The Components of Matter
... is found in a fixed amount in nature, and rarely are these amounts equal among the given isotopes of an element we must have a way to take this into account when talking about a naturally occurring element; enter Average Mass: ...
... is found in a fixed amount in nature, and rarely are these amounts equal among the given isotopes of an element we must have a way to take this into account when talking about a naturally occurring element; enter Average Mass: ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical
... “We may lay it down as an incontestable axiom that, in all the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of performing chemical experiments depends.” --Antoine Lavoisier, 1789 ...
... “We may lay it down as an incontestable axiom that, in all the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of performing chemical experiments depends.” --Antoine Lavoisier, 1789 ...
Intensities of analogous Rydberg series in CF3Cl, CF3Br and in
... In this Letter, the calculation and analysis of the absorption in the discrete spectral region by CF3Cl and CF3Br, as relevant representatives of the halogenated methanes, will be presented. Resonance, as well as Rydberg transitions will be dealt with through the molecular-adapted quantum defect orb ...
... In this Letter, the calculation and analysis of the absorption in the discrete spectral region by CF3Cl and CF3Br, as relevant representatives of the halogenated methanes, will be presented. Resonance, as well as Rydberg transitions will be dealt with through the molecular-adapted quantum defect orb ...
PC 4421 Lecture 1: Nuclei and Nuclear Forces
... radii can be obtained (isotope shifts). The energies of X-rays in atoms formed with muons instead of electrons can also be sensitive to the charge radius. In general, measurements yield a value for r0 between 1.2 and 1.25 fm. Matter distributions are generally measured by probes which interact with ...
... radii can be obtained (isotope shifts). The energies of X-rays in atoms formed with muons instead of electrons can also be sensitive to the charge radius. In general, measurements yield a value for r0 between 1.2 and 1.25 fm. Matter distributions are generally measured by probes which interact with ...
Theory of x-ray absorption by laser-dressed atoms
... In this paper, we devise an ab initio theory for the x-ray absorption cross section of an isolated atom in the presence of an optical laser. The Hartree-FockSlater mean-field model [23, 24] is utilized to treat the atomic many-electron problem. This choice is adequate as shakeup and shakeoff effects ...
... In this paper, we devise an ab initio theory for the x-ray absorption cross section of an isolated atom in the presence of an optical laser. The Hartree-FockSlater mean-field model [23, 24] is utilized to treat the atomic many-electron problem. This choice is adequate as shakeup and shakeoff effects ...
chemistry
... prediction. If you read a description of matter which indicates that it is a solid, nonmetallic molecular compound, then (by the end of this textbook at least) you will have a good idea of its properties in general. There are many different classification systems used, some linked together, others s ...
... prediction. If you read a description of matter which indicates that it is a solid, nonmetallic molecular compound, then (by the end of this textbook at least) you will have a good idea of its properties in general. There are many different classification systems used, some linked together, others s ...
The nucleus, a unique many-body system - IPN Orsay
... When temperature decreases and density increases, a system of constituents interacting with a short range attractive interaction undergoes from a classical gaseous state to a liquid one. When further decreasing the temperature and increasing the density, the system becomes a solid, which is microsco ...
... When temperature decreases and density increases, a system of constituents interacting with a short range attractive interaction undergoes from a classical gaseous state to a liquid one. When further decreasing the temperature and increasing the density, the system becomes a solid, which is microsco ...
Fusion Video Workbook.Final - General Atomics Fusion Education
... This workbook is part of an educational outreach program sponsored by the General Atomics Fusion Group and the U.S. Department of Energy. The overall program consists of a pre-tour video to be shown in the classroom, a half-day educational tour of the DIII–D magnetic fusion research facility located ...
... This workbook is part of an educational outreach program sponsored by the General Atomics Fusion Group and the U.S. Department of Energy. The overall program consists of a pre-tour video to be shown in the classroom, a half-day educational tour of the DIII–D magnetic fusion research facility located ...
Chapter 2: Mass Relations in Formulas, Chemical Reactions, and
... isotopes of the element carbon present in a typical sample on earth. Note: Atomic masses are also called atomic weights. ...
... isotopes of the element carbon present in a typical sample on earth. Note: Atomic masses are also called atomic weights. ...
Special roles of loose neutron-halo nucleus structure on the
... results in Fig. 2 are outside the statistical error bars and above point of view on the role of loose neutron-halo structure on the fragmentation is reasonable. In addition we calculated also the time evolutions of the neutron and proton RMS radii (with respect to the center of mass for each nucleus ...
... results in Fig. 2 are outside the statistical error bars and above point of view on the role of loose neutron-halo structure on the fragmentation is reasonable. In addition we calculated also the time evolutions of the neutron and proton RMS radii (with respect to the center of mass for each nucleus ...